
Edwin Powell Hubble was an American astronomer. He played a crucial role in establishing the fields of extragalactic astronomy and observational cosmology.

A space telescope or space observatory is a telescope in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO-2 launched in 1968, and the Soviet Orion 1 ultraviolet telescope aboard space station Salyut 1 in 1971. Space telescopes avoid the filtering and distortion (scintillation) of electromagnetic radiation which they observe, and avoid light pollution which ground-based observatories encounter. They are divided into two types: Satellites which map the entire sky, and satellites which focus on selected astronomical objects or parts of the sky and beyond. Space telescopes are distinct from Earth imaging satellites, which point toward Earth for satellite imaging, applied for weather analysis, espionage, and other types of information gathering.

The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned both as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft.
Hubble's law, also known as the Hubble–Lemaître law, is the observation in physical cosmology that galaxies are moving away from Earth at speeds proportional to their distance. In other words, the farther they are, the faster they are moving away from Earth. The velocity of the galaxies has been determined by their redshift, a shift of the light they emit toward the red end of the visible spectrum.

A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. They are the second-largest known gravitationally bound structures in the universe after galaxy filaments and were believed to be the largest known structures in the universe until the 1980s, when superclusters were discovered. One of the key features of clusters is the intracluster medium (ICM). The ICM consists of heated gas between the galaxies and has a peak temperature between 2–15 keV that is dependent on the total mass of the cluster. Galaxy clusters should not be confused with galactic clusters (also known as open clusters), which are star clusters within galaxies, or with globular clusters, which typically orbit galaxies. Small aggregates of galaxies are referred to as galaxy groups rather than clusters of galaxies. The galaxy groups and clusters can themselves cluster together to form superclusters.
Verne Hedges Winchell was the founder of Winchell's Donuts and also served as a chairman, president, and chief executive officer of the Denny's restaurant chain.
The Hubble Space Telescope is a telescope in low Earth orbit.

The Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF) is a deep-field image of a small region of space in the constellation Fornax, containing an estimated 10,000 galaxies. The original data for the image was collected by the Hubble Space Telescope from September 2003 to January 2004. It includes light from galaxies that existed about 13 billion years ago, some 400 to 800 million years after the Big Bang.

Vesto Melvin Slipher was an American astronomer who performed the first measurements of radial velocities for galaxies. He was the first to discover that distant galaxies are redshifted, thus providing the first empirical basis for the expansion of the universe. He was also the first to relate these redshifts to velocity.
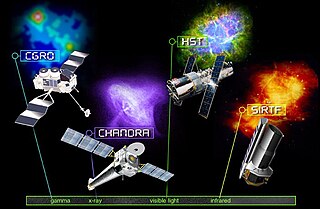
NASA's series of Great Observatories satellites are four large, powerful space-based astronomical telescopes launched between 1990 and 2003. They were built with different technology to examine specific wavelength/energy regions of the electromagnetic spectrum: gamma rays, X-rays, visible and ultraviolet light, and infrared light.
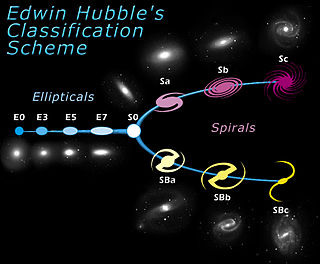
Galaxy morphological classification is a system used by astronomers to divide galaxies into groups based on their visual appearance. There are several schemes in use by which galaxies can be classified according to their morphologies, the most famous being the Hubble sequence, devised by Edwin Hubble and later expanded by Gérard de Vaucouleurs and Allan Sandage. However, galaxy classification and morphology are now largely done using computational methods and physical morphology.
The Hubble Origins Probe (HOP) was a proposal for an orbital telescope made in 2005 in response to the first cancellation of the fourth Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission. It would have used an Atlas V rocket or similar launch vehicle to launch a much lighter, unaberrated mirror and optical telescope assembly, using the instruments that had already been built for SM4, along with a new wide-field imager. It would have cost between $700 million and $1 billion.

STS-125, or HST-SM4, was the fifth and final Space Shuttle mission to the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and the last solo flight of the Space Shuttle Atlantis and of any Space Shuttle. The launch of the Space Shuttle Atlantis occurred on May 11, 2009, at 2:01 pm EDT. Landing occurred on May 24 at 11:39 am EDT, with the mission lasting a total of just under 13 days.
The expansion of the universe is the increase in distance between any two given gravitationally unbound parts of the observable universe with time. It is an intrinsic expansion whereby the scale of space itself changes. The universe does not expand "into" anything and does not require space to exist "outside" it. This expansion involves neither space nor objects in space "moving" in a traditional sense, but rather it is the metric that changes in scale. As the spatial part of the universe's spacetime metric increases in scale, objects become more distant from one another at ever-increasing speeds. To any observer in the universe, it appears that all of space is expanding, and that all but the nearest galaxies recede at speeds that are proportional to their distance from the observer. While objects within space cannot travel faster than light, this limitation does not apply to the effects of changes in the metric itself. Objects that recede beyond the cosmic event horizon will eventually become unobservable, as no new light from them will be capable of overcoming the universe's expansion, limiting the size of our observable universe.

Pillars of Creation is a photograph taken by the Hubble Space Telescope of elephant trunks of interstellar gas and dust in the Eagle Nebula, in the Serpens constellation, some 6,500–7,000 light-years from Earth. These elephant trunks had been discovered by John Charles Duncan in 1920 on a plate made with the Mount Wilson Observatory 60-inch telescope. They are named so because the gas and dust are in the process of creating new stars, while also being eroded by the light from nearby stars that have recently formed. Taken on April 1, 1995, it was named one of the top ten photographs from Hubble by Space.com. The astronomers responsible for the photo were Jeff Hester and Paul Scowen from Arizona State University. The region was rephotographed by ESA's Herschel Space Observatory in 2011, again by Hubble in 2014 with a newer camera, and the James Webb Space Telescope in 2022.

Hubble is a 2010 American documentary film about Space Shuttle missions to repair and upgrade the Hubble Space Telescope. It is narrated by the actor Leonardo DiCaprio.
The 2010 Fifth Third Bank Tennis Championships was a professional men's tennis tournament played on hard court. It was a sixteenth edition of the tournament which was part of the 2010 ATP Challenger Tour. It took place in Lexington, Kentucky, United States, between 19 July and 24 July 2010.

Mystic Mountain is a photograph and a term for a region in the Carina Nebula imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope. The view was captured by the then-new Wide Field Camera 3, though the region was also viewed by the previous generation instrument. The new view celebrated the telescope's 20th anniversary of being in space in 2010. Mystic Mountain contains multiple Herbig–Haro objects where nascent stars are firing off jets of gas which interact with surrounding clouds of gas and dust. This region is about 7,500 light-years away from Earth. The pillar measures around three light-years in height. The name was influenced by the works of H. P. Lovecraft.

WHL0137-LS, also known as Earendel, is a star in the constellation of Cetus. Discovered in 2022 by the Hubble Space Telescope, it is the earliest and most distant known star, at a comoving distance of 28 billion light-years. The previous furthest known star, MACS J1149 Lensed Star 1, also known as Icarus, at a comoving distance of 14.4 billion light-years, was discovered by Hubble in 2018. Stars like Earendel can be observed at cosmological distances thanks to the large magnification factors involved, that can exceed 1000. Other stars have been observed through this technique, such as Godzilla.














