
Tabernaemontana is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae. It has a pan-tropical distribution, found in Asia, Africa, Australia, North America, South America, and a wide assortment of oceanic islands. These plants are evergreen shrubs and small trees growing to 1–15 m tall. The leaves are opposite, 3–25 cm long, with milky sap; hence it is one of the diverse plant genera commonly called "milkwood". The flowers are fragrant, white, 1–5 cm in diameter.

Voacangine is an alkaloid found predominantly in the root bark of the Voacanga africana tree, as well as in other plants such as Tabernanthe iboga, Tabernaemontana africana, Trachelospermum jasminoides, Tabernaemontana divaricata and Ervatamia yunnanensis. It is an iboga alkaloid which commonly serves as a precursor for the semi-synthesis of ibogaine. It has been demonstrated in animals to have similar anti-addictive properties to ibogaine itself. It also potentiates the effects of barbiturates. Under UV-A and UV-B light its crystals fluoresce blue-green, and it is soluble in ethanol.

Ibogamine is an anti-convulsant, anti-addictive, CNS stimulant alkaloid found in Tabernanthe iboga and Crepe Jasmine. Basic research related to how addiction affects the brain has used this chemical.

Tabernanthine is an alkaloid found in Tabernanthe iboga.

(–)-18-Methylaminocoronaridine (18-MAC) is a second generation synthetic derivative of ibogaine developed by the research team led by the pharmacologist Stanley D. Glick from the Albany Medical College and the chemist Martin E. Kuehne from the University of Vermont.

Voacamine, also known under the older names voacanginine and vocamine, is a naturally occurring dimeric indole alkaloid of the secologanin type, found in a number of plants, including Voacanga africana and Tabernaemontana divaricata. It is approved for use as an antimalarial drug in several African countries. Voacamine exhibits cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonistic activity.

Tabernaemontana donnell-smithii is an evergreen tree in the dogbane family Apocynaceae commonly known as the horse balls tree. In Spanish, it is huevos de caballo, cojones de burro, cojón de mico, or cojotón. The name, huevos de caballo, comes from the oval shape of the tree's hanging fruit. It is native to Mexico and Central America. The type locality is San Felipe, Retalhuleu in Guatemala. Tabernaemontana donnell-smithii is similar to Tabernaemontana glabra, except that its leaves and flowers are smaller and its fruit is larger.

Tabernaemontana divaricata, commonly called pinwheel flower, crape jasmine, East India rosebay, and Nero's crown, is an evergreen shrub or small tree native to South Asia, Southeast Asia and China. In zones where it is not hardy it is grown as a house/glasshouse plant for its attractive flowers and foliage. The stem exudes a milky latex when broken, whence comes the name milk flower

Tabernaemontana pandacaqui, known as windmill bush and banana bush, is a species of plant in the dogbane family Apocynaceae.

Catharanthine is a terpene indole alkaloid produced by the medicinal plant Catharanthus roseus and Tabernaemontana divaricata. Catharanthine is derived from strictosidine, but the exact mechanism by which this happens is currently unknown. Catharanthine is one of the two precursors that form vinblastine, the other being vindoline.

Affinine is a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid which can be isolated from plants of the genus Tabernaemontana. Structurally it can be considered a member of the vobasine alkaloid family and may be synthesized from tryptophan. Limited pharmacological testing has indicated that it may be an effective inhibitor of both acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase.

Conodurine is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitor isolated from Tabernaemontana.
Tabernaemontana sananho is a tropical tree species in the family Apocynaceae known as lobo sanango. Lobo sanango grows in the Amazon Basin of northern South America.

Apparicine is a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid. It is named after Apparicio Duarte, a Brazilian botanist who studied the Aspidosperma species from which apparicine was first isolated. It was the first member of the vallesamine group of alkaloids to be isolated and have its structure established, which was first published in 1965. It has also been known by the synonyms gomezine, pericalline, and tabernoschizine.
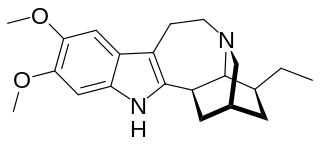
Ibogaline is an alkaloid found in Tabernanthe iboga along with the related chemical compounds ibogaine, ibogamine, and other minor alkaloids. It is a relatively smaller component of Tabernanthe iboga root bark total alkaloids (TA) content. It is also present in Tabernaemontana species such as Tabernaemontana australis which shares similar ibogan-biosynthetic pathways. The percentage of ibogaline in T. iboga root bark is up to 15% TA with ibogaine constituting 80% of the alkaloids and ibogamine up to 5%.

Amsonia tabernaemontana, the eastern bluestar, is a North American species of flowering plant in the family Apocynaceae, found in central and eastern North America.

Tabernaemontanine is a naturally occurring monoterpene indole alkaloid found in several species in the genus Tabernaemontana including Tabernaemontana divaricata.

Vobasine is a naturally occurring monoterpene indole alkaloid found in several species in the genus Tabernaemontana including Tabernaemontana divaricata.

19,20-Dihydroervahanine A is an alkaloid, a natural product which is found in the root of the South-East Asian plant Tabernaemontana divaricata. It inhibits acetylcholinesterase more potently than galantamine in vitro.

Conopharyngine is the major alkaloid present in the leaves and stem-bark of Tabernaemontana pachysiphon and Conopharyngia durissima. It is closely related voacangine and coronaridine. Conopharyngine pseudoindoxyl, a derivative of it, is also found in the same plant Tabernaemontana pachysiphon.



















