| Heliomata cycladata | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Euarthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Lepidoptera |
| Family: | Geometridae |
| Genus: | Heliomata |
| Species: | H. cycladata |
| Binomial name | |
| Heliomata cycladata | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
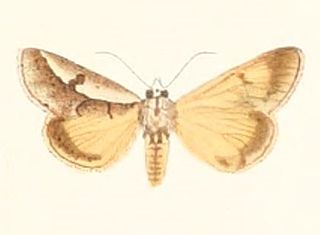
Heliomata cycladata, the common spring moth, is a moth of the family Geometridae. The species was first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote and Coleman Townsend Robinson in 1866. It is found in eastern North America, with records from southern Ontario, southern Quebec, Maine, New Hampshire, Michigan, Wisconsin to South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, northern Mississippi and Arkansas.

Moths comprise a group of insects related to butterflies, belonging to the order Lepidoptera. Most lepidopterans are moths, and there are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species.
A species description is a formal description of a newly discovered species, usually in the form of a scientific paper. Its purpose is to give a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differs from species which have been described previously or are related. The species description often contains photographs or other illustrations of the type material and states in which museums it has been deposited. The publication in which the species is described gives the new species a formal scientific name. Some 1.9 million species have been identified and described, out of some 8.7 million that may actually exist. Millions more have become extinct.

Augustus Radcliffe Grote was a British entomologist who worked mainly in America.
The wingspan is about 20 mm. [2] Adults are on wing from March to July.

The wingspan of a bird or an airplane is the distance from one wingtip to the other wingtip. For example, the Boeing 777-200 has a wingspan of 60.93 metres, and a wandering albatross caught in 1965 had a wingspan of 3.63 metres, the official record for a living bird. The term wingspan, more technically extent, is also used for other winged animals such as pterosaurs, bats, insects, etc., and other fixed-wing aircraft such as ornithopters. In humans, the term wingspan also refers to the arm span, which is distance between the length from one end of an individual's arms to the other when raised parallel to the ground at shoulder height at a 90º angle. Former professional basketball player Manute Bol stands at 7 ft 7 in (2.31 m) and owns one of the largest wingspans at 8 ft 6 in (2.59 m).
The larvae feed on Robinia pseudoacacia and Gleditsia triacanthos . [3]

Robinia pseudoacacia, commonly known in its native territory as black locust, is a medium-sized hardwood deciduous tree endemic to a few small areas of the United States, but it has been widely planted and naturalized elsewhere in temperate North America, Europe, Southern Africa and Asia and is considered an invasive species in some areas. Another common name is false acacia, a literal translation of the specific name It was introduced into Britain in 1636.