The Isle of Wight NHS Trust is an NHS trust which provides physical health, mental health and ambulance services for the Isle of Wight. The trust is unique in being the only integrated acute, community, mental health and ambulance health care provider in England. It runs St Mary's Hospital and the Isle of Wight Ambulance Service.
Southern Health NHS Foundation Trust is an NHS foundation trust which provides community health, mental health and learning disability services across Hampshire. It is one of the largest providers of such services in England.
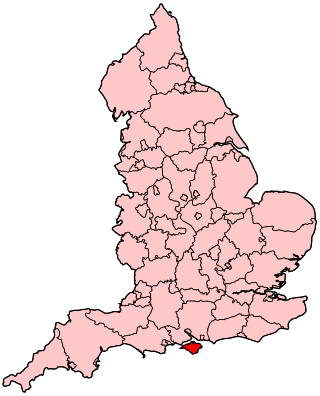
Healthcare in Dorset was primarily the responsibility of Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group until July 2022. Dorset County Council is leading in the development of an electronic health record, to be called the Dorset Care Record, provided by Orion Health. It is intended to enable all health and social care providers to share records.
Healthcare in Cumbria was the responsibility of Cumbria Clinical Commissioning Group until July 2022. On 1 April 2017 32 GP practices left the CCG and merged with Lancashire North CCG to form Morecambe Bay CCG.
Healthcare in Bedfordshire is the responsibility of Bedfordshire and Luton Integrated Care Systems.
Healthcare in Somerset, England was the responsibility of three clinical commissioning groups (CCGs) until July 2022. These covered the ceremonial county of Somerset, which comprises the areas governed by the three unitary authorities of Somerset, North Somerset and Bath and North East Somerset.
Healthcare in Sussex is the responsibility of NHS Sussex, an integrated care system and the NHS Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust.
Healthcare in Staffordshire was the responsibility of six clinical commissioning groups until July 2022, covering Stafford & Surrounds, North Staffordshire, South East Staffordshire and Seisdon Peninsula, East Staffordshire, Cannock Chase, and Stoke-on-Trent.
Healthcare in Cornwall was until July 2022 the responsibility of Kernow clinical commissioning group, until it got replaced by Integrated care system, as a result of the Health and Care Act 2022. As far as the NHS is concerned, Cornwall includes the Isles of Scilly.
Healthcare in the West Midlands was, until July 2022, the responsibility of five integrated care groups: Birmingham and Solihull, Sandwell and West Birmingham, Dudley, Wolverhampton, and Walsall.
Healthcare in Surrey, England was the responsibility of five Clinical Commissioning Groups: East Surrey, North West Surrey, Surrey Downs, Guildford and Waverley, and Surrey Heath from 2013 to 2020 when East Surrey, North West Surrey, Surrey Downs, Guildford and Waverley merged to form Surrey Heartlands CCG. The new organisation started with a £62 million deficit.
Healthcare in Essex is now the responsibility of six clinical commissioning groups: Basildon and Brentwood, Mid Essex, North East Essex, Southend, Thurrock and West Essex.
Healthcare in Northumberland was the responsibility of the Northumberland, Newcastle Gateshead, and North Tyneside clinical commissioning groups from 2013 to 2022 before being replaced by integrated care systems.
Healthcare in Northamptonshire was the responsibility of Northamptonshire Clinical Commissioning Group until July 2022, with some involvement of Cambridgeshire and Peterborough CCG.
Healthcare in Norfolk was the responsibility of five clinical commissioning groups: Great Yarmouth and Waveney CCG, Norwich CCG, North Norfolk CCG, West Norfolk CCG and South Norfolk CCG, they merged in April 2020 becoming the Norfolk and Waveney CCG until they were replaced by an integrated care system in July 2022. Social Care is the responsibility of Norfolk County Council.
Healthcare in Berkshire was the responsibility of five clinical commissioning groups until July 2022: Windsor, Ascot and Maidenhead, Slough, Bracknell and Ascot and Wokingham.
Healthcare in Derbyshire was the responsibility of five clinical commissioning groups covering North Derbyshire, Southern Derbyshire, Erewash, Hardwick, and Tameside and Glossop. North Derbyshire, Southern Derbyshire, Erewash and Hardwick announced in November 2018 that they planned to merge.
Healthcare in Hertfordshire was the responsibility of the Herts Valleys, East, and North Hertfordshire clinical commissioning groups until July 2022.

Gosport War Memorial Hospital is a hospital in Gosport, Hampshire, England, part of the Southern Health NHS Foundation Trust.

