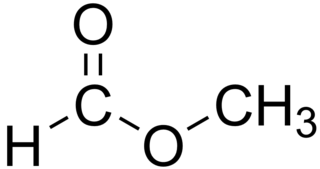
Methyl formate, also called methyl methanoate, is the methyl ester of formic acid. The simplest example of a carboxylate ester, it is a colorless liquid with an ethereal odour, high vapor pressure, and low surface tension. It is a precursor to many other compounds of commercial interest.

Stearidonic acid (SDA: C18H28O2; 18:4, n-3) is an ω-3 fatty acid, sometimes called moroctic acid.

Protoporphyrin IX is an organic compound, classified as a porphyrin, that plays an important role in living organisms as a precursor to other critical compounds like heme (hemoglobin) and chlorophyll. It is a deeply colored solid that is not soluble in water. The name is often abbreviated as PPIX.

Trimesic acid, also known as benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid, is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(CO2H)3. It is one of three isomers of benzenetricarboxylic acid. A colorless solid, trimesic acid has some commercial value as a precursor to some plasticizers.
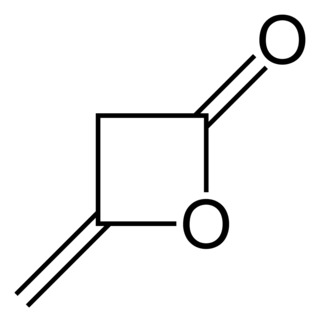
Diketene is an organic compound with the molecular formula C4H4O2, and which is sometimes written as (CH2CO)2. It is formed by dimerization of ketene, H2C=C=O. Diketene is a member of the oxetane family. It is used as a reagent in organic chemistry. It is a colorless liquid.
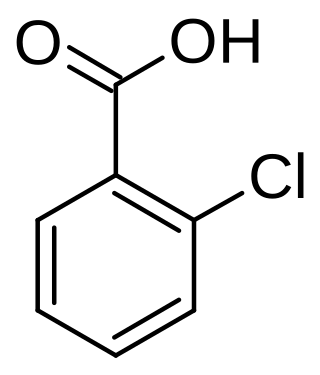
2-Chlorobenzoic acid is an organic compound with the formula ClC6H4CO2H. It is one of three isomeric chlorobenzoic acids, the one that is the strongest acid. This white solid is used as a precursor to a variety of drugs, food additives, and dyes.

Acetoxolone is a drug used for peptic ulcer and gastroesophageal reflux disease. It is an acetyl derivative of glycyrrhetinic acid. It is found in Echinopora lamellosa.

Argininosuccinic acid is a non-proteinogenic amino acid that is an important intermediate in the urea cycle. It is also known as argininosuccinate.
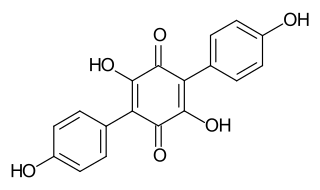
Atromentin is a natural chemical compound found in Agaricomycetes fungi in the orders Agaricales and Thelephorales. It can also be prepared by laboratory synthesis. Chemically, it is a polyphenol and a benzoquinone.
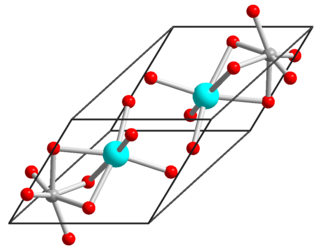
Nickel(II) titanate, also known as nickel titanium oxide, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NiTiO3. It is a coordination compound between nickel(II), titanium(IV) and oxide ions. It has the appearance of a yellow powder. Nickel(II) titanate has been used as a catalyst for toluene oxidation.

Aminomethyl propanol (AMP) is an organic compound with the formula H2NC(CH3)2CH2OH. It is colorless liquid that is classified as an alkanolamine. It is a useful buffer and a precursor to numerous other organic compounds.
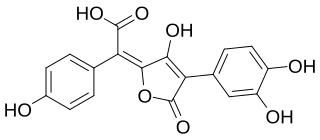
Xerocomic acid is a red-orange pigment found in fungi of the order Boletales. It is the precursor to variegatic acid, and is preceded by atromentic acid and atromentin. As an example, it is isolated from Serpula lacrymans. It is soluble in methanol. An oxidase acting on xerocomic acid is responsible for the "bluing" reaction seen in mushrooms.

Atromentic acid is a red-organge pigment found in fungi within the Boletales group. It is the precursor to variegatic acid and xerocomic acid, and is preceded by atromentin. As an example, it is isolated from Serpula lacrymans. It is soluble in methanol. Variants include homoatromentic acid. This pigment has been studied and elucidated by Wolfgang Steglich and colleagues over decades. When atromentin is oxidised with hydrogen peroxide a yellow product is produced. A sodium hydroxide solution is also yellow, but when this is neutralized with acid the red atromentic acid crystallises. Concentrated potassium hydroxide breaks up the compound to p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid and oxalic acid.

Xerocomorubin is a pigment from the fungus order Boletales. It is the oxidized form of isoxerocomic acid. Air oxidation is responsible its formation, and it oxidizes faster to a similar pulvinic acid type pigment oxidized variant, variegatorubin. The long wavelength has an absorption at 497 nm, 106 nm higher than its precursor isoxerocomic acid. Synthesis experiments have shown tetra-acetylation by acetic anhydride and sulfuric acid. Although xerocomorubin and variegatorubin give off the same deep red color and could simultaneously occur in a mushroom, extracts from the deep red colored mushroom Boletus rubellus Krombh. identified only variegatorubin by thin layer chromatography (TLC), leading to the question the natural abundance of xerocomorubin.

Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), is a cannabinoid produced in cannabis plants. It is the precursor to cannabidiol (CBD). It is most abundant in the glandular trichomes on the female seedless flowers or more accurately infructescence often colloquially referred to as buds or flowers.

Pterobilin also called biliverdin IXγ in the Fischer nomenclature, is a blue bile pigment found in Nessaea spp., Graphium agamemnon, G. antiphates, G. doson, and G. sarpedon. It is one of only a few blue pigments found in any animal species, as most animals use iridescence to create blue coloration. Other blue pigments of animal origin include phorcabilin, used by other butterflies in Graphium and Papilio, and sarpedobilin, which is used by Graphium sarpedon.

Lithium lactate is a chemical compound, a salt of lithium and lactic acid with the formula CH3CH(OH)COOLi, an amorphous solid, very soluble in water.
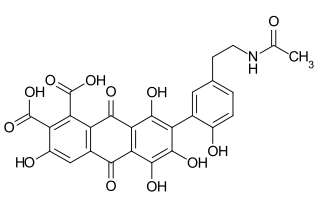
Laccaic acids or laccainic acids are a group of five anthraquinone derivatives, designated A through E, which are components of the red shellac obtained from the insect Kerria lacca, similar to carminic acid and kermesic acid. This article focuses primarily on laccaic acid A (LCA).


















