
Ionospheric absorption (or ISAB) is the scientific name for absorption occurring as a result of the interaction between various types of electromagnetic waves and the free electrons in the ionosphere, which can interfere with radio transmissions.

Ionospheric absorption (or ISAB) is the scientific name for absorption occurring as a result of the interaction between various types of electromagnetic waves and the free electrons in the ionosphere, which can interfere with radio transmissions.
Ionosphere absorption is of critical importance when radio networks, telecommunication systems or interlinked radio systems are being planned, particularly when trying to determine propagation conditions. [1]
The ionosphere can be described as an area of the atmosphere in which radio waves on shortwave bands are refracted or reflected back to Earth. As a result of this reflection, which is often key in the long-distance propagation of radio waves, some of the shortwave signal strength is decreased. In this regard, ISAB is the primary limiting factor in radio propagation. [2]

ISAB is only a factor in the period of the day where radio signals travel through the portion of the ionosphere facing the Sun. The solar wind and radiation cause the ionosphere to become charged with electrons in the first place. At night, the atmosphere becomes drained of its charge, and radio signals can go much farther with less loss of signal. In particular, low frequency signals that would be attenuated to nothing during the day will be received much farther away at night. [3] [4]
The specific amount of attenuation can be derived as a function of the Inverse-square law. The lower the frequency, the greater the attenuation. [2]
Relative ionospheric absorption can be measured using a riometer.

The ionosphere is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about 48 km (30 mi) to 965 km (600 mi) above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. It also affects GPS signals that travel through this layer.
In physics, attenuation is the gradual loss of flux intensity through a medium. For instance, dark glasses attenuate sunlight, lead attenuates X-rays, and water and air attenuate both light and sound at variable attenuation rates.
In radio transmission, maximum usable frequency (MUF) is the highest radio frequency that can be used for transmission between two points on Earth by reflection from the ionosphere at a specified time, independent of transmitter power. This index is especially useful for shortwave transmissions.
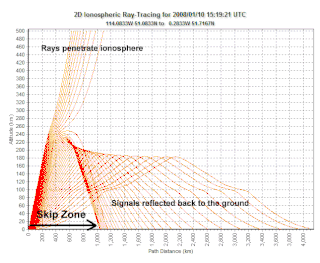
A skip zone, also called a silent zone or zone of silence, is a region where a radio transmission can not be received. The zone is located between regions both closer and farther from the transmitter where reception is possible.
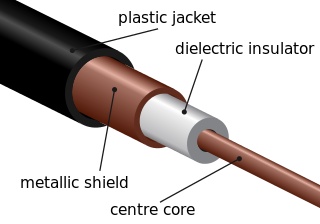
A transmission medium is a system or substance that can mediate the propagation of signals for the purposes of telecommunication. Signals are typically imposed on a wave of some kind suitable for the chosen medium. For example, data can modulate sound, and a transmission medium for sounds may be air, but solids and liquids may also act as the transmission medium. Vacuum or air constitutes a good transmission medium for electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves. While a material substance is not required for electromagnetic waves to propagate, such waves are usually affected by the transmission media they pass through, for instance, by absorption or reflection or refraction at the interfaces between media. Technical devices can therefore be employed to transmit or guide waves. Thus, an optical fiber or a copper cable is used as transmission media.

Shortwave radio is radio transmission using shortwave (SW) radio frequencies. There is no official definition of the band, but the range always includes all of the high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30 MHz ; above the medium frequency band (MF), to the bottom of the VHF band.
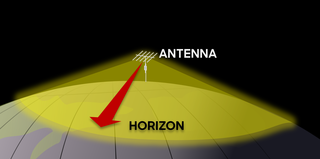
Line-of-sight propagation is a characteristic of electromagnetic radiation or acoustic wave propagation which means waves can only travel in a direct visual path from the source to the receiver without obstacles. Electromagnetic transmission includes light emissions traveling in a straight line. The rays or waves may be diffracted, refracted, reflected, or absorbed by the atmosphere and obstructions with material and generally cannot travel over the horizon or behind obstacles.

Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies of 300 gigahertz (GHz) and below. At 300 GHz, the corresponding wavelength is 1mm, which is shorter than the diameter of a grain of rice. At 30 Hz the corresponding wavelength is ~10,000 kilometers longer than the radius of the Earth. Wavelength of a radio wave is inversely proportional to its frequency, because its velocity is constant. Like all electromagnetic waves, radio waves in a vacuum travel at the speed of light, and in the Earth's atmosphere at a slightly slower speed. Radio waves are generated by charged particles undergoing acceleration, such as time-varying electric currents. Naturally occurring radio waves are emitted by lightning and astronomical objects, and are part of the blackbody radiation emitted by all warm objects.

Very low frequency or VLF is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 3–30 kHz, corresponding to wavelengths from 100 to 10 km, respectively. The band is also known as the myriameter band or myriameter wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten myriameters. Due to its limited bandwidth, audio (voice) transmission is highly impractical in this band, and therefore only low data rate coded signals are used. The VLF band is used for a few radio navigation services, government time radio stations and for secure military communication. Since VLF waves can penetrate at least 40 meters (131 ft) into saltwater, they are used for military communication with submarines.

A whistler is a very low frequency (VLF) electromagnetic (radio) wave generated by lightning. Frequencies of terrestrial whistlers are 1 kHz to 30 kHz, with maximum frequencies usually at 3 kHz to 5 kHz. Although they are electromagnetic waves, they occur at audio frequencies, and can be converted to audio using a suitable receiver. They are produced by lightning strikes where the impulse travels along the Earth's magnetic field lines from one hemisphere to the other. They undergo dispersion of several kHz due to the slower velocity of the lower frequencies through the plasma environments of the ionosphere and magnetosphere. Thus they are perceived as a descending tone which can last for a few seconds. The study of whistlers categorizes them into Pure Note, Diffuse, 2-Hop, and Echo Train types.

High frequency (HF) is the ITU designation for the range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves between 3 and 30 megahertz (MHz). It is also known as the decameter band or decameter wave as its wavelengths range from one to ten decameters. Frequencies immediately below HF are denoted medium frequency (MF), while the next band of higher frequencies is known as the very high frequency (VHF) band. The HF band is a major part of the shortwave band of frequencies, so communication at these frequencies is often called shortwave radio. Because radio waves in this band can be reflected back to Earth by the ionosphere layer in the atmosphere – a method known as "skip" or "skywave" propagation – these frequencies are suitable for long-distance communication across intercontinental distances and for mountainous terrains which prevent line-of-sight communications. The band is used by international shortwave broadcasting stations (3.95–25.82 MHz), aviation communication, government time stations, weather stations, amateur radio and citizens band services, among other uses.
Radio propagation is the behavior of radio waves as they travel, or are propagated, from one point to another in vacuum, or into various parts of the atmosphere. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, like light waves, radio waves are affected by the phenomena of reflection, refraction, diffraction, absorption, polarization, and scattering. Understanding the effects of varying conditions on radio propagation has many practical applications, from choosing frequencies for amateur radio communications, international shortwave broadcasters, to designing reliable mobile telephone systems, to radio navigation, to operation of radar systems.
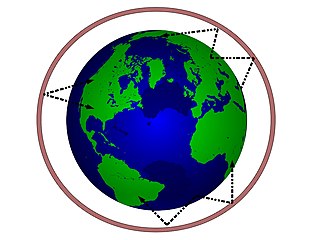
In radio communication, skywave or skip refers to the propagation of radio waves reflected or refracted back toward Earth from the ionosphere, an electrically charged layer of the upper atmosphere. Since it is not limited by the curvature of the Earth, skywave propagation can be used to communicate beyond the horizon, at intercontinental distances. It is mostly used in the shortwave frequency bands.
Extremely high frequency (EHF) is the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) designation for the band of radio frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum from 30 to 300 gigahertz (GHz). It lies between the super high frequency band and the far infrared band, the lower part of which is the terahertz band. Radio waves in this band have wavelengths from ten to one millimetre, so it is also called the millimetre band and radiation in this band is called millimetre waves, sometimes abbreviated MMW or mmWave. Millimetre-length electromagnetic waves were first investigated by Bengali physicist Jagadish Chandra Bose, who generated waves of frequency up to 60 GHz during experiments in 1894–1896.

In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is how matter takes up a photon's energy — and so transforms electromagnetic energy into internal energy of the absorber. A notable effect is attenuation, or the gradual reduction of the intensity of light waves as they propagate through a medium. Although the absorption of waves does not usually depend on their intensity, in certain conditions (optics) the medium's transparency changes by a factor that varies as a function of wave intensity, and saturable absorption occurs.
Non-line-of-sight (NLOS) radio propagation occurs outside of the typical line-of-sight (LOS) between the transmitter and receiver, such as in ground reflections. Near-line-of-sight conditions refer to partial obstruction by a physical object present in the innermost Fresnel zone.
A sudden ionospheric disturbance (SID) is any one of several ionospheric perturbations, resulting from abnormally high ionization/plasma density in the D region of the ionosphere and caused by a solar flare and/or solar particle event (SPE). The SID results in a sudden increase in radio-wave absorption that is most severe in the upper medium frequency (MF) and lower high frequency (HF) ranges, and as a result often interrupts or interferes with telecommunications systems.
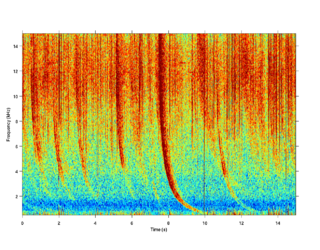
A radio atmospheric signal or sferic is a broadband electromagnetic impulse that occurs as a result of natural atmospheric lightning discharges. Sferics may propagate from their lightning source without major attenuation in the Earth–ionosphere waveguide, and can be received thousands of kilometres from their source. On a time-domain plot, a sferic may appear as a single high-amplitude spike in the time-domain data. On a spectrogram, a sferic appears as a vertical stripe that may extend from a few kHz to several tens of kHz, depending on atmospheric conditions.
The Earth–ionosphere waveguide refers to the phenomenon in which certain radio waves can propagate in the space between the ground and the boundary of the ionosphere. Because the ionosphere contains charged particles, it can behave as a conductor. The earth operates as a ground plane, and the resulting cavity behaves as a large waveguide.
This is an index to articles about terms used in discussion of radio propagation.