
Indigenous peoples in Brazil or Native Brazilians are the peoples who lived in Brazil before European contact around 1500 and their descendants. Indigenous peoples once comprised an estimated 2,000 district tribes and nations inhabiting what is now Brazil. The 2010 Brazil census recorded 305 ethnic groups of Indigenous people who spoke 274 Indigenous languages; however, almost 77% speak Portuguese.
The Tupi people, a subdivision of the Tupi-Guarani linguistic families, were one of the largest groups of indigenous peoples in Brazil before its colonization. Scholars believe that while they first settled in the Amazon rainforest, from about 2,900 years ago the Tupi started to migrate southward and gradually occupied the Atlantic coast of Southeast Brazil.
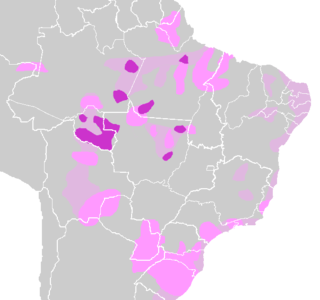
Tupi–Guarani is the most widely distributed subfamily of the Tupian languages of South America. It consists of about fifty languages, including Guarani and Old Tupi. The most widely spoken in modern times by far is Guarani, which is one of the two official languages of Paraguay.

The Tupi or Tupian language family comprises some 70 languages spoken in South America, of which the best known are Tupi proper and Guarani.

Old Tupi, Ancient Tupi or Classical Tupi is a classical Tupian language which was spoken by the indigenous Tupi people of Brazil, mostly those who inhabited coastal regions in South and Southeast Brazil. In the words of Brazilian tupinologist Eduardo Navarro, "it is the classical indigenous language of Brazil, and the one which had the utmost importance to the cultural and spiritual formation of the country".
Omagua is a Tupi-Guarani language closely related to Cocama, belonging to the Group III subgroup of the Tupí-Guaraní family, according to Aryon Rodrigues' classification of the family. Alternate names for Omagua include: Agua, Anapia, Ariana, Cambeba, Cambeeba, Cambela, Campeba, Canga-Peba, Compeva, Janbeba, Kambeba, Macanipa, Omagua-Yete, Pariana, Umaua, Yhuata.

Je–Tupi–Carib is a proposed language family composed of the Macro-Je, Tupian and Cariban languages of South America. Aryon Rodrigues (2000) based this proposal on shared morphological patterns. In an earlier proposal, Rodrigues (1985) had also proposed a Tupí-Cariban language family.

The Nheengatu or Nenhengatu language, or Nenhengatu, also known as Modern Tupi and Amazonic Tupi, is a Tupi–Guarani language.
The Tupí or Tupinambá languages are a subgroup of the Tupi–Guarani language family.

Rede Tupi was a Brazilian commercial terrestrial television network. Its flagship station, located in the city of São Paulo, was the first TV station to operate in the country, being inaugurated on 18 September 1950 by journalist Assis Chateaubriand. It was owned by Diários Associados, one of the largest media conglomerates of the 20th century, owner of several newspapers, magazines, and radio stations.

Tupi Football Club, commonly referred to as Tupi, is a Brazilian professional club based in Juiz de Fora, Minas Gerais founded on 26 May 1912. It competes in the Campeonato Mineiro Segunda Divisão, the third tier of the Minas Gerais state football league.
Kawahíva is a Tupi–Guarani dialect cluster of Brazil. The major variety is Tenharim.

Cleyde Yáconis was a Brazilian actress.

Hemilophini is a tribe of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae.
Isomerida is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:
Isomerida invicta is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Galileo and Martins in 1996. It is known from Peru.
Isomerida santamarta is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Galileo and Martins in 2001. It is known from Colombia.
Isomerida lineata is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Henry Walter Bates in 1874. It is known from Brazil, Bolivia, Colombia, Nicaragua and Peru.
Isomerida lanifica is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Ernst Friedrich Germar in 1824. It is known from Brazil.
The Northern Tupi–Guarani languages are a subgroup of the Tupi–Guarani language family.








