Related Research Articles
The Janjaweed are an Arab nomad militia group from the Sahel region that operates in Sudan, particularly in Darfur, and eastern Chad. They have also been speculated to be active in Yemen. According to the United Nations definition, Janjaweed membership consists of Arab nomad tribes from the Sahel, the core of whom are from the Abbala Arabs, traditionally employed in camel herding, with significant recruitment from the Baggara.

The War in Darfur, also nicknamed the Land Cruiser War, was a major armed conflict in the Darfur region of Sudan that began in February 2003 when the Sudan Liberation Movement (SLM) and the Justice and Equality Movement (JEM) rebel groups began fighting against the government of Sudan, which they accused of oppressing Darfur's non-Arab population. The government responded to attacks by carrying out a campaign of ethnic cleansing against Darfur's non-Arabs. This resulted in the death of hundreds of thousands of civilians and the indictment of Sudan's president, Omar al-Bashir, for genocide, war crimes, and crimes against humanity by the International Criminal Court.

Sudan–United States relations are the bilateral relations between Sudan and the United States. The United States government has been critical of Sudan's human rights record and has dispatched a strong UN Peacekeeping force to Darfur. Relations between both countries in recent years have greatly improved, with Sudan's post-revolutionary government compensating American victims of al-Qaeda terror attacks, the removal of Sudan from the State Department's blacklist of state sponsors of terrorism and the United States Congress having reinstated Sudan's sovereign immunity in December 2020.
Sudanese nomadic conflicts are non-state conflicts between rival nomadic tribes taking place in the territory of Sudan and, since 2011, South Sudan. Conflict between nomadic tribes in Sudan is common, with fights breaking out over scarce resources, including grazing land, cattle and drinking water. Some of the tribes involved in these clashes have been the Messiria, Maalia, Rizeigat and Bani Hussein Arabic tribes inhabiting Darfur and West Kordofan, and the Dinka, Nuer and Murle African ethnic groups inhabiting South Sudan. Conflicts have been fueled by other major wars taking place in the same regions, in particular the Second Sudanese Civil War, the War in Darfur and the Sudanese conflict in South Kordofan and Blue Nile.

The Rapid Support Forces is a paramilitary force formerly operated by the Government of Sudan. The RSF grew out of, and is primarily composed of, the Janjaweed militias which previously fought on behalf of the Sudanese government. Its actions in Darfur qualify as crimes against humanity in the opinion of Human Rights Watch.

Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo, generally referred to mononymously as Hemedti, Hemetti, Hemeti, or Hemitte, is a Janjaweed leader from the Rizeigat tribe in Darfur, who was the Deputy head of the Transitional Military Council (TMC) following the 2019 Sudanese coup d'état. Since 2013, Hemetti has commanded the Rapid Support Forces (RSF). He was considered by The Economist to be the most powerful person in Sudan as of early July 2019.

In September 2020, profuse and continuous rainfall in Sudan caused a devastating flood across 17 out of the 18 states Sudanese states with the Blue Nile reaching water levels not seen for nearly a century. It ranks among the most severe floods recorded in the region. A state of emergency was declared, and teams have worked to prevent damage to threatened archaeological sites. The flood affected more than 3,000,000 people, destroyed more than 100,000 homes, and left more than 100 people dead.
The following lists events during 2023 in the Republic of the Sudan.

A civil war between two rival factions of the military government of Sudan, the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) under Abdel Fattah al-Burhan, and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF) under the Janjaweed leader, Hemedti, began during Ramadan on 15 April 2023. Fighting has been concentrated around the capital city of Khartoum and the Darfur region. As of 21 January 2024, at least 13,000–15,000 people had been killed and 33,000 others were injured. As of 21 March, over 6.5 million were internally displaced and more than two million others had fled the country as refugees, and many civilians in Darfur have been reported dead as part of the 2023 Masalit massacres.

The battle of Khartoum is an ongoing battle for control of Khartoum, the capital city of Sudan, with fighting in and around the city between the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF), and the Sudanese Armed Forces. The battle began on 15 April 2023, after the RSF captured Khartoum International Airport, several military bases, and the presidential palace, starting an escalating series of clashes.

An ongoing refugee crisis began in Africa in mid-April 2023 after the outbreak of the 2023 Sudan conflict. By April 2024, around 1.8 million people have fled the country, while around 9-10 million had been internally displaced. These included at least 75,000 migrant returnees and other third-country nationals.

The Battle of Geneina, also known as the Geneina massacre, was a battle for control of Geneina, the capital of West Darfur in Sudan, between the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF) and the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF). By 25 April 2023, fighting intensified and devolved along tribal lines, with Masalit and non-Arab peoples supporting the SAF and the aligned Joint Darfur Force—consisting of former rebel groups including the Sudan Liberation Movement/Army and the Justice and Equality Movement—against the RSF and allied Arab militias.

The Darfur campaign or Darfur offensive is a theatre of operation in the war in Sudan that affects five states in Darfur: South Darfur, East Darfur, North Darfur, Central Darfur and West Darfur. The offensive mainly started on 15 April 2023 in West Darfur where the Rapid Support Forces (RSF) forces captured Geneina, the conflict came after several days of high tensions between the forces and the government.
The following is a timeline of the War in Sudan (2023-present).
The Battle of Nyala was a battle for control of Nyala, the capital of South Darfur in Sudan, between the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF), and the Sudanese Armed Forces during the ongoing Darfur campaign. The first battle occurred between 15 and 20 April 2023, during which hundreds were reported dead. A civilian-brokered ceasefire paused the fighting by April 20. Sporadic clashes broke out between May and July. In August 2023, the RSF launched an offensive on the city. The SAF launched air campaigns against the RSF in Nyala, with many civilian casualties in Taiba and El Matar. In late September, the RSF besieged the headquarters the SAF's 16th Infantry Division headquarters, capturing it on October 26.
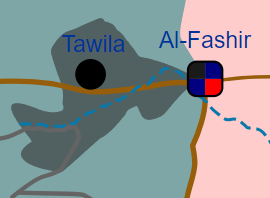
The Battle of El Fasher is an ongoing battle for control of the town of El Fasher in North Darfur during the 2023 Sudan conflict. The first battle for the city took place between April 15 and April 20 2023, and resulted in a ceasefire that held until May 12. Clashes broke out again between May 12 and 29, and ended with a more stable ceasefire that lasted until August. By September, the city had become a haven for refugees across the region, and was also suffering from food and water shortages.
The Treaty of Jeddah or Jeddah Declaration is an international agreement that was made to make peace in Sudan. The Treaty of Jeddah, which was signed by the United States, Saudi Arabia, and Sudan and representatives of both warring sides on 20 May 2023, entered into force 48 hours later on 22 May 2023. The agreement was supposed to create a week-long ceasefire and the distribution of humanitarian aid within the country. The agreement expired suddenly after a surge of clashes on 23 May 2023, a day after the agreement came into effect. With the actual date of expiry being 27 May 2023, the nations agreed on an extension for five days but was shortened due to the agreement's ineffectiveness.

The siege of El Obeid was a siege in El-Obeid, North Kordofan, Sudan, during the 2023 Sudan conflict. The battle began on April 15, and saw the Rapid Support Forces (RSF) capture the El Obeid airport from the Sudanese Army contingent in the city. Throughout April and May, the Sudanese Army repelled several RSF assaults on the city, although by May 30, the RSF fully surrounded the city and laid siege to it.

The war in Sudan, which started on 15 April 2023, has seen a widespread of war crimes committed by both the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and the Rapid Support Forces (RSF), with the RSF being singled out by the Human Rights Watch, and the United Kingdom and United States governments for committing crimes against humanity. The conflict was marked by heavy indiscriminate shelling, gunfire, and airstrikes on markets and populated residential neighbourhoods, causing a high number of fatalities. Hospitals were targeted during aerial bombings and artillery fire, and medical supplies were looted. These attacks severely impacted Sudan’s healthcare system, disrupting medical services and leaving the majority of the hospitals in conflict-affected states out of service. The UN declared Sudan the most dangerous country for humanitarian workers after South Sudan.
References
- ↑ Dahir, Abdi Latif (17 April 2023). "As New Wave of Violence Hits Sudan's Capital, Civilians Feel the Strain". The New York Times . Archived from the original on 17 April 2023. Retrieved 17 April 2023.
- ↑ "Sudan crisis: Civilians facing 'catastrophe' as 100,000 flee fighting - UN". BBC . 2 May 2023. Retrieved 2 May 2023.
- ↑ "More than 60% of hospitals out of service". Aljazeera . 22 April 2023. Archived from the original on 20 April 2023. Retrieved 23 April 2023.
- ↑ Uras, Umut (25 April 2023). "Supply shortages becoming 'extremely acute' – UN". Al Jazeera . Archived from the original on 25 April 2023. Retrieved 25 April 2023.
- ↑ "Sudan residents face cash shortage as sources dry up". Al Jazeera . 28 April 2023.
- ↑ "President Biden authorises sanctions against Sudan". BBC . 4 May 2023. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- ↑ "As Sudan war rages, rival sides accused of looting, diverting aid". Al Jazeera . 16 June 2023. Retrieved 25 June 2023.
- ↑ "Sudan civil war: UN receiving reports of starvation deaths". BBC News. 2024-02-02. Retrieved 2024-02-06.
- ↑ "Crisis in Sudan: What is happening and how to help". www.rescue.org. 2024-03-25. Retrieved 2024-04-09.
- ↑ "CDonors raise more than 2 billion euros for Sudan aid a year into war". Reuters. 2024-04-15. Retrieved 2024-04-17.
- ↑ "'Stop bombing hospitals', doctors tell warring sides". Al Jazeera . Archived from the original on 17 April 2023. Retrieved 2023-04-17.
- ↑ Picheta, Rob; Salem, Mostafa; Akbarza, Sahar (20 April 2023). "People scramble to leave Sudan's capital after attempted ceasefires fail to stop violence". CNN . Archived from the original on 20 April 2023. Retrieved 2023-04-20.
- ↑ "Only five out of 59 hospitals open in Khartoum – doctor". BBC News . Archived from the original on 17 April 2023. Retrieved 19 April 2023.
- ↑ "Sudan's RSF 'occupying 12 hospitals' – ministry". BBC News . Retrieved 28 April 2023.
- ↑ "Sudan residents describe raids, evictions by RSF soldiers". Aljazeera . Retrieved 8 May 2023.
- ↑ "Sudan fighting: Khartoum violence mapped as civilians flee city". BBC News . Archived from the original on 23 April 2023. Retrieved 24 April 2023.
- ↑ "Sudan crisis: 'I thought we'd die' – hospital patients cry for help". BBC News . 17 April 2023. Archived from the original on 18 April 2023. Retrieved 2023-04-18.
- ↑ "Warring sides seized ambulances: WHO". Al Jazeera . Archived from the original on 18 April 2023. Retrieved 19 April 2023.
- ↑ "Doctors sound alarm over health crisis". Al Jazeera . Archived from the original on 18 April 2023. Retrieved 18 April 2023.
- ↑ "Power cuts and looting impact daily life across Khartoum". Al Jazeera . Archived from the original on 19 April 2023. Retrieved 19 April 2023.
- ↑ "Red Cross cautions against Sudan evacuation". BBC News . Archived from the original on 17 April 2023. Retrieved 19 April 2023.
- ↑ "Desperate Khartoum residents go to the Nile for water". BBC News . Archived from the original on 20 April 2023. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ↑ "Sudan fighting: The unsung heroes keeping Khartoum residents alive". BBC News . 21 April 2023. Archived from the original on 21 April 2023. Retrieved 21 April 2023.
- ↑ "Lion reserve warns it is running low on food, fighting nearby". Aljazeera . 21 April 2023. Archived from the original on 23 April 2023. Retrieved 23 April 2023.
- ↑ "Sudan's RSF set up 'humanitarian' call centre". BBC News . 20 April 2023. Archived from the original on 17 April 2023. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ↑ "UN accuses RSF of removing people from their homes". Aljazeera . 28 April 2023. Retrieved 28 April 2023.
- ↑ "How conflict is jeopardizing Sudan's museums and cultural heritage". Arab News . 6 June 2023. Retrieved 16 June 2023.
- ↑ "Sudan's cultural treasures destroyed in conflict". DW News . 15 June 2023. Retrieved 16 June 2023.
- ↑ "Sudan's National Museum Reportedly Raided by Paramilitary". Hyperallergic . 6 June 2023. Retrieved 16 June 2023.
- ↑ "Sudan conflict: pro-democracy artists under attack and museums at risk of looting, sources say". The Art Newspaper . 27 April 2023. Retrieved 1 May 2023.
- ↑ السودان.. اشتباكات عنيفة بين الجيش وقوات الدعم السريع (لحظة بلحظة). Al Jazeera (in Arabic). Archived from the original on 15 April 2023. Retrieved 2023-04-16.
- ↑ "Students trapped, hospitals shelled and diplomats assaulted as Sudan fighting intensifies". CNN. 18 April 2023. Archived from the original on 18 April 2023. Retrieved 2023-04-18.
- 1 2 3 "Fierce battles for army headquarters and airport are underway in Sudan". CNN . 19 April 2023. Archived from the original on 19 April 2023. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ↑ "Medical supplies have been looted – Save the Children". www.bbc.com. Archived from the original on 15 April 2023. Retrieved 2023-04-18.
- ↑ "Islamic Relief unable to provide aid, offices looted, staff told to hibernate". Al Jazeera . Archived from the original on 20 April 2023. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- 1 2 3 "WFP temporarily halts operations in Sudan". BBC . 16 April 2023. Archived from the original on 15 April 2023. Retrieved 16 April 2023.
- ↑ "UN: Reports of attacks, sexual violence against aid workers". Al Jazeera . Archived from the original on 18 April 2023. Retrieved 19 April 2023.
- 1 2 "Sudan fighting forces aid groups to halt, spreading suffering". Al Jazeera . Retrieved 27 April 2023.
- ↑ "Situation in el-Geneina, capital of West Darfur, is dire". Al Jazeera . Retrieved 1 May 2023.
- ↑ "Sudan updates: UN admits failure to avert war as aid looted". DW . 4 May 2023. Retrieved 2023-05-04.
- ↑ "More than 3,000 people killed, 6,000 injured in Sudan conflict". The Jerusalem Post. 17 June 2023. Retrieved 20 June 2023.
- ↑ "'Almost impossible' to provide aid in Sudanese capital: IFRC". Al Jazeera . Archived from the original on 18 April 2023. Retrieved 2023-04-18.
- ↑ "UN humanitarian program in 'total shutdown'". Al Jazeera . Archived from the original on 19 April 2023. Retrieved 19 April 2023.
- ↑ "Armed groups loot medical supplies from Save the Children: Organisation". Al Jazeera . Archived from the original on 17 April 2023. Retrieved 17 April 2023.
- ↑ "Sudanese and foreign aid workers arrive in Chad from Sudan". Al Jazeera . Retrieved 1 May 2023.
- ↑ "First Red Cross aid flight lands in Sudan as fighting rages". France 24 . Retrieved 1 May 2023.
- ↑ "World Food Programme resumes operations in Sudan". Al Jazeera . Retrieved 1 May 2023.
- ↑ "Fighting Shakes Khartoum As Displaced Battle Disease". Barron's. AFP. 2 July 2023. Retrieved 3 July 2023.
- ↑ "Sudan fighting sparks communications blackout in Khartoum, disease outbreaks". France 24. 14 July 2023. Retrieved 14 July 2023.
- ↑ Barber, Harriet (2023-08-08). "Thousands of decomposing corpses on Khartoum's streets lead to outbreak fears". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235 . Retrieved 2023-08-08.
- ↑ "War in Sudan: more than 7 million displaced - UN". Africanews. 23 December 2023. Retrieved 23 December 2023.
- ↑ "Sudan conflict displaces more than 5 million people: OCHA". Sudan Tribune. 7 September 2023. Retrieved 8 September 2023.
- ↑ "Sudan's raging war forces more than two million from their homes". Al Jazeera . 14 June 2023. Retrieved 19 June 2023.
- ↑ "7 million people internally displaced in Sudan: IOM". Sudan Tribune. 5 September 2023.