
Penicillium is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that is part of the mycobiome of many species and is of major importance in the natural environment, in food spoilage, and in food and drug production.

The longhorn beetles (Cerambycidae), also known as long-horned or longicorns, are a large family of beetles, with over 35,000 species described.

The glucose oxidase enzyme also known as notatin is an oxidoreductase that catalyses the oxidation of glucose to hydrogen peroxide and D-glucono-δ-lactone. This enzyme is produced by certain species of fungi and insects and displays antibacterial activity when oxygen and glucose are present.

Paspalum is a genus of plants in the grass family.

Paspalum notatum, known commonly as bahiagrass, common bahia, and Pensacola bahia, is a tropical to subtropical perennial grass. It is known for its prominent V-shaped inflorescence consisting of two spike-like racemes containing multiple tiny spikelets, each about 2.8–3.5 millimetres (0.11–0.14 in) long.

Arachis glabrata is a high-quality forage plant native to Argentina, Brazil, and Paraguay vegetation. This plant is also used for soil conservation and as an ornamental plant. It is adapted to sandy soils in the Gulf Coast region of the United States.

The Disteniidae are a small family of beetles in the superfamily Chrysomeloidea, traditionally treated as a group within the Cerambycidae.
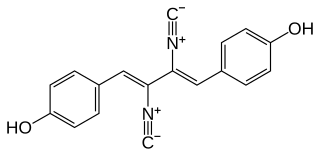
Xantocillin (INN), also known as xanthocillin X or ophthocillin, was the first reported natural product found to contain the isocyanide functional group. It was first isolated from Penicillium notatum by Rothe in 1950 and subsequently from several other sources.

Zodion is a large genus of flies from the family Conopidae.

Sehima is a genus of mostly Asian and African plants in the grass family.

Penicillium chrysogenum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is common in temperate and subtropical regions and can be found on salted food products, but it is mostly found in indoor environments, especially in damp or water-damaged buildings. It has been recognised as a species complex that includes P. notatum, P. meleagrinum, and P. cyaneofulvum. Molecular phylogeny has established that Alexander Fleming's first discovered penicillin producing strain is of a distinct species, P. rubens, and not of P. notatum. It has rarely been reported as a cause of human disease. It is the source of several β-lactam antibiotics, most significantly penicillin. Other secondary metabolites of P. chrysogenum include roquefortine C, meleagrin, chrysogine, 6-MSA YWA1/melanin, andrastatin A, fungisporin, secalonic acids, sorbicillin, and PR-toxin.

Heterachthes is a genus of beetles in the family Cerambycidae, containing the following species:

Penicillium rubens is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium and was the first species known to produce the antibiotic penicillin. It was first described by Philibert Melchior Joseph Ehi Biourge in 1923. For the discovery of penicillin from this species Alexander Fleming shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945. The original penicillin-producing type has been variously identified as Penicillium rubrum, P. notatum, and P. chrysogenum among others, but genomic comparison and phylogenetic analysis in 2011 resolved that it is P. rubens. It is the best source of penicillins and produces benzylpenicillin (G), phenoxymethylpenicillin (V) and octanoylpenicillin (K). It also produces other important bioactive compounds such as andrastin, chrysogine, fungisporin, roquefortine, and sorbicillins.
Gladys Elizabeth Baker was an American mycologist, teacher, and botanical illustrator, known for her extensive work in biological and mycological education, and the morphological study of myxomycete fructifications. She further contributed studies to the Island Ecosystems Integrated Research Program of the U. S. International Biological Program.
Heterachthes x-notatum is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Linsley in 1935. Under Article 31.2.1 of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, the species name must be spelled x-notatum, as letters of the alphabet are neuter in gender.
Heterachthes v-flavum is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Martins in 2009. Under Article 31.2.1 of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, the species name must be spelled v-flavum, despite being originally spelled v-flavus by the original author, as letters of the alphabet are neuter in gender.
Compsosoma v-notatum is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Vigors in 1825. It is known from Brazil.
Penicillium resticulosum is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which produces notatin.

Anthidiellum notatum, the northern rotund resin bee, is a species of bee in the family Megachilidae. It is found in North America.














