
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North and Central European Plain.

Frisia is a cross-border cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Stretching along the Wadden Sea, it encompasses the north of the Netherlands and parts of northwestern Germany. Wider definitions of "Frisia" may include the island of Rem and the other Danish Wadden Sea Islands. The region is traditionally inhabited by the Frisians, a West Germanic ethnic group.
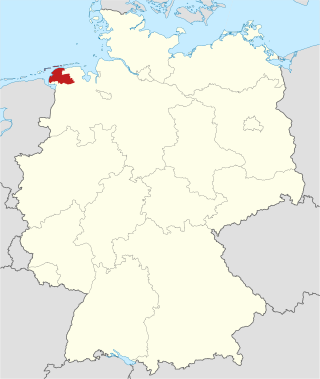
Aurich is a district (Landkreis) in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is bounded by the North Sea, the districts of Wittmund and Leer, and the city of Emden.

The East Frisian Islands are a chain of islands in the North Sea, off the coast of East Frisia in Lower Saxony, Germany. The islands extend for some 90 kilometres (56 mi) from west to east between the mouths of the Ems and Jade / Weser rivers and lie about 3.5 to 10 km offshore. Between the islands and the mainland are extensive mudflats, known locally as Watten, which form part of the Wadden Sea. In front of the islands are Germany's territorial waters, which occupy a much larger area than the islands themselves. The islands, the surrounding mudflats and the territorial waters form a close ecological relationship. The island group makes up about 5% of the Lower Saxony Wadden Sea National Park.
Leer is a district (Landkreis) in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is bounded by the city of Emden, the districts of Aurich, Wittmund, Friesland, Ammerland, Cloppenburg and Emsland, and by the Netherlands.
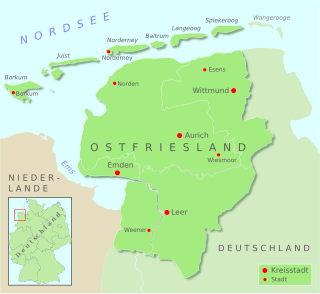
East Frisia or East Friesland is a historic region in modern Lower Saxony, Germany. The modern province is primarily located on the western half of the East Frisian peninsula, to the east of West Frisia and to the west of Landkreis Friesland but is known to have extended much further inland before modern representations of the territory. Administratively, East Frisia consists of the districts Aurich, Leer and Wittmund and the city of Emden. It has a population of approximately 469,000 people and an area of 3,142 square kilometres (1,213 sq mi).

Jomsborg or Jómsborg was a semi-legendary Viking stronghold at the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, that existed between the 960s and 1043. Its inhabitants were known as Jomsvikings. Jomsborg's exact location, or its existence, has not yet been established, though it is often maintained that Jomsborg was located on the eastern outlet of the Oder river. Historian Lauritz Weibull dismissed Jomsborg as a legend.

Greetsiel is a small port on the bight of Leybucht in western East Frisia, Germany, that was first documented in letters from the year 1388. Since 1972, Greetsiel has been part of the municipality of Krummhörn, which has its administrative seat in Pewsum. The nearest railway station is at Emden, about 15–20 kilometres (9.3–12.4 mi) away, and the two towns are linked by a bus service.

The title Earl of Dunbar, also called Earl of Lothian or Earl of March, applied to the head of a comital lordship in south-eastern Scotland between the early 12th century and the early 15th century. The first man to use the title of Earl in this capacity was Gospatric II, Earl of Lothian, son of Gospatric, Earl of Northumbria. It descended to George de Dunbar, 11th Earl of March, whose titles & estates were declared forfeit by the Scottish parliament in 1435, and retired into obscurity in England. His son Patrick retained a barony at Kilconquhar in Fife.

Logabirum is a quarter in the city of Leer in East Frisia, Lower Saxony, Germany.

Reric or Rerik was one of the Viking Age multi-ethnic Slavic-Scandinavian emporia on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, located near Wismar in the present-day German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern Reric was established probably in 735 shortly after Slavs of the Obodrite tribe had started to settle the region. At the turn of the 9th century, the citizens of Reric allied with Charlemagne, who used the port as part of a strategic trade route that would avoid areas of Saxon and Danish control. It was destroyed in 808 AD by the Viking (Danish) king Gudfred. The destroyed place was rebuilt by the Obodrites and continued to operate for a short until Drasco was murdered in Reric in 810 at the instigation of Gudfred. After that, the tradespeople were reportedly moved by the king to the Viking emporium of Hedeby near modern Schleswig.

Dornum is a village and a municipality in the East Frisian district of Aurich, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is located near the North Sea coast, approx. 15 km east of Norden, and 20 km north of Aurich.

The Rheiderland is a region of Germany and the Netherlands between the River Ems and the Bay of Dollart. The German part of the Rheiderland lies in East Frisia, west of the Ems. The Dutch part lies in the Dutch province of Groningen and is mostly part of Oldambt. The Rheiderland is one of the four historic regions on the mainland in the district of Leer; the others being the Overledingerland, the Moormerland and the Lengenerland.

Land Hadeln is a historic landscape and former administrative district in Northern Germany with its seat in Otterndorf on the Lower Elbe, the lower reaches of the River Elbe, in the Elbe-Weser Triangle between the estuaries of the Elbe and Weser.

The Leybucht is the second largest bay in East Frisia in northwest Germany after the Dollart. The Jade Bight is larger than both, but belongs historically to Oldenburg.

Groothusen is an old Langwurtendorf – a village on an artificially-built ridge – in the municipality of Krummhörn in western East Frisia on Germany's North Sea coast. It lies about 15 kilometres northwest of the seaport of Emden and has a population of 474 (2006). The ridge or warf has a length of about 500 metres and a width of some 130 metres and was built to raise the village above the water level should flooding from the sea occur, for instance, during a storm tide.
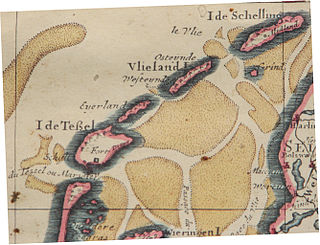
Eierland is a former island in the Netherlands. It is now the northern part of the island of Texel. The name means "egg land", named for the seagull eggs that were collected on the island and sent to Amsterdam.

Nesse is an East Frisian village in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is an Ortsteil of the municipality of Dornum, in the district of Aurich. It is situated near the Wadden Sea coast, approximately 2.5 km west of the village of Dornum, and 20 km north of the town of Aurich. As of 2021, the village and surrounding farms had a population of 639.

The Bay of Sielmönken or Bight of Sielmönken is a former bay on the territory of the present day municipality of Krummhörn in the west of East Frisia in Germany. The bight reached its greatest extent during the Carolingian transgression of 800 to 950 A. D. After that it silted up heavily and was completely enclosed by dykes between 1,000 A. D. and the 13th century.

Church Bay is a settlement on the north-west coast of Anglesey, Wales, United Kingdom, about a mile and a half north-west of the village of Llanfaethlu. The bay shores are rocky but there is also a sandy beach which is popular with visitors. There are a handful of houses near the beach. The Anglesey Coastal Path runs along the cliff tops. There are records of the Swttan settlement going back to the reign of King Henry VIII, but there has probably been a settlement there for many centuries before this. Most of the properties are holiday homes for rent. Amenities include a cafe and a small museum based in a preserved 17th-century thatched cottage. This cottage's position could indicate that there has been a dwelling on this site since Neolithic times. The cottage won the Rural Wales Award from the Campaign for the Protection of Rural Wales (CPRW) in 2003.



















