
A pump is a device that moves fluids, or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic or pneumatic energy.

A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tight by piston rings. In an engine, its purpose is to transfer force from expanding gas in the cylinder to the crankshaft via a piston rod and/or connecting rod. In a pump, the function is reversed and force is transferred from the crankshaft to the piston for the purpose of compressing or ejecting the fluid in the cylinder. In some engines, the piston also acts as a valve by covering and uncovering ports in the cylinder.

In mechanical engineering, an end-face mechanical seal is a type of seal used in rotating equipment, such as pumps, mixers, blowers, and compressors. When a pump operates, the liquid could leak out of the pump between the rotating shaft and the stationary pump casing. Since the shaft rotates, preventing this leakage can be difficult. Earlier pump models used mechanical packing to seal the shaft. Since World War II, mechanical seals have replaced packing in many applications.

A gasket is a mechanical seal which fills the space between two or more mating surfaces, generally to prevent leakage from or into the joined objects while under compression. It is a deformable material that is used to create a static seal and maintain that seal under various operating conditions in a mechanical assembly.

An O-ring, also known as a packing or a toric joint, is a mechanical gasket in the shape of a torus; it is a loop of elastomer with a round cross-section, designed to be seated in a groove and compressed during assembly between two or more parts, forming a seal at the interface.
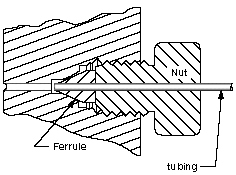
A seal is a device or material that helps join systems, mechanisms or other materials together by preventing leakage, containing pressure, or excluding contamination. The effectiveness of a seal is dependent on adhesion in the case of sealants and compression in the case of gaskets. The seals are installed in pumps in a wide range of industries including chemicals, water supply, paper production, food processing and many other applications.
A hermetic seal is any type of sealing that makes a given object airtight. The term originally applied to airtight glass containers, but as technology advanced it applied to a larger category of materials, including rubber and plastics. Hermetic seals are essential to the correct and safe functionality of many electronic and healthcare products. Used technically, it is stated in conjunction with a specific test method and conditions of use. Colloquially, the exact requirements of such a seal varies with the application.
A stuffing box or gland package is an assembly which is used to house a gland seal. It is used to prevent leakage of fluid, such as water or steam, between sliding or turning parts of machine elements.

A hydraulic cylinder is a mechanical actuator that is used to give a unidirectional force through a unidirectional stroke. It has many applications, notably in construction equipment, manufacturing machinery, elevators, and civil engineering. A hydraulic cylinder is a hydraulic actuator that provides linear motion when hydraulic energy is converted into mechanical movement. It can be likened to a muscle in that, when the hydraulic system of a machine is activated, the cylinder is responsible for providing the motion.

Pneumatic cylinder, also known as air cylinder, is a mechanical device which uses the power of compressed gas to produce a force in a reciprocating linear motion.

An axial piston pump is a positive displacement pump that has a number of pistons in a circular array within a cylinder block.

In mechanical engineering, a face seal is a seal in which the sealing surfaces are normal to the axis of the seal. Face seals are typically used in static applications and are used to prevent leakage in the radial direction with respect to the axis of the seal. Face seals are often located in a groove or cavity on a flange. Face seals are a category of products where there is no dynamic movement on the part of either the seal or the hardware surface.

A fitting or adapter is used in pipe systems to connect sections of pipe or tube, adapt to different sizes or shapes, and for other purposes such as regulating fluid flow. These fittings are used in plumbing to manipulate the conveyance of fluids such as water for potatory, irrigational, sanitary, and refrigerative purposes, gas, petroleum, liquid waste, or any other liquid or gaseous substances required in domestic or commercial environments, within a system of pipes or tubes, connected by various methods, as dictated by the material of which these are made, the material being conveyed, and the particular environmental context in which they will be used, such as soldering, mortaring, caulking, plastic welding, welding, friction fittings, threaded fittings, and compression fittings.
Artificial lift is the use of artificial means to increase the flow of liquids, such as crude oil or water, from a production well. Generally this is achieved by the use of a mechanical device inside the well or by decreasing the weight of the hydrostatic column by injecting gas into the liquid some distance down the well. A newer method called Continuous Belt Transportation (CBT) uses an oil absorbing belt to extract from marginal and idle wells. Artificial lift is needed in wells when there is insufficient pressure in the reservoir to lift the produced fluids to the surface, but often used in naturally flowing wells to increase the flow rate above what would flow naturally. The produced fluid can be oil, water or a mix of oil and water, typically mixed with some amount of gas.

Hydraulic clearance. Flow in narrow clearances are of vital importance in hydraulic system component design. The flow in a narrow circular clearance of a spool valve can be calculated according to the formula below if the height is negligible compared to the width of the clearance, such as most of the clearances in hydraulic pumps, hydraulic motors, and spool valves. Flow is considered to be laminar. The formula below is valid for a spool valve when the spool is steady.

A plunger pump is a type of positive displacement pump where the high-pressure seal is stationary and a smooth cylindrical plunger slides through the seal. This makes them different from piston pumps and allows them to be used at higher pressures. This type of pump is often used to transfer municipal and industrial sewage.
A pipe support or pipe hanger is a designed element that transfer the load from a pipe to the supporting structures. The load includes the weight of the pipe proper, the content that the pipe carries, all the pipe fittings attached to pipe, and the pipe covering such as insulation. The four main functions of a pipe support are to anchor, guide, absorb shock, and support a specified load. Pipe supports used in high or low temperature applications may contain insulation materials. The overall design configuration of a pipe support assembly is dependent on the loading and operating conditions.
High-density solids pumps are hydrostatically operating machines which displace the medium being pumped and thus create a flow.
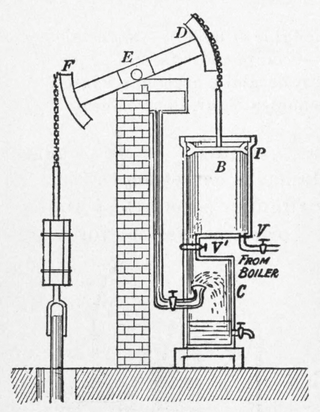
In mechanical engineering, the cylinders of reciprocating engines are often classified by whether they are single- or double-acting, depending on how the working fluid acts on the piston.
A Wills Ring or Cooper Ring is a form of all-metallic O-ring seal. They are used for extremely arduous service, such as sealing the head gasket of high performance piston engines.













