
Modern paganism, also known as contemporary paganism and neopaganism, is a term for a religion or a family of religions which is influenced by the various historical pre-Christian beliefs of pre-modern peoples in Europe and adjacent areas of North Africa and the Near East. Although they share similarities, contemporary pagan movements are diverse and as a result, they do not share a single set of beliefs, practices, or texts. Scholars of religion often characterise these traditions as new religious movements. Some academics who study the phenomenon treat it as a movement that is divided into different religions while others characterize it as a single religion of which different pagan faiths are denominations.

Wicca, also known as The Craft, is a modern neo-pagan syncretic religion. Scholars of religion categorize it as both a new religious movement and as part of occultist Western esotericism. It was developed in England during the first half of the 20th century and was introduced to the public in 1954 by Gerald Gardner, a retired British civil servant. Wicca draws upon a diverse set of ancient pagan and 20th-century hermetic motifs for its theological structure and ritual practices.
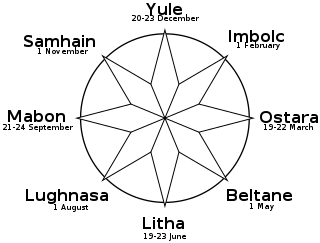
The Wheel of the Year is an annual cycle of seasonal festivals, observed by a range of modern pagans, marking the year's chief solar events and the midpoints between them. British neopagans crafted the Wheel of the Year in the mid-20th century, combining the four solar events marked by many European peoples, with the four seasonal festivals celebrated by Insular Celtic peoples. Different paths of modern paganism may vary regarding the precise timing of each celebration, based on such distinctions as the lunar phase and geographic hemisphere.

Zsuzsanna Emese Mokcsay is an American writer, activist, playwright and songwriter living in America who writes about feminist spirituality and Dianic Wicca under the pen name Zsuzsanna Budapest or Z. Budapest. She is the founder of the Susan B. Anthony Coven #1, which was founded in 1971 as the first women-only witches' coven. She founded the female-only type of Dianic Wicca.
The Feri Tradition is an American neo-pagan tradition related to Neopagan witchcraft. It was founded in the west coast of the United States between the 1950s and 1960s by Victor Henry Anderson and his wife, Cora Anderson. Practitioners have described it as an ecstatic tradition, rather than a fertility tradition. Strong emphasis is placed on sensual experience and awareness, including sexual mysticism, which is not limited to heterosexual expression.
Silver RavenWolf is an American writer on New Age magic, witchcraft and Wicca.

Drawing Down the Moon: Witches, Druids, Goddess-Worshippers, and Other Pagans in America Today is a sociological study of contemporary Paganism in the United States written by the American Wiccan and journalist Margot Adler. First published in 1979 by Viking Press, it was later republished in a revised and expanded edition by Beacon Press in 1986, with third and fourth revised editions being brought out by Penguin Books in 1996 and then 2006 respectively.
Sam Webster is an American writer, founder of Concrescent Press, and an advocate for open source religion—the use of the open source paradigm in the field of spirituality. He is a Thelemite, a member of the Golden Dawn tradition, Bishop Tau Ty of Ecclesia Gnostica Universalis, and an initiate of Wicca.

Wiccan views of divinity are generally theistic, and revolve around a Goddess and a Horned God, thereby being generally dualistic. In traditional Wicca, as expressed in the writings of Gerald Gardner and Doreen Valiente, the emphasis is on the theme of divine gender polarity, and the God and Goddess are regarded as equal and opposite divine cosmic forces. In some newer forms of Wicca, such as feminist or Dianic Wicca, the Goddess is given primacy or even exclusivity. In some forms of traditional witchcraft that share a similar duotheistic theology, the Horned God is given precedence over the Goddess.
Modern paganism in the United States is represented by widely different movements and organizations. The largest modern pagan religious movement is Wicca, followed by Neodruidism. Both of these religions or spiritual paths were introduced during the 1950s and 1960s from Great Britain. Germanic Neopaganism and Kemetism appeared in the US in the early 1970s. Hellenic Neopaganism appeared in the 1990s.

Neopagan witchcraft, sometimes referred to as The Craft, is an umbrella term for some neo-pagan traditions that include the attempted practice of magic. These traditions began in the mid-20th century and were influenced by the witch-cult hypothesis, a now-rejected theory that persecuted witches in Europe had actually been followers of a surviving pagan religion. Traditions classed as neopagan witchcraft include Wicca and the various movements that describe themselves as "Traditional Witchcraft".

A Community of Witches: Contemporary Neo-Paganism and Witchcraft in the United States is a sociological study of the Wiccan and wider Pagan community in the Northeastern United States. It was written by American sociologist Helen A. Berger of the West Chester University of Pennsylvania and first published in 1999 by the University of South Carolina Press. It was released as a part of a series of academic books entitled Studies in Comparative Religion, edited by Frederick M. Denny, a religious studies scholar at the University of Chicago.
Pagan studies is the multidisciplinary academic field devoted to the study of modern paganism, a broad assortment of modern religious movements, which are typically influenced by or claiming to be derived from the various pagan beliefs of premodern Europe. Pagan studies embrace a variety of different scholarly approaches to studying such religions, drawing from history, sociology, anthropology, archaeology, folkloristics, theology and other religious studies.

Witching Culture: Folklore and Neo-Paganism in America is a folkloric and anthropological study of the Wiccan and wider Pagan community in the United States. It was written by the American anthropologist and folklorist Sabina Magliocco of California State University, Northridge and first published in 2004 by the University of Pennsylvania Press. It was released as a part of a series of academic books titled 'Contemporary Ethnography', edited by the anthropologists Kirin Narayan of the University of Wisconsin and Paul Stoller of West Chester University.

Enchanted Feminism: The Reclaiming Witches of San Francisco is an anthropological study of the Reclaiming Wiccan community of San Francisco. It was written by the Scandinavian theologian Jone Salomonsen of the California State University, Northridge and first published in 2002 by the Routledge.

Never Again the Burning Times: Paganism Revisited is an anthropological study of the Wiccan and wider Pagan community in the United States. It was written by the American anthropologist Loretta Orion and published by Waveland Press in 1995.

Living Witchcraft: A Contemporary American Coven is a sociological study of an American coven of Wiccans who operated in Atlanta, Georgia during the early 1990s. It was co-written by the sociologist Allen Scarboro, psychologist Nancy Campbell and literary critic Shirley Stave and first published by Praeger in 1994. Although largely sociological, the study was interdisciplinary, and included both insider and outsider perspectives into the coven; Stave was an initiate and a practicing Wiccan while Scarboro and Campbell remained non-initiates throughout the course of their research.

Persuasions of the Witches' Craft: Ritual Magic in Contemporary England is a study of several Wiccan and ceremonial magic groups that assembled in southern England during the 1980s. It was written by the American anthropologist Tanya M. Luhrmann (1959–) of the University of California, San Diego, and first published in 1989.

Witchcraft and Paganism in Australia is an anthropological study of the Wiccan and wider Pagan community in Australia. It was written by the Australian anthropologist Lynne Hume and first published in 1997 by Melbourne University Press.

Modern paganviews on LGBT people vary considerably among different paths, sects, and belief systems. LGBT individuals comprise a much larger percentage of the population in neopagan circles than larger, mainstream religious populations. There are some popular neopagan traditions which have beliefs often in conflict with the LGBT community, and there are also traditions accepting of, created by, or led by LGBT individuals. The majority of conflicts concern heteronormativity and cisnormativity.














