
Lyngbya is a genus of cyanobacteria, unicellular autotrophs that form the basis of the oceanic food chain.

Nodularia is a genus of filamentous nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria, or blue-green algae. They occur mainly in brackish or salinic waters, such as the hypersaline Makgadikgadi Pans, the Peel-Harvey Estuary in Western Australia or the Baltic Sea. Nodularia cells occasionally form heavy algal blooms. Some strains produce a cyanotoxin called nodularin R, which is harmful to humans.

Oscillatoria is a genus of sugar making microscopic creatures.
Oocystaceae is a family of green algae, in the order Chlorellales. The type genus is Oocystis.

Botryococcus is a genus of green algae. The cells form an irregularly shaped aggregate. Thin filaments connect the cells. The cell body is ovoid, 6 to 10 μm long, and 3 to 6 μm wide. Fossils of the genus are known since Precambrian times, and form the single largest biological contributor to crude oil, and are a major component of oil shales.

Scytonema is a genus of photosynthetic cyanobacteria that contains over 100 species. It grows in filaments that form dark mats. Many species are aquatic and are either free-floating or grow attached to a submerged substrate, while others species grow on terrestrial rocks, wood, soil, or plants. Scytonema is a nitrogen fixer, and can provide fixed nitrogen to the leaves of plants on which it is growing. Some species of Scytonema form a symbiotic relationship with fungi to produce a lichen.

Planktothrix is a diverse genus of filamentous cyanobacteria observed to amass in algal blooms in water ecosystems across the globe. Like all Oscillatoriales, Planktothrix species have no heterocysts and no akinetes. Planktothrix are unique because they have trichomes and contain gas vacuoles unlike typical planktonic organisms. Previously, some species of the taxon were grouped within the genus Oscillatoria, but recent work has defined Planktothrix as its own genus. A tremendous body of work on Planktothrix ecology and physiology has been done by Anthony E. Walsby, and the 55.6 kb microcystin synthetase gene which gives these organisms the ability to synthesize toxins has been sequenced. P. agardhii is an example of a type species of the genus. P. agardhii and P. rubescens are commonly observed in lakes of the Northern Hemisphere where they are known producers of potent hepatotoxins called microcystins.

Dendrocoelum is a genus of freshwater triclad. Over one hundred species have been described.

The Pseudanabaenaceae are a family of cyanobacteria.
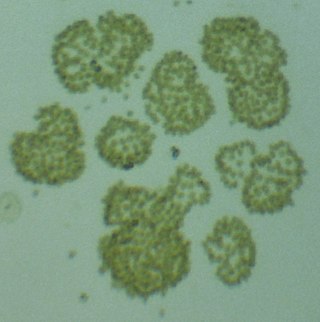
Woronichinia is a genus of cyanobacteria, belonging to the family Coelosphaeriaceae.
Eucapsis is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Merismopediaceae.
Gloeocapsopsis is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Chroococcaceae.
Kamptonema is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Microcoleaceae.

Chamaesiphon is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Chamaesiphonaceae.

Dolichospermum is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Nostocaceae.
Heteroleibleinia is a genus of algae belonging to the family Pseudanabaenaceae.
Komvophoron is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Borziaceae.
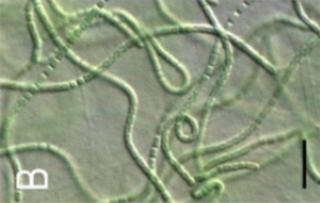
Leptolyngbya is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Leptolyngbyaceae.
Phormidium aerugineo-caeruleum is a species of cyanobacteria in the genus Phormidium.

Agraphydrus is a genus of water scavenger beetle in the family Hydrophilidae represented by 205 described species. It is distributed across the Afrotropical, Australasian, and Indomalayan realms.












