
The Kuomintang is a major political party in Taiwan that originated as a revolutionary political party for the Republic of China on the Chinese mainland. Founded in 1919, the KMT was the dominant ruling party of the Republic of China on the mainland from 1928 to 1949, during which it fought the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) for control over China in the Chinese Civil War. The KMT was defeated and retreated to Taiwan in 1949, which was placed under martial law, where it remained the sole legal ruling party in Taiwan under the Dang Guo system until political reforms were enacted in the 1990s. The KMT is currently the main opposition political party in the Legislative Yuan.

Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. Neighbouring countries include the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. The main island of Taiwan has an area of 35,808 square kilometres (13,826 sq mi), with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its highly urbanised population is concentrated. The capital is Taipei, which, along with New Taipei and Keelung, forms the largest metropolitan area of Taiwan. Other major cities include Kaohsiung, Taichung, Tainan and Taoyuan. With 23.57 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the most densely populated countries.

Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is an island country in East Asia. The main island of Taiwan, known historically in English as Formosa, makes up 99% of the area controlled by the ROC, measuring 35,808 square kilometres (13,826 sq mi) and lying some 180 kilometres (112 mi) across the Taiwan Strait from the southeastern coast of mainland China. The East China Sea lies to the north of the island, the Philippine Sea to its east, the Luzon Strait directly to its south and the South China Sea to its southwest. The ROC also controls a number of smaller islands: some in the Taiwan Strait, and some of the South China Sea Islands.
The Taiwan independence movement is a political movement to seek formal international recognition of Taiwan as an independent, sovereign state and in opposition to Chinese unification.
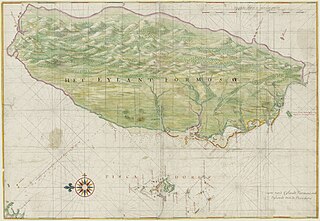
The history of the island of Taiwan dates back tens of thousands of years to the earliest known evidence of human habitation. The sudden appearance of a culture based on agriculture around 3000 BC is believed to reflect the arrival of the ancestors of today's Taiwanese indigenous peoples. The island was colonized by the Dutch in the 17th century, followed by an influx of Hoklo people including Hakka immigrants from the Fujian and Guangdong areas of mainland China, across the Taiwan Strait. The Spanish built a settlement in the north for a brief period but were driven out by the Dutch in 1642.

Chinese people are people or ethnic groups identified with China, usually through ethnicity, nationality, citizenship, or other affiliation.

The Third Taiwan Strait Crisis, also called the 1995–1996 Taiwan Strait Crisis or the 1996 Taiwan Strait Crisis, was the effect of a series of missile tests conducted by the People's Republic of China in the waters surrounding Taiwan, including the Taiwan Strait from 21 July 1995 to 23 March 1996. The first set of missiles fired in mid-to-late 1995 were allegedly intended to send a strong signal to the ROC government under Lee Teng-hui, who had been seen as moving its foreign policy away from the One-China policy. The second set of missiles were fired in early 1996, allegedly intending to intimidate the Taiwanese electorate in the run-up to the 1996 presidential election.

The First Taiwan Strait Crisis was a brief armed conflict between the Communist People's Republic of China (PRC) and the Nationalist Republic of China (ROC) in Taiwan. The conflict focused on several groups of islands in the Taiwan Strait that were held by the ROC but were located only a few miles from mainland China. The crisis began when the PRC shelled the ROC-held island of Kinmen (Quemoy). Later, the PRC seized the Yijiangshan Islands from the ROC. Under pressure by the PRC, the ROC then abandoned the Tachen Islands, which were evacuated by the navies of the ROC and the US.

The Second Taiwan Strait Crisis, also called the 1958 Taiwan Strait Crisis, was a conflict that took place between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the Republic of China (ROC). In this conflict, the PRC shelled the islands of Kinmen (Quemoy) and the Matsu Islands along the east coast of mainland China to "liberate" Taiwan from the Chinese Nationalist Party, also known as the Kuomintang (KMT); and to probe the extent of the United States defense of Taiwan's territory. A naval battle also took place around Dongding Island when the ROC Navy repelled an attempted amphibious landing by the PRC Navy.

Taiwan Province is a province claimed by the People's Republic of China (PRC). The PRC claims the island of Taiwan to be part of its territory under its Constitution. In combination with the Republic of China-controlled Fujian islands, it is usually referred to by mainland media as the Taiwan Region or Taiwan Area.

The Thyrididae comprise the family of picture-winged leaf moths. They are the only family in the superfamily Thyridoidea, which sometimes has been included in the Pyraloidea, but this isn't supported by cladistic analysis.
Bopomofo or Mandarin Phonetic Symbols, also named Zhuyin, is a major Chinese transliteration system for Mandarin Chinese and other related languages and dialects which is nowadays most commonly used in Taiwanese Mandarin. It is also used to transcribe other varieties of Chinese, particularly other varieties of Mandarin Chinese dialects, as well as Taiwanese Hokkien. Consisting of 37 characters and four tone marks, it transcribes all possible sounds in Mandarin. Bopomofo was introduced in China by the Republican Government in the 1910s and used alongside the Wade–Giles system, which used a modified Latin alphabet. Bopomofo is an official transliteration system in Taiwan, being widely used as the main electronic input method for Mandarin Chinese in Taiwan (ROC) and used in dictionaries and other documents.

Hypolamprus is a genus of moths of the family Thyrididae described by George Hampson in 1893.
Hypolamprus angulalis is a moth of the family Thyrididae first described by Frederic Moore in 1888. It is found in Malaysia, Myanmar and Sri Lanka.
Hypolamprus bastialis is a moth of the family Thyrididae first described by Francis Walker in 1859. It is found in India, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, New Guinea and Australia.
Hypolamprus lepraota is a moth of the family Thyrididae first described by George Hampson in 1910. It is found in Sri Lanka.
Hypolamprus striatalis is a moth of the family Thyrididae first described by Charles Swinhoe in 1886. It is found in Sri Lanka. and India.
Hypolamprus subrosealis is a moth of the family Thyrididae first described by John Henry Leech in 1889. It is found in Sri Lanka.










