
Hawaii is an island state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about 2,000 miles (3,200 km) southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, it is the only state not on the North American mainland, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state in the tropics.

Honolulu is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, located in the Pacific Ocean. It is the county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the island of Oʻahu, and is the westernmost and southernmost major U.S. city. Honolulu is Hawaii's main gateway to the world. It is also a major hub for business, finance, hospitality, and military defense in both the state and Oceania. The city is characterized by a mix of various Asian, Western, and Pacific cultures, reflected in its diverse demography, cuisine, and traditions.

Midway Atoll is a 2.4 sq mi (6.2 km2) atoll in the North Pacific Ocean. Midway Atoll is an insular area of the United States and is an unorganized and unincorporated territory. The largest island is Sand Island, which has housing and an airstrip. Immediately east of Sand Island, across the narrow Brooks Channel, is Eastern Island, which is uninhabited and no longer has any facilities. Forming a rough, incomplete circle around the two main islands and creating Midway Lagoon is Spit Island, a narrow reef.

Oceania is a geographical region including Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is generally considered a continent, while Mainland Australia is regarded as its continental landmass. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, at the centre of the water hemisphere, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of about 9,000,000 square kilometres (3,500,000 sq mi) and a population of around 46.3 million as of 2024. Oceania is the smallest continent in land area and the second-least populated after Antarctica.

Niʻihau, anglicized as Niihau, is the westernmost main and seventh largest inhabited island in Hawaii. It is 17.5 miles (28.2 km) southwest of Kauaʻi across the Kaulakahi Channel. Its area is 69.5 square miles (180 km2). Several intermittent playa lakes provide wetland habitats for the Hawaiian coot, the Hawaiian stilt, and the Hawaiian duck. The island is designated as critical habitat for Brighamia insignis, an endemic and endangered species of Hawaiian lobelioid. The United States Census Bureau defines Niʻihau and the neighboring island and State Seabird Sanctuary of Lehua as Census Tract 410 of Kauai County, Hawaii. Its 2000 census population was 160, most of whom are native Hawaiians; its 2010 census population was 170. At the 2020 census, the population had fallen to 84.

Oahu is the third-largest and most populated island of the Hawaiian Islands and of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The state capital, Honolulu, is on Oahu's southeast coast. The island of Oahu and the uninhabited Northwestern Hawaiian Islands constitute the City and County of Honolulu. In 2021, Oahu had a population of 995,638, up from 953,207 in 2010.

Kamehameha I, also known as Kamehameha the Great, was the conqueror and first ruler of the Kingdom of Hawaii. The state of Hawaii gave a statue of him to the National Statuary Hall Collection in Washington, D.C., as one of two statues it is entitled to install there.

Maui is the second largest island in the Hawaiian archipelago, at 727.2 square miles (1,883 km2). It is the 17th-largest in the United States. Maui is one of Maui County's five islands, along with Molokaʻi, Lānaʻi, Kahoʻolawe, and Molokini.
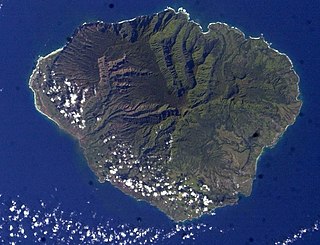
Kauaʻi, anglicized as Kauai, is one of the main Hawaiian Islands.

Hawaii is the largest island in the United States, located in the eponymous state of Hawaii. It is the southeasternmost of the Hawaiian Islands, a chain of volcanic islands in the North Pacific Ocean. With an area of 4,028 square miles (10,430 km2), it has 63% of the Hawaiian archipelago's combined landmass. However, it has only 13% of the archipelago's population. The island of Hawaiʻi is the third largest island in Polynesia, behind the north and south islands of New Zealand.
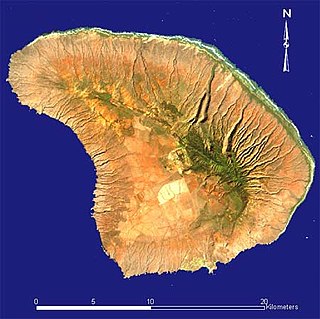
Lānaʻi is the sixth-largest of the Hawaiian Islands and the smallest publicly accessible inhabited island in the chain. It is colloquially known as the Pineapple Island because of its past as an island-wide pineapple plantation. The island's only settlement of note is the small town of Lanai City. The island is 98% owned by Larry Ellison, cofounder and chairman of Oracle Corporation; the remaining 2% is owned by the state of Hawaii or individual homeowners.

The Hawaiian Islands are an archipelago of eight major volcanic islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some 1,500 miles from the island of Hawaiʻi in the south to northernmost Kure Atoll. Formerly called the Sandwich Islands by Europeans, the present name for the archipelago is derived from the name of its largest island, Hawaiʻi.

Molokai is the fifth most populated of the eight major islands that make up the Hawaiian Islands archipelago in the middle of the Pacific Ocean. It is 38 by 10 miles at its greatest length and width with a usable land area of 260 sq mi (673.40 km2), making it the fifth-largest in size of the main Hawaiian Islands and the 27th largest island in the United States. It lies southeast of Oʻahu across the 25 mi (40 km) wide Kaʻiwi Channel and north of Lānaʻi, separated from it by the Kalohi Channel.

The Hawaii–Aleutian Time Zone observes Hawaii–Aleutian Standard Time (HST) by subtracting ten hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC−10:00). The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time of the 150th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory.

The Territory of Hawaii or Hawaii Territory was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from April 30, 1900, until August 21, 1959, when most of its territory, excluding Palmyra Island, was admitted to the United States as the 50th US state, the State of Hawaii. The Hawaii Admission Act specified that the State of Hawaii would not include Palmyra Island, the Midway Islands, Kingman Reef, and Johnston Atoll, which includes Johnston Island and Sand Island.

Native Hawaiians are the Indigenous Polynesian people of the Hawaiian Islands.

This is a list of properties and historic districts in Hawaii listed on the National Register of Historic Places. More than 370 listings appear on all but one of Hawaii's main islands and the Northwestern Islands, and in all of its five counties. Included are houses, schools, archeological sites, ships, shipwrecks and various other types of listings. These properties and districts are listed by island, beginning at the northwestern end of the chain.
This National Park Service list is complete through NPS recent listings posted December 20, 2024.
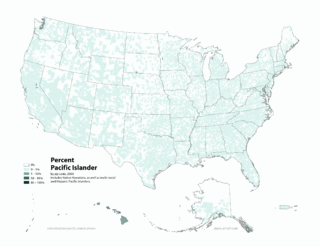
Pacific Islander Americans are Americans who are of Pacific Islander ancestry. For its purposes, the United States census also counts Aboriginal Australians as part of this group.

Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. It was often visited by the naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the Reciprocity Treaty of 1875. Much of the harbor and surrounding lands are now a United States Navy deep-water naval base. It is also the headquarters of the United States Pacific Fleet. The U.S. government first obtained exclusive use of the inlet and the right to maintain a repair and coaling station for ships here in 1887. The surprise attack on the harbor by the Imperial Japanese Navy on December 7, 1941, led the United States to declare war on the Empire of Japan, marking the United States' entry into World War II.

The Hawaiian Kingdom, also known as the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi, was an archipelagic country consisting of the Hawaiian Islands in the Pacific Ocean that existed from 1795 to 1893. It was established during the late 18th century when Kamehameha I, then Aliʻi nui of Hawaii, conquered the islands of Oʻahu, Maui, Molokaʻi, and Lānaʻi, and unified them under one government. In 1810, the Hawaiian Islands were fully unified when the islands of Kauaʻi and Niʻihau voluntarily joined the Hawaiian Kingdom. Two major dynastic families ruled the kingdom, the House of Kamehameha and the House of Kalākaua.


















