
A barcode or bar code is a method of representing data in a visual, machine-readable form. Initially, barcodes represented data by varying the widths, spacings and sizes of parallel lines. These barcodes, now commonly referred to as linear or one-dimensional (1D), can be scanned by special optical scanners, called barcode readers, of which there are several types.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter. When triggered by an electromagnetic interrogation pulse from a nearby RFID reader device, the tag transmits digital data, usually an identifying inventory number, back to the reader. This number can be used to track inventory goods.
Traceability is the capability to trace something. In some cases, it is interpreted as the ability to verify the history, location, or application of an item by means of documented recorded identification.

Logistics automation is the application of computer software or automated machinery to logistics operations in order to improve its efficiency. Typically this refers to operations within a warehouse or distribution center, with broader tasks undertaken by supply chain engineering systems and enterprise resource planning systems.

The Electronic Product Code (EPC) is designed as a universal identifier that provides a unique identity for every physical object anywhere in the world, for all time. The EPC structure is defined in the EPCglobal Tag Data Standard, which is a freely available standard. The canonical representation of an EPC is a URI, namely the 'pure-identity URI' representation that is intended for use when referring to a specific physical object in communications about EPCs among information systems and business application software.
WebSphere Application Server (WAS) is a software product that performs the role of a web application server. More specifically, it is a software framework and middleware that hosts Java-based web applications. It is the flagship product within IBM's WebSphere software suite. It was initially created by Donald F. Ferguson, who later became CTO of Software for Dell. The first version was launched in 1998. This project was an offshoot from IBM HTTP Server team starting with the Domino Go web server.

GS1 is a not-for-profit, international organization developing and maintaining its own standards for barcodes and the corresponding issue company prefixes. The best known of these standards is the barcode, a symbol printed on products that can be scanned electronically.
IBM InfoSphere DataStage is an ETL tool and part of the IBM Information Platforms Solutions suite and IBM InfoSphere. It uses a graphical notation to construct data integration solutions and is available in various versions such as the Server Edition, the Enterprise Edition, and the MVS Edition. It uses a client-server architecture. The servers can be deployed in both Unix as well as Windows.

A tracking system, also known as a locating system, is used for the observing of persons or objects on the move and supplying a timely ordered sequence of location data for further processing.
In the distribution and logistics of many types of products, track and trace or tracking and tracing concerns a process of determining the current and past locations of a unique item or property. Mass serialization is the process that manufacturers go through to assign and mark each of their products with a unique identifier such as an Electronic Product Code (EPC) for track and trace purposes. The marking or "tagging" of products is usually completed within the manufacturing process through the use of various combinations of human readable or machine readable technologies such as DataMatrix barcodes or RFID.

Intermec was a manufacturer and supplier of automated identification and data capture equipment, including barcode scanners, barcode printers, mobile computers, RFID systems, voice recognition systems, and life cycle services.
Collaborative Planning, Forecasting and Replenishment (CPFR) is an approach to the supply chain process which focuses on joint practices. This is done through cooperative management of inventory through joint visibility and replenishment of products throughout the supply chain. Information shared between suppliers and retailers aids in satisfying customer demands through a system of shared information. This allows for continuous updating of inventory and upcoming requirements, making the end-to-end supply chain process more efficient. Efficiency is created through the decrease expenditures for merchandising, inventory, logistics, and transportation across all trading partners.
Information Management Software is one of the brands within IBM Software Group (SWG) division. The major Information Management products include:

ILOG S.A. was an international software company purchased and incorporated into IBM announced in January, 2009. It created enterprise software products for supply chain, business rule management, visualization and optimization. The main product line for Business Rules Management Systems (BRMS) has been rebranded as IBM Operational Decision Management. Many of the related components retain the ILOG brand as a part of their name.

Omni-ID is a vendor of passive UHF Radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags. Founded in 2007 as Omni-ID, Ltd., its products are a range of RFID tags designed to operate in all environments, including on metal and liquids.
Produce traceability makes it possible to track produce from its point of origin to a retail location where it is purchased by consumers.
Inventory management software is a software system for tracking inventory levels, orders, sales and deliveries. It can also be used in the manufacturing industry to create a work order, bill of materials and other production-related documents. Companies use inventory management software to avoid product overstock and outages. It is a tool for organizing inventory data that before was generally stored in hard-copy form or in spreadsheets.

CYBRA Corporation is a software developer, publisher, and systems integrator in the IBM midrange market. CYBRA provides bar codes, RFID, and RTLS systems for IBM Power Systems and other server lines and other major computing platforms, bar code label and tag printing, and bar code scanning systems.
B.O.S. Better Online Solutions Ltd. is a publicly traded company, headquartered in Israel, that provides RFID and supply chain solutions. Its shares are traded on the NASDAQ Capital Market.
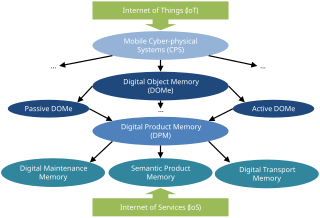
A digital object memory (DOMe) is a digital storage space intended to keep permanently all related information about a concrete physical object instance that is collected during the lifespan of this object and thus forms a basic building block for the Internet of Things (IoT) by connecting digital information with physical objects.








