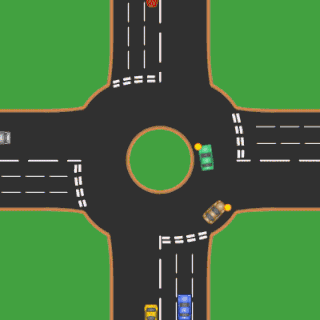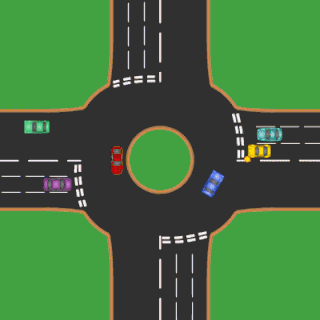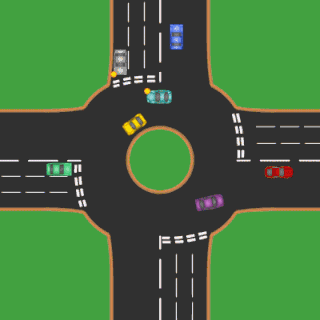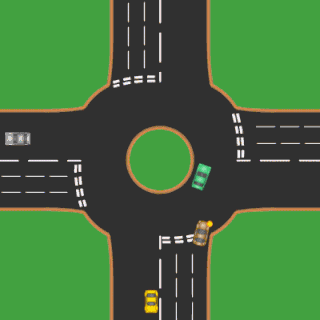
A roundabout is a type of circular intersection or junction in which road traffic is permitted to flow in one direction around a central island, and priority is typically given to traffic already in the junction.
Level of service (LOS) is a qualitative measure used to relate the quality of motor vehicle traffic service. LOS is used to analyze roadways and intersections by categorizing traffic flow and assigning quality levels of traffic based on performance measure like vehicle speed, density, congestion, etc. In a more general sense, levels of service can apply to all services in asset management domain.
The American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) is a standards setting body which publishes specifications, test protocols, and guidelines that are used in highway design and construction throughout the United States. Despite its name, the association represents not only highways but air, rail, water, and public transportation as well.
The Texas A&M Transportation Institute (TTI) in Bryan/College Station, Texas is a transportation research agency in the United States. The institute was created in 1950, primarily in response to the needs of the Texas Highway Department. TTI is a state agency and a member of the Texas A&M University System.

The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) is a division of the United States Department of Transportation that specializes in highway transportation. The agency's major activities are grouped into two programs, the Federal-aid Highway Program and the Federal Lands Highway Program. Its role had previously been performed by the Office of Road Inquiry, Office of Public Roads and the Bureau of Public Roads.
The National Bridge Inventory (NBI) is a database, compiled by the Federal Highway Administration, with information on all bridges and tunnels in the United States that have roads passing above or below. This is similar to the grade crossing identifier number database compiled by the Federal Railroad Administration which identifies all railroad crossings. This bridge information includes the design of the bridge and the dimensions of the usable portion. The data is often used to analyze bridges and judge their conditions. The inventory is developed with the purpose of having a unified database for bridges to ensure the safety of the traveling public as required by the Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1968. It includes identification information, bridge types and specifications, operational conditions, bridge data including geometric data and functional description, and inspection data. Any bridge more than 20 feet long used for vehicular traffic is included.

The GEH Statistic is a formula used in traffic engineering, traffic forecasting, and traffic modelling to compare two sets of traffic volumes. The GEH formula gets its name from Geoffrey E. Havers, who invented it in the 1970s while working as a transport planner in London, England. Although its mathematical form is similar to a chi-squared test, is not a true statistical test. Rather, it is an empirical formula that has proven useful for a variety of traffic analysis purposes.
The Transportation Research Board (TRB) is a division of the National Academy of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, formerly the National Research Council of the United States, which serves as an independent adviser to the on scientific and technical questions of national importance. It is jointly administered by the National Academy of Sciences, the National Academy of Engineering, and the National Academy of Medicine.

A quadrant roadway intersection adds an additional "quadrant roadway" between two legs of an intersection. This roadway adds two three-way intersections in addition to the original four-way intersection moving all left turns or right turns from the main intersection. The design is intended to improve traffic flow by reducing signal timing phases from four to two in the main intersection. The design is intended for intersections where large artery routes meet in an area of dense development and high pedestrian volume.
Channelization is a traffic engineering concept which employs the use of secondary roads to separate certain flows of traffic from the main traffic lanes. This method came into favor in the United States in the 1950s. One of the most effective and efficient methods of controlling the traffic on a highway is the adoption of high intersection geometric design standards. Channelization is an integral part of at-grade intersections and is used to separate turning movements from through movements where this is considered advisable and hence helps reduce the intensity and frequency of loss of life and property due to accidents to a large extent. Proper channelization increases capacity, improves safety, provides maximum convenience, and instils driver confidence. Improper channelization has the opposite effect and may be worse than none at all. Over-channelization should be avoided because it could create confusion and worsen operations. Channelization of at-grade intersections is the separation or regulation of conflicting traffic movements into definite paths of travel by the use of pavement markings, raised islands, or other suitable means to facilitate the safe and orderly movement of both vehicles and pedestrians.

The Canadian Capacity Guide for Signalized Intersections (CCG) is a publication of the Canadian Institute of Transportation Engineers (CITE). It provides a methodology that allows Traffic Engineers to plan, design, and evaluate traffic signal controlled roadway intersections.

Traffic simulation or the simulation of transportation systems is the mathematical modeling of transportation systems through the application of computer software to better help plan, design, and operate transportation systems. Simulation of transportation systems started over forty years ago, and is an important area of discipline in traffic engineering and transportation planning today. Various national and local transportation agencies, academic institutions and consulting firms use simulation to aid in their management of transportation networks.

The National Cooperative Highway Research Program (NCHRP) conducts research in problem areas that affect highway planning, design, construction, operation, and maintenance in the United States. Spearheaded by the Transportation Research Board (TRB), part of the National Academies of Sciences Engineering and Medicine, it is jointly supported by federal agencies, state departments of transportation, and other nonprofit organizations.
Sidra Intersection is a software package used for intersection (junction) and network capacity, level of service and performance analysis, and signalised intersection and network timing calculations by traffic design, operations and planning professionals.
David Shinar is one of the most prominent and productive researchers in the area of traffic safety, and a professor emeritus at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Israel.
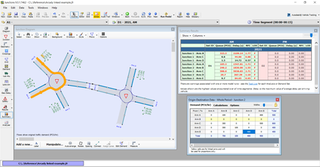
Junctions is a software package by Transport Research Laboratory. It incorporates the previously separate programs ARCADY, PICADY and OSCADY. The latest version, Junctions 10, was launched Wednesday 3 February 2021.
The flail space model (FSM) is a model of how a car passenger moves in a vehicle that collides with a roadside feature such as a guardrail or a crash cushion. Its principal purpose is to assess the potential risk of harm to the hypothetical occupant as he or she impacts the interior of the passenger compartment and, ultimately, the efficacy of an experimental roadside feature undergoing full-scale vehicle crash testing.

An offset T-intersection is an at-grade road intersection where a conventional four leg intersection is split into two three-leg T-intersections to reduce the number of conflicts and improve traffic flow. Building the offset T-intersections as continuous green T-intersections, there is a single stop on the arterial road, only. A higher volume of through traffic on the cross road, or on unsignalized intersections, a rebuild to a conventional four-leg intersection may be adequate, also when the offset is a few feet only like staggered junctions causing slower traffic for a longer time on the arterial road.
Kumares C. Sinha is an Indian-American engineer, researcher and educator known for contributions to transportation systems analysis, transportation infrastructure economics and management, transportation safety, and the use of emerging technologies in transportation. He has served as Edgar B. and Hedwig M. Olson Distinguished Professor of Civil Engineering at Purdue University. since 1998.
The Highway Capacity Software (HCS) is a traffic simulation software tool developed by the McTrans Center at University of Florida.









