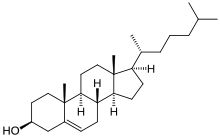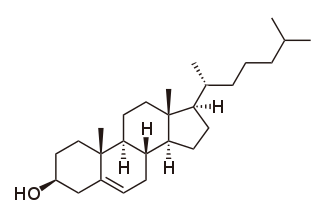
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in animal fats and oils.

Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons, very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL delivers fat molecules to cells. LDL has been associated with the progression of atherosclerosis.

Statins are a class of medications that reduce illness and mortality in people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease.
Lipid-lowering agents, also sometimes referred to as hypolipidemic agents, cholesterol-lowering drugs, or antihyperlipidemic agents are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals that are used to lower the level of lipids and lipoproteins, such as cholesterol, in the blood (hyperlipidemia). The American Heart Association recommends the descriptor 'lipid lowering agent' be used for this class of drugs rather than the term 'hypolipidemic'.

The Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study, was a multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, which provided the initial data that supported the use of the cholesterol-lowering drug, simvastatin, in people with a moderately raised cholesterol and coronary heart disease (CHD); that is people who had previously had a heart attack or angina. The study was sponsored by the pharmaceutical company Merck and enrolled 4,444 people from 94 centres in Scandinavia.

In pharmacology, the fibrates are a class of amphipathic carboxylic acids and esters. They are derivatives of fibric acid. They are used for a range of metabolic disorders, mainly hypercholesterolemia, and are therefore hypolipidemic agents.

Hypercholesterolemia, also called high cholesterol, is the presence of high levels of cholesterol in the blood. It is a form of hyperlipidemia, hyperlipoproteinemia, and dyslipidemia.
Dyslipidemia is a metabolic disorder characterized by abnormally high or low amounts of any or all lipids or lipoproteins in the blood. Dyslipidemia is a risk factor for the development of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, which include coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, and peripheral artery disease. Although dyslipidemia is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, abnormal levels do not mean that lipid lowering agents need to be started. Other factors, such as comorbid conditions and lifestyle in addition to dyslipidemia, is considered in a cardiovascular risk assessment. In developed countries, most dyslipidemias are hyperlipidemias; that is, an elevation of lipids in the blood. This is often due to diet and lifestyle. Prolonged elevation of insulin resistance can also lead to dyslipidemia.

The Heart Protection Study was a randomized controlled trial run by the Clinical Trial Service Unit, and funded by the Medical Research Council (MRC) and the British Heart Foundation (BHF) in the United Kingdom. It studied the use of the cholesterol lowering drug, simvastatin 40 mg and vitamin supplementation in people who were at risk of cardiovascular disease. It was led by Jane Armitage, an epidemiologist at the Clinical Trial Service Unit.

Atorvastatin is a statin medication used to prevent cardiovascular disease in those at high risk and to treat abnormal lipid levels. For the prevention of cardiovascular disease, statins are a first-line treatment. It is taken by mouth.
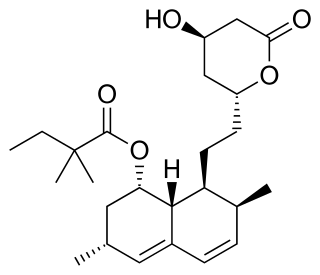
Simvastatin, sold under the brand name Zocor among others, is a statin, a type of lipid-lowering medication. It is used along with exercise, diet, and weight loss to decrease elevated lipid levels. It is also used to decrease the risk of heart problems in those at high risk. It is taken by mouth.

Ezetimibe, sold under the brand name Zetia among others, is a medication used to treat high blood cholesterol and certain other lipid abnormalities. Generally it is used together with dietary changes and a statin. Alone, it is less preferred than a statin. It is taken by mouth. It is also available in the fixed-dose combinations ezetimibe/simvastatin, ezetimibe/atorvastatin, ezetimibe/rosuvastatin, and ezetimibe/bempedoic acid.
A polypill or single pill combination (SPC) is a type of drug combination consisting of a single drug product in pill form and thus combines multiple medications. The prefix "poly" means "multiple", referring to the multiplicity of distinct drugs in a given "pill". In precise usage, a pill is a polypill if it contains at least 4 drugs. An occasional synonym is combopill. A polypill commonly targets treatment or prevention of chronic conditions.
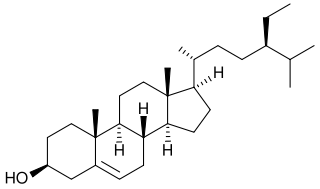
Phytosterols are phytosteroids, similar to cholesterol, that serve as structural components of biological membranes of plants. They encompass plant sterols and stanols. More than 250 sterols and related compounds have been identified. Free phytosterols extracted from oils are insoluble in water, relatively insoluble in oil, and soluble in alcohols.
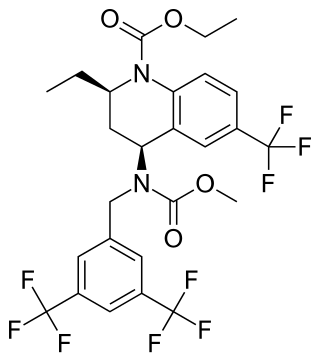
Torcetrapib was a drug being developed to treat hypercholesterolemia and prevent cardiovascular disease. Its development was halted in 2006 when phase III studies showed excessive all-cause mortality in the treatment group receiving a combination of atorvastatin (Lipitor) and torcetrapib.

Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetic disorder characterized by high cholesterol levels, specifically very high levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, in the blood and early cardiovascular diseases. The most common mutations diminish the number of functional LDL receptors in the liver or produce abnormal LDL receptors that never go to the cell surface to function properly. Since the underlying body biochemistry is slightly different in individuals with FH, their high cholesterol levels are less responsive to the kinds of cholesterol control methods which are usually more effective in people without FH. Nevertheless, treatment is usually effective.
The JUPITER trial was a clinical trial aimed at evaluating whether statins reduce heart attacks and strokes in people with normal cholesterol levels.
The West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study was a landmark randomized controlled trial, published in 1995, that investigated the effects of pravastatin, a cholesterol-lowering drug, on primary prevention of coronary heart disease (CHD) in men with hypercholesterolemia. Conducted in the early 1990s, this study provided critical evidence on the benefits of statins in reducing cardiovascular events in individuals without a history of CHD. It concluded that statin treatment reduced CHD events by 31% after nearly five years of treatment.
Atherothrombosis Intervention in Metabolic Syndrome with Low HDL/High Triglycerides: Impact on Global Health Outcomes was a randomized control trial designed to assess the efficacy of niacin (extended-release) added to statin therapy in reducing cardiovascular events in patients with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). These patients had well-controlled low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol but persistently low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and elevated triglycerides. 3,414 patients with established ASCVD were enrolled. The mean follow-up period was three years. The trial was stopped early due to a lack of efficacy and a trend towards an increase in the incidence of ischemic stroke.