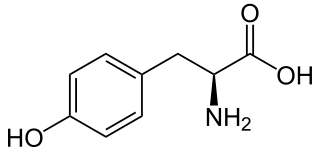
L-Tyrosine or tyrosine or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek tyrós, meaning cheese, as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is encoded by the codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA.

Dopamine is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% of the catecholamine content in the brain. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor chemical, L-DOPA, which is synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by neurons to send signals to other nerve cells. Neurotransmitters are synthesized in specific regions of the brain, but affect many regions systemically. The brain includes several distinct dopamine pathways, one of which plays a major role in the motivational component of reward-motivated behavior. The anticipation of most types of rewards increases the level of dopamine in the brain, and many addictive drugs increase dopamine release or block its reuptake into neurons following release. Other brain dopamine pathways are involved in motor control and in controlling the release of various hormones. These pathways and cell groups form a dopamine system which is neuromodulatory.
Melanin is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. The melanin pigments are produced in a specialized group of cells known as melanocytes.

A catecholamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol and a side-chain amine.

Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contrast, have a class of cells called melanocytes for coloration.
The quinones are a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds [such as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C(=O)– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds, resulting in "a fully conjugated cyclic dione structure". The archetypical member of the class is 1,4-benzoquinone or cyclohexadienedione, often called simply "quinone". Other important examples are 1,2-benzoquinone (ortho-quinone), 1,4-naphthoquinone and 9,10-anthraquinone.

Potassium permanganate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula KMnO4. It is a purplish-black crystalline salt, that dissolves in water as K+ and MnO−
4, an intensely pink to purple solution.

Browning is the process of food turning brown due to the chemical reactions that take place within. The process of browning is one of the chemical reactions that take place in food chemistry and represents an interesting research topic regarding health, nutrition, and food technology. Though there are many different ways food chemically changes over time, browning in particular falls into two main categories: enzymatic versus non-enzymatic browning processes.

Tyrosinase is an oxidase that is the rate-limiting enzyme for controlling the production of melanin. The enzyme is mainly involved in two distinct reactions of melanin synthesis otherwise known as the Raper Mason pathway. Firstly, the hydroxylation of a monophenol and secondly, the conversion of an o-diphenol to the corresponding o-quinone. o-Quinone undergoes several reactions to eventually form melanin. Tyrosinase is a copper-containing enzyme present in plant and animal tissues that catalyzes the production of melanin and other pigments from tyrosine by oxidation. It is found inside melanosomes which are synthesized in the skin melanocytes. In humans, the tyrosinase enzyme is encoded by the TYR gene.

Neuromelanin (NM) is a dark pigment found in the brain which is structurally related to melanin. It is a polymer of 5,6-dihydroxyindole monomers. Neuromelanin is found in large quantities in catecholaminergic cells of the substantia nigra pars compacta and locus coeruleus, giving a dark color to the structures.

1,4-Benzoquinone, commonly known as para-quinone, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H4O2. In a pure state, it forms bright-yellow crystals with a characteristic irritating odor, resembling that of chlorine, bleach, and hot plastic or formaldehyde. This six-membered ring compound is the oxidized derivative of 1,4-hydroquinone. The molecule is multifunctional: it exhibits properties of a ketone, being able to form oximes; an oxidant, forming the dihydroxy derivative; and an alkene, undergoing addition reactions, especially those typical for α,β-unsaturated ketones. 1,4-Benzoquinone is sensitive toward both strong mineral acids and alkali, which cause condensation and decomposition of the compound.
Catechol oxidase is a copper oxidase that contains a type 3 di-copper cofactor and catalyzes the oxidation of ortho-diphenols into ortho-quinones coupled with the reduction of molecular oxygen to water. It is present in a variety of species of plants and fungi including Ipomoea batatas and Camellia sinensis. Metalloenzymes with type 3 copper centers are characterized by their ability to reversibly bind dioxygen at ambient conditions. In plants, catechol oxidase plays a key role in enzymatic browning by catalyzing the oxidation of catechol to o-quinone in the presence of oxygen, which can rapidly polymerize to form the melanin that grants damaged fruits their dark brown coloration.
Polyphenol oxidase, an enzyme involved in fruit browning, is a tetramer that contains four atoms of copper per molecule.

Smoker's melanosis is seen with the naked eye as a brown to black pigmentation of the oral tissue i.e. the gums, cheeks or palate as well as in larynx. It is most often seen in the lower labial gingiva of tobacco users. Most easily it is found in Caucasians, due to their lack of a genetically caused melanin pigmentation.
In enzymology, a L-dopachrome isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
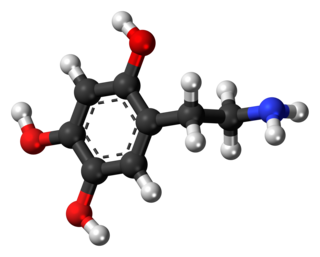
Oxidopamine, also known as 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) or 2,4,5-trihydroxyphenethylamine, is a neurotoxic synthetic organic compound used by researchers to selectively destroy dopaminergic and noradrenergic neurons in the brain.

Chloranil is a quinone with the molecular formula C6Cl4O2. Also known as tetrachloro-1,4-benzoquinone, it is a yellow solid. Like the parent benzoquinone, chloranil is a planar molecule that functions as a mild oxidant.

5,6-Dihydroxyindole is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C8H7NO2. It is an intermediate in the production of the biological pigment eumelanin. 5,6-Dihydroxyindole is biosynthesized from L-dopachrome in a reaction catalyzed by a tyrosinase enzyme and is further converted into indole-5,6-quinone. In humans, 5,6-dihydroxyindole is involved in the metabolic disorder hawkinsinuria.

6PPD is an organic chemical widely used as stabilising additive in rubbers, such as NR, SBR and BR; all of which are common in vehicle tires. Although it is an effective antioxidant it is primarily used because of its excellent antiozonant performance. It is one of several antiozonants based around p-phenylenediamine (PPD).















