Byblos, also known as Jebeil, Jbeil or Jubayl, is an ancient city in the Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate of Lebanon. The area is believed to have been first settled between 8800 and 7000 BC and continuously inhabited since 5000 BC. During its history, Byblos was part of numerous cultures including Egyptian, Phoenician, Assyrian, Persian, Hellenistic, Roman, Genoese, Mamluk and Ottoman. Urbanisation is thought to have begun during the third millennium BC and it developed into a city making it one of the oldest cities in the world, if not the oldest. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Arbet Kozhaya, also known as Arbet Qozhaya or Arabet Kozhaya, is one of the fifty-six towns and villages, which make up the Zgharta District in the North Governorate of Lebanon.

Anfeh, or Enfe, Enfeh, Anfe, is a town in the Koura district of the North Governorate of Lebanon. Anfeh borders the towns of Chekka, Al-Qalamoun, Barghoun and Zakroun. It is located 65 kilometres (40 mi) north of Beirut and 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) south of Tripoli. Its total area is 4.93 square kilometres (1.90 sq mi), and its population is around 6,500.

Kfarsghab is a village located in the Zgharta District in the North Governorate of Lebanon. It is situated in the Valley of Qadisha, which is considered a holy and spiritual place in Eastern Christianity. The main religion of its residents is Maronite Catholicism.

Byblos District, also called the Jbeil District, is a district (qadaa) of the Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate of Lebanon. It is located to the northeast of Lebanon's capital Beirut. The capital is Byblos. The rivers of al-Madfoun and Nahr Ibrahim form the district's natural northern and southern borders respectively, with the Mediterranean Sea bordering it from the west and Mount Lebanon from the east, separating it from the adjacent district of Baalbek in the Beqaa Valley.
Bishmizzine, or Bishmezzine, Bechmezzine, Beshmizzine, Bishmezzine, thought to be neo-Assyrian, is a Greek Orthodox village, in the Koura district of the North Governorate of Lebanon. It is about 275 meters above sea level. Bishmizzine borders the villages of Afisdeeq, Kfar-Hazir, Amyoun, Fi', and B'terram.
Deir El Ahmar is a Lebanese town, located 100km from Beirut and 22km northwest of Baalbek in the Bekaa Valley in Lebanon.

The National Museum of Beirut is the principal museum of archaeology in Lebanon. The collection begun after World War I, and the museum was officially opened in 1942. The museum has collections totaling about 100,000 objects, most of which are antiquities and medieval finds from excavations undertaken by the Directorate General of Antiquities.
Qartaba is a town in the mountains of the Byblos District of the Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate, Lebanon. It is located 57 kilometers north Beirut on the mountains above Byblos at an average altitude of 1,250 meters. It is the second-most populous city in the district after Byblos.

Coccodus is an extinct genus of marine pycnodontid fish that lived during the Late Cretaceous. The various species had a pair of massive, curved spines emanating from the lower sides of the head, and one curved spine on the top of its head. Unlike most pycnodontids, Coccodus species had a comparatively long body, giving the living animals a superficial resemblance to a scaly chimaera.
Styletoctopus is an extinct genus of octopus. The genus consists of the single species Styletoctopus annae, which lived approximately 95 million years ago during the late Cenomanian,. It was first discovered in 2009 by a team led by Dirk Fuchs of Freie University in the Hâqel and Hjoula localities in Lebanon. Very few octopus species appear in the fossil record, as octopuses consist of soft tissue that usually decomposes before it has time to fossilize.

Keuppia is an extinct genus of octopus.

Tannourine is a Lebanese town located in the Batroun District, part of the Governorate of North Lebanon, 80 km from the capital Beirut. Tannourine is formed by a cluster of mountain settlements located in the highs of the Batroun District, the largest of which is Tannourine El-Fawqa, followed by Chatine,Tannourine El-Tahta, and Wata Houb. Tannourine has a population of approximately 25,000.

Mansourieh, also known by various spellings, including: el-Mansourieh, Mansouriyeh, Mansouriyet el-Matn, and el-Mansouria is a town in the Matn District of the Mount Lebanon Governorate, in Lebanon. This place holds significant historical importance due to the presence of well-preserved archaeological remains, specifically a Roman aqueduct.

The paleontological sites of Lebanon contain deposits of well preserved fossils and include some species found nowhere else. Notable among these is the Lebanese lagerstätten of the Late Cretaceous age, which contain a well-preserved variety of different fossils. Some fossils date back to the Jurassic period, and younger fossils of mammals from a different site belong to the Miocene through the Pleistocene.

The Phoenicians were an ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon. They developed a maritime civilization which expanded and contracted throughout history, with the core of their culture stretching from Arwad in modern Syria to Mount Carmel. The Phoenicians extended their cultural influence through trade and colonization throughout the Mediterranean, from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula.

Ghabat is a village in Lebanon located in the Jurd area of the district of Byblos in the Mount Lebanon region, about 74 kilometres northeast of Beirut. Its inhabitants are predominantly Maronite Catholics.

The Sannine Formation, also called the Sannine Limestone, is a Cretaceous geologic formation in Lebanon. It is a Konservat-Lagerstätte that contains a high diversity of well-preserved fish, reptiles, and invertebrates from the Tethys Ocean within its three main localities: Haqel, Hjoula, and Nammoura.
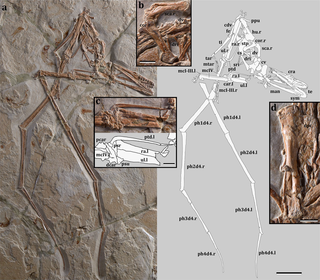
Mimodactylus is a genus of istiodactyliform pterosaur that lived in what is now Lebanon during the Late Cretaceous, 95 million years ago. The only known specimen was discovered in a limestone quarry near the town of Hjoula, belonging to the Sannine Formation. The owner of the quarry allowed the specimen to be prepared and scientifically described by an international team of researchers, and when it was eventually sold, the buyer donated it to the MIM Museum in Beirut. In 2019, the researchers named the new genus and species Mimodactylus libanensis; the generic name refers to the MIM Museum, combined with the Greek word daktylos for "digit", and the specific name refers to Lebanon. The well-preserved holotype specimen is the first complete pterosaur from the Afro-Arabian continent, and the third pterosaur fossil known from Lebanon.