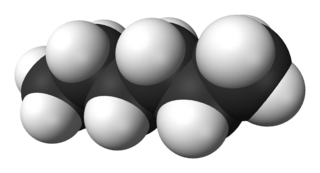
Hexane or n-hexane is an organic compound, a straight-chain alkane with six carbon atoms and has the molecular formula C6H14.
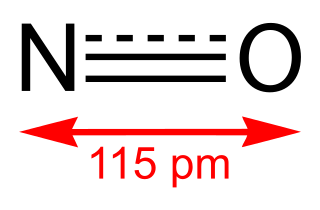
Nitric oxide is a colorless gas with the formula NO. It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its chemical formula. Nitric oxide is also a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, a class of molecules whose study spawned early modern theories of chemical bonding.
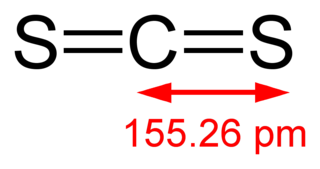
Carbon disulfide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CS2 and structure S=C=S. It is a colorless, flammable, neurotoxic liquid that is used as a building block in organic synthesis. Pure carbon disulfide has a pleasant, ether- or chloroform-like odor, but commercial samples are usually yellowish and are typically contaminated with foul-smelling impurities.

Iron(II) chloride, also known as ferrous chloride, is the chemical compound of formula FeCl2. It is a paramagnetic solid with a high melting point. The compound is white, but typical samples are often off-white. FeCl2 crystallizes from water as the greenish tetrahydrate, which is the form that is most commonly encountered in commerce and the laboratory. There is also a dihydrate. The compound is highly soluble in water, giving pale green solutions.
Vanadium(V) oxide (vanadia) is the inorganic compound with the formula V2O5. Commonly known as vanadium pentoxide, it is a brown/yellow solid, although when freshly precipitated from aqueous solution, its colour is deep orange. Because of its high oxidation state, it is both an amphoteric oxide and an oxidizing agent. From the industrial perspective, it is the most important compound of vanadium, being the principal precursor to alloys of vanadium and is a widely used industrial catalyst.

Hydrogen selenide is an inorganic compound with the formula H2Se. This hydrogen chalcogenide is the simplest and most commonly encountered hydride of selenium. H2Se is a colorless, flammable gas under standard conditions. It is the most toxic selenium compound with an exposure limit of 0.05 ppm over an 8-hour period. Even at extremely low concentrations, this compound has a very irritating smell resembling that of decayed horseradish or 'leaking gas', but smells of rotten eggs at higher concentrations.

Iron pentacarbonyl, also known as iron carbonyl, is the compound with formula Fe(CO)5. Under standard conditions Fe(CO)5 is a free-flowing, straw-colored liquid with a pungent odour. Older samples appear darker. This compound is a common precursor to diverse iron compounds, including many that are useful in small scale organic synthesis.
Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable gas with an ammonia-like odor. Dimethylamine is commonly encountered commercially as a solution in water at concentrations up to around 40%. An estimated 270,000 tons were produced in 2005.

Diethylenetriamine (abbreviated Dien or DETA) and also known as 2,2’-Iminodi(ethylamine)) is an organic compound with the formula HN(CH2CH2NH2)2. This colourless hygroscopic liquid is soluble in water and polar organic solvents, but not simple hydrocarbons. Diethylenetriamine is structural analogue of diethylene glycol. Its chemical properties resemble those for ethylene diamine, and it has similar uses. It is a weak base and its aqueous solution is alkaline. DETA is a byproduct of the production of ethylenediamine from ethylene dichloride.

Propylene glycol dinitrate (PGDN, 1,2-propylene glycol dinitrate, or 1,2-propanediol dinitrate) is an organic chemical, an ester of nitric acid and propylene glycol. It is structurally similar to nitroglycerin, except that it has one fewer nitrate group. It is a characteristically and unpleasantly smelling colorless liquid, which decomposes at 121 °C, below its boiling point. It is flammable and explosive. It is shock-sensitive and burns with a clean flame producing water vapor, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen gas.

Iron(III) nitrate, or ferric nitrate, is the name used for a series of inorganic compounds with the formula Fe(NO3)3.(H2O)n. Most common is the nonahydrate Fe(NO3)3.(H2O)9. The hydrates are all pale colored, water-soluble paramagnetic salts.

n-Butylamine is an organic compound (specifically, an amine) with the formula CH3(CH2)3NH2. This colourless liquid is one of the four isomeric amines of butane, the others being sec-butylamine, tert-butylamine, and isobutylamine. It is a liquid having the fishy, ammonia-like odor common to amines. The liquid acquires a yellow color upon storage in air. It is soluble in all organic solvents. Its vapours are heavier than air and it produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion.

Iron(III) sulfate (or ferric sulfate), is a family of inorganic compounds with the formula Fe2(SO4)3(H2O)n. A variety of hydrates are known, including the most commonly encountered form of "ferric sulfate". Solutions are used in dyeing as a mordant, and as a coagulant for industrial wastes. Solutions of ferric sulfate are also used in the processing of aluminum and steel.

Zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate is a coordination complex of zinc with dimethyldithiocarbamate. It is a pale yellow solid that is used as a fungicide, the sulfur vulcanization of rubber, and other industrial applications.
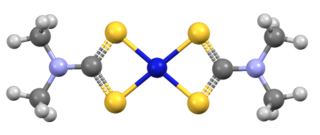
Nickel bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) is the coordination complex on nickel and dimethyldithiocarbamate, with the formula Ni(S2CNMe2)2 (Me = methyl). It is the prototype for a large number of bis(dialkhyldithiocarbamate)s of nickel(II), which feature diverse organic substituents, all of which have similar structures. Nickel bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) has been marketed as a fungicide and related complexes are used as stabilizers in polymers.

Iron tris(diethyldithiocarbamate) is the coordination complex of iron with diethyldithiocarbamate with the formula Fe(S2CNEt2)3 (Et = ethyl). It is a black solid that is soluble in organic solvents.

Cobalt tris(diethyldithiocarbamate) is the coordination complex of cobalt with diethyldithiocarbamate with the formula Co(S2CNEt2)3 (Et = ethyl). It is a diamagnetic green solid that is soluble in organic solvents.

Transition metal dithiocarbamate complexes are coordination complexes containing one or more dithiocarbamate ligand, which are typically abbreviated R2dtc−. Many complexes are known. Several homoleptic derivatives have the formula M(R2dtc)n where n = 2 and 3.

Iron(II) nitrate is the nitrate salt of iron(II). It is commonly encountered as the green hexahydrate, Fe(NO3)2·6H2O, which is a metal aquo complex, however it is not commercially available unlike iron(III) nitrate due to its instability to air. The salt is soluble in water serves as a ready source of ferrous ions.

Iron bis(diethyldithiocarbamate) is a coordination complex with the formula [Fe(S2CNEt2)2]2 where Et = C2H5. A red solid, it is representative of several ferrous dithiocarbamates with diverse substituents in place of ethyl. In terms of structure, the species is dimeric, consisting of two pentacoordinate iron(II) centers. It is isostructural with [Zn(S2CNEt2)2]2, which in turn is similar to zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate).



















