Both nations are members of the Council of Europe, European Union, OECD and OSCE.

The nations of Ireland and Mexico established diplomatic relations in 1974. The relationship has been often associated with the Irish migration to Mexico. Both nations are members of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, United Nations and the World Trade Organization.

Australia and Uruguay have had consular relations since 1923 and diplomatic relations since 1948. Australia is represented in Uruguay through its embassy in Buenos Aires (Argentina). Uruguay has an embassy in Canberra a consulate general in Sydney.
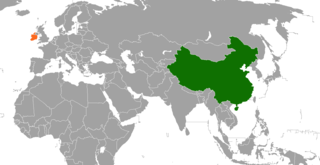
China–Ireland relations are interstate relations of China and Ireland. Ireland and China first established their bilateral foreign relations after they signed the Communique on the Establishment of Diplomatic Relations on 22 June 1979. This milestone opened the gate for trades, businesses, politics, education, and tourism between the two countries; both nations have gained enormous growth of economic values. Both countries exchanged ambassadors in 1980. Ireland has an embassy in Beijing, a general consulate in Shanghai and an honorary consulate in Hong Kong; China has an embassy in Dublin. The first historical meeting for the two headers of China and Ireland governments took place in November 1996 when Premier Li Peng met with Taoiseach John Bruton at the World Food Summit. By 2019, this bilateral relationship has boomed to a high point, and a ceremony of their 40th anniversary of diplomatic relations was held in Dublin, Ireland in June 2019. More recently, the Ireland Sino Institute has been strengthening Ireland-China relations through various initiatives. During Irish Deputy Prime Minister and Minister for Foreign Affairs Micheál Martin's visit to China in November 2023, there was a notable exchange between the Deputy Prime Minister and the Ireland Sino Institute delegation at the China Europe International Business School in Shanghai. Representatives from the Ireland Sino Institute, who had overcome blizzard conditions, discussed how their non-profit rural initiatives in Liaoning were fostering stronger ties between Ireland and China. They emphasized the role of the Ireland Sino Institute in representing both the Irish in China and Ireland in China.

Indonesia and Romania established diplomatic relations on 20 February 1950, two days following Romania's recognition of Indonesian sovereignty on 18 February 1950. Indonesia and Romania have agreed to enhance cooperation in the trade sector. The nations are expecting the other to be the gate to enter each regional market: Indonesia as the gate to enter the ASEAN market and Romania as the gate to enter the European Union's. Indonesia has an embassy in Bucharest and Romania has an embassy in Jakarta.

The bilateral relations of the Philippines and Ukraine began with a formal agreement in 1992. Neither country has a resident ambassador. Ukraine has a non-resident ambassador in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. The Philippines is represented by its embassy in Warsaw, Poland.

Austria and Indonesia established diplomatic relations on 20 November 1954. Austria recognizes Indonesia as a stable and reliable partner, and both countries enjoy excellent relations. The two nations have agreed to expand relations in business, trade and investment, tourism, culture, environment and green technology. Austria has an embassy in Jakarta and honorary consulates in Yogyakarta, Bandung and Surabaya, while Indonesia has an embassy in Vienna that is also accredited to Slovenia.

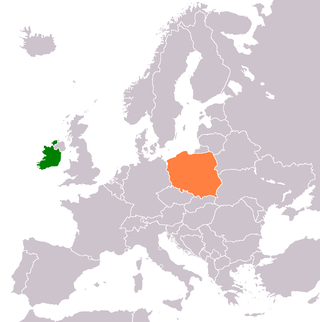
Indonesia and Poland established diplomatic relations on 19 September 1955. Indonesia has an embassy in Warsaw, while Poland has an embassy in Jakarta. Other than similar red-and-white flags, Indonesia and Poland share a similar course of history through enduring revolutions, wars for independence and maintaining national unity. Both nations have agreed to expand bilateral relations in trade, culture and education sectors, through programs such as staging art exhibitions to proposing student exchange programs and provide scholarships.
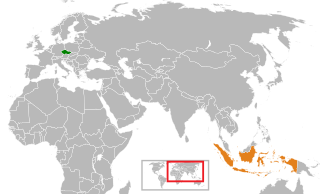
The Czech Republic and the Republic of Indonesia established diplomatic relations in 1950. Both nations have agreed to forge ties to deepen relations, especially in the business and trade sector. Indonesia has an embassy in Prague, while the Czech Republic has an embassy in Jakarta that is also accredited to Brunei, Timor Leste and ASEAN.

The nations of Mexico and Mongolia established diplomatic relations in 1975. Both nations are members of the Forum of East Asia–Latin America Cooperation and the United Nations.

Poland–Tanzania relations are the diplomatic relations between the Republic of Poland and the United Republic of Tanzania. Both nations are members of the United Nations and the World Trade Organization.

Diplomatic relations exist between Armenia and Chile. There are over 600 Armenians and descendants residing in Chile today. Both nations are members of the United Nations.

Spain–Thailand relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Thailand has an embassy in Madrid and two honorary consulates in Barcelona and Santa Cruz de Tenerife. Spain has an embassy in Bangkok.

Kenya–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Kenya has an embassy in Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Nairobi and an honorary consulate in Mombasa.

Rwanda–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Rwanda does not have an embassy in Spain, however its embassy in Paris, France, is accredited to Spain and maintains an honorary consulate in Madrid. Spain does not have an embassy in Rwanda, however, its embassy in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania, is accredited to Rwanda and maintains an honorary consulate in Kigali.

The nations of Mexico and Oman established diplomatic relations in 1975. Both nations are members of the United Nations.

Indonesia–Mozambique relations are the bilateral relations between Indonesia and Mozambique. Both countries are members of the Non-Aligned Movement, Organization of Islamic Cooperation and the Indian-Ocean Rim Association.

Armenia–Indonesia relations refer to foreign relations between Armenia and Indonesia. Both nations are members of the Asian Development Bank, the World Trade Organization and the United Nations.

Brazil and Thailand began diplomatic relations in 1959. Brazil is Thailand's main trading partner in Latin America. The two nations are members of the G20 developing nations, Non-Aligned Movement, World Trade Organization (WTO) and Forum of East Asia-Latin America Cooperation.

Indonesia–Rwanda relations refer to foreign relations between Indonesia and Rwanda since the establishment of diplomatic ties on 16 January 1984. Both countries are members of the World Trade Organization, Non-Aligned Movement and the G77. Additionally, the two nations make major contributions to UN peacekeeping forces.






















