Related Research Articles

Hockessin is a census-designated place (CDP) in New Castle County, Delaware, United States. The population was 13,478 at the 2020 Census.

Ward's Point is the southernmost point in the U.S. state of New York and lies within Tottenville, Staten Island, New York City. It is located at the mouth of Arthur Kill, across from Perth Amboy, New Jersey, at the head of Raritan Bay. The site is part of modern-day Conference House Park.

The Pinson Mounds comprise a prehistoric Native American complex located in Madison County, Tennessee, in the region that is known as the Eastern Woodlands. The complex, which includes 17 mounds, an earthen geometric enclosure, and numerous habitation areas, was most likely built during the Middle Woodland period. The complex is the largest group of Middle Woodland mounds in the United States. Sauls' Mound, at 72 feet (22 m), is the second-highest surviving mound in the United States.

Moundville Archaeological Site, also known as the Moundville Archaeological Park, is a Mississippian culture archaeological site on the Black Warrior River in Hale County, near the modern city of Tuscaloosa, Alabama. Extensive archaeological investigation has shown that the site was the political and ceremonial center of a regionally organized Mississippian culture chiefdom polity between the 11th and 16th centuries. The archaeological park portion of the site is administered by the University of Alabama Museums and encompasses 185 acres (75 ha), consisting of 29 platform mounds around a rectangular plaza.

Shiloh Indian Mounds Site (40HR7) is an archaeological site of the South Appalachian Mississippian culture. It is located beside the Tennessee River on the grounds of the Shiloh National Military Park, in Hardin County of southwestern Tennessee. A National Historic Landmark, it is one of the largest Woodland era sites in the southeastern United States.

The Kolomoki Mounds is one of the largest and earliest Woodland period earthwork mound complexes in the Southeastern United States and is the largest in Georgia. Constructed from 350 to 600, the mound complex is located in southwest Georgia, in present-day Early County near the Chattahoochee River.
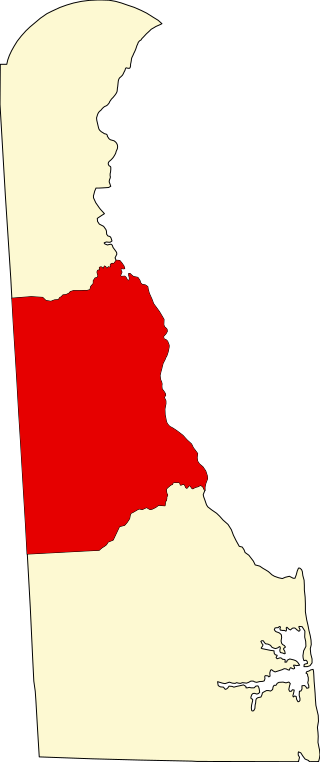
List of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Kent County, Delaware
This National Park Service list is complete through NPS recent listings posted October 25, 2024.

Town Creek Indian Mound is a prehistoric Native American archaeological site located near present-day Mount Gilead, Montgomery County, North Carolina, in the United States. The site, whose main features are a platform mound with a surrounding village and wooden defensive palisade, was built by the Pee Dee, a South Appalachian Mississippian culture people that developed in the region as early as 980 CE. They thrived in the Pee Dee River region of North and South Carolina during the Pre-Columbian era. The Town Creek site was an important ceremonial site occupied from about 1150—1400 CE. It was abandoned for unknown reasons. It is the only ceremonial mound and village center of the Pee Dee located within North Carolina.

The Nodena site is an archeological site east of Wilson, Arkansas, and northeast of Reverie, Tennessee, in Mississippi County, Arkansas, United States. Around 1400–1650 CE an aboriginal palisaded village existed in the Nodena area on a meander bend of the Mississippi River. The Nodena site was discovered and first documented by Dr. James K. Hampson, archaeologist and owner of the plantation on which the Nodena site is located. Artifacts from this site are on display in the Hampson Museum State Park in Wilson, Arkansas. The Nodena site is the type site for the Nodena phase, believed by many archaeologists to be the province of Pacaha visited by Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto in 1542.

Minisink Archeological Site, also known as Minisink Historic District, is an archeological site of 1320 acres located in both Sussex County, New Jersey and Pike County, Pennsylvania. It was part of a region occupied by Munsee-speaking Lenape that extended from southern New York across northern New Jersey to northeastern Pennsylvania. The Munsee were speakers of one of the three major language dialects of the Lenape Native American tribe. This interstate territory became the most important Munsee community for the majority of the 17th and 18th centuries.
The Bull Thistle Cave Archaeological Site is an archaeological site on the National Register of Historic Places, located in Tazewell County, Virginia. It is a vertical shaft pit burial cave. The distribution of the skeletal remains indicates that bodies were either thrown or lowered into the cave. On the surface of the cave floor, researchers have discovered the remains of a minimum of 11 bodies. Based on an artifact recovered from the site, it is estimated that the cave was used for burials between 1300 and 1600 AD.
Walker Prehistoric Village Archeological Site is an archeological site located near Poolesville, Montgomery County, Maryland. The site is a large Late Woodland village located on Selden Island in the Potomac River. Excavations carried out in the 1930s and 1940s revealed a 40-foot section of a palisade, circular house patterns, shallow oval pits and cylindrical pits, and flexed burials interred in the floors of the houses.

The Book site is an archaeological site in Juniata County, Pennsylvania, United States. Consisting of the remnants of a burial mound and a prehistoric village, the site lies on both sides of Camp Resort Road in Beale Township, near the community of Beale.

South Bowers is an unincorporated community in Kent County, Delaware, United States. South Bowers is located on the Delaware Bay on the south side of the Murderkill River opposite Bowers. It was a part of the James D. Sipple home farm containing 421 acres of upland, marsh and beachland and he subdivided a small part of the farm into the lots comprising South Bowers before he died in 1890. His son, James H. Sipple acquired the interests of his siblings and conveyed the farm to his daughter, Sarah E. Webb in 1920.The Webb family are in ownership of this land to this day.
The Carey Farm Site (7K-D-3) is a prehistoric Native American archaeological site in central Kent County, Delaware, near Dover. The site, located along the St. Jones River, encompasses what is believed to be a major seasonal base camp from the Woodland Period. Ceramics dating back to 200 CE have been found at the site.
The Byfield Historic District encompasses the remains of an early colonial community in eastern Kent County, in the U.S. state of Delaware. The district includes four separate archaeological sites, each of which have been associated with early English settlers of the area. The site designated K-929 is the location of a brick kiln, which documentary evidence suggests was associated with Daniel Jones, the first settler in the area. K-917 is speculated to be associated with William Rodney, who married Jones' daughter. K-916 is a site that may have been a slave residence, and K-890 is believed to be the site of one of the homes of Caesar Rodney, Sr., the father of Delaware Revolutionary War leader Caesar Rodney. The only 19th century structure in the district is the S. A. Sipple House.
The Townsend Site is a major prehistoric Native American site in Sussex County, Delaware. The Late Woodland site includes at least 90 significant features, including numerous burial sites. The site received its first thorough study in 1948, and was the first Late Woodland site in the state to be examined in consultation with professional archaeologists of the Smithsonian Institution, and resulted in the creation of a typology of ceramics found.
7K-F-4 and 7K-F-23 are a pair of archaeological sites in southern Kent County, Delaware, near the town of Milford. Both are Early Woodland Period Native American camp sites, at which ceramics have been found.
The Dill Farm Site (7K-E-12) is a prehistoric archaeological site in Kent County, Delaware, near the town of Sandtown. The site located in a formerly swampy area, has yielded dates of 500 BC and 8000 BC. Carey Complex ceramics have also been found at the 55-acre (22 ha) site.
References
- 1 2 "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places . National Park Service. July 9, 2010.
- ↑ Custer, Jay (Fall 1990). "A Re-examination of the Island Field Site (7K-F-17), Kent County, Delaware". Archaeology of Eastern North America. 18. JSTOR 40914323.
- ↑ "Sacred Del. Indians Want Remains Returned To Burial Ground". Philadelphia Inquirer. May 17, 1986. Archived from the original on July 18, 2015.