
Acetazolamide, sold under the trade name Diamox among others, is a medication used to treat glaucoma, epilepsy, altitude sickness, periodic paralysis, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, and heart failure. It may be used long term for the treatment of open angle glaucoma and short term for acute angle closure glaucoma until surgery can be carried out. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein.

Zonisamide, sold under the brand name Zonegran, is a medication used to treat the symptoms of epilepsy and Parkinson's disease. Chemically it is a sulfonamide. It serves as an anticonvulsant used primarily as an adjunctive therapy in adults with Parkinson's disease, partial-onset seizures; infantile spasm, mixed seizure types of Lennox–Gastaut syndrome, myoclonic and generalized tonic clonic seizure. Despite this it is also sometimes used as a monotherapy for partial-onset seizures.

Ethoxzolamide is a sulfonamide medication that functions as a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. It is used in the treatment of glaucoma and duodenal ulcers, and as a diuretic. It may also be used in the treatment of some forms of epilepsy.

Mafenide is a sulfonamide-type medication used as an antibiotic. It was approved by the FDA in 1948.

Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are a class of pharmaceuticals that suppress the activity of carbonic anhydrase. Their clinical use has been established as anti-glaucoma agents, diuretics, antiepileptics, in the management of mountain sickness, gastric and duodenal ulcers, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, neurological disorders, or osteoporosis.
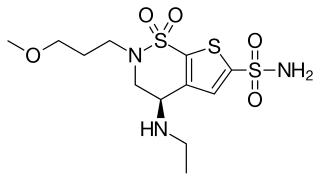
Brinzolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor used to lower intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.

Diclofenamide is a sulfonamide and a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor of the meta-disulfamoylbenzene class.

Dorzolamide, sold under the brand name Trusopt among others, is a medication used to treat high pressure inside the eye including glaucoma. It is used as an eye drop. Effects begin within three hours and lasts for at least eight hours. It is also available as the combination dorzolamide/timolol.

Sultiame, also known as sulthiame, is a sulfonamide and inhibitor of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase. It is used as an anticonvulsant.
Carbonic anhydrase IX is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA9 gene. It is one of the 14 carbonic anhydrase isoforms found in humans and is a transmembrane dimeric metalloenzyme with an extracellular active site that facilitates acid secretion in the gastrointestinal tract. CA IX is overexpressed in many types of cancer including clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) as well as carcinomas of the cervix, breast and lung where it promotes tumor growth by enhancing tumor acidosis.

Carbonic anhydrase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA1 gene.

Carbonic anhydrase-related protein 10 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA10 gene.

Carbonic anhydrase 7 (CA7) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA7 gene.

Xipamide is a sulfonamide diuretic drug marketed by Eli Lilly under the trade names Aquaphor and Aquaphoril. It is used for the treatment of oedema and hypertension.

Granatin A is an ellagitannin found in the pericarp of Punica granatum (pomegranate). It is a weak carbonic anhydrase inhibitor.

The carbonic anhydrases form a family of enzymes that catalyze the interconversion between carbon dioxide and water and the dissociated ions of carbonic acid. The active site of most carbonic anhydrases contains a zinc ion. They are therefore classified as metalloenzymes. The enzyme maintains acid-base balance and helps transport carbon dioxide.

Polmacoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat osteoarthritis. It was developed as CG100649 and approved for use in South Korea in February 2015. It inhibits the enzymes carbonic anhydrase and COX-2. A study in healthy volunteers showed drug effects on urinary prostaglandin metabolites for both polmacoxib and celecoxib that suggest a similar cardiovascular risk profile. Further work by this group developed dose-exposure relationships of polmacoxib to guide clinical development strategies.

Estradiol sulfamate, or estradiol-3-O-sulfamate, is a steroid sulfatase (STS) inhibitor which is under development for the treatment of endometriosis. It is the C3 sulfamate ester of estradiol, and was originally thought to be a prodrug of estradiol. The drug was first synthesized as an STS inhibitor along with its oxidized version estrone 3-O-sulfamate (EMATE) in the group of Professor Barry V L Potter at the University of Bath, UK, working together with Professor Michael J Reed at Imperial College, London and was found to be highly estrogenic in rodents. Such aryl sulfamate esters were shown to be "first-in-class" highly potent active site-directed irreversible STS inhibitors. Compounds of this class are thought to irreversibly modify the active site formylglycine residue of STS. The drug shows profoundly reduced susceptibility to first-pass metabolism relative to estradiol, and was believed to be the first "potent" estradiol prodrug to be discovered. It was clinically investigated for possible use as an estrogen for indications like hormonal contraception and menopausal hormone therapy. However, it showed no estrogenic effects in women. The potent non-estrogenic clinical STS inhibitor Irosustat (STX64/667-Coumate) was used to explore the possibility that STS might be responsible for the hydrolysis of estrogen sulphamates. Results demonstrated convincingly that STS is the enzyme responsible for the removal of the sulfamoyl group from estrogen sulfamates and has a crucial role in regulating the estrogenicity associated with this class of drug. Thus, STS inhibition blocks the conversion of E2MATE into estradiol and thereby abolishes its estrogenicity in humans. Irosustat has completed a number of clinical trials in oncology as an STS inhibitor currently up to Phase II.
Indane is a hydrocarbon petrochemical compound, with formula C9H10.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.


















