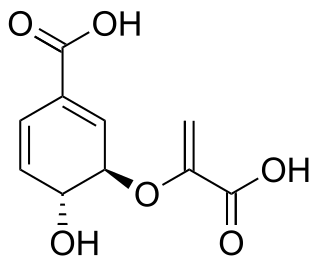
Chorismic acid, more commonly known as its anionic form chorismate, is an important biochemical intermediate in plants and microorganisms. It is a precursor for:

The acetolactate synthase (ALS) enzyme is a protein found in plants and micro-organisms. ALS catalyzes the first step in the synthesis of the branched-chain amino acids.
In enzymology, a ketol-acid reductoisomerase (EC 1.1.1.86) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a pyrroloquinoline-quinone synthase (EC 1.3.3.11) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a stizolobinate synthase (EC 1.13.11.30) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Isochorismate synthase ( EC 5.4.4.2) is an isomerase enzyme that catalyzes the first step in the biosynthesis of vitamin K2 (menaquinone) in Escherichia coli.
In enzymology, a trans-epoxysuccinate hydrolase (EC 3.3.2.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoyl-CoA synthase catalyzes the sixth step in the biosynthesis of phylloquinone and menaquinone, the two forms of vitamin K. In E. coli, 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoyl-CoA synthase, formerly known as naphthoate synthase, is encoded by menB and uses O-succinylbenzoyl-CoA as a substrate and converts it to 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoyl-CoA.
The enzyme dihydroxy-acid dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.9) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a proclavaminate amidinohydrolase (EC 3.5.3.22) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-ethylmalate synthase (EC 2.3.3.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-isopropylmalate synthase (EC 2.3.3.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a homocitrate synthase (EC 2.3.3.14) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase (EC 2.2.1.7) is an enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 3-deoxy-8-phosphooctulonate synthase (EC 2.5.1.55) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetylneuraminate synthase (EC 2.5.1.56) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, SEPHCHC synthase (EC EC 2.2.1.9), encoded by menD gene in E. coli, is an enzyme that catalyzes the second step of menaquinone (vitamin K2) biosynthesis. The two substrates of this enzyme are 2-oxoglutarate and isochorismate. The products of this enzyme are 5-enolpyruvoyl-6-hydroxy-2-succinyl-cyclohex-3-ene-1-carboxylate and CO2. It belongs to the transferase family.
The enzyme 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoyl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.28; systematic name 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoyl-CoA hydrolase) catalyses the following reaction:
Acireductone synthase (EC number 3.1.3.77, E1, E-1 enolase-phosphatase) is an enzyme with systematic name 5-(methylsulfanyl)-2,3-dioxopentyl-phosphate phosphohydrolase (isomerizing). It catalyses the following reaction:

Isochorismate pyruvate lyase is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing part of the pathway involved in the formation of salicylic acid. More specifically, IPL will use isochorismate as a substrate and convert it into salicylate and pyruvate. IPL is a PchB enzyme originating from the pchB gene in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.









