
USS Gato (SS-212) was the lead ship of her class of submarine in the United States Navy. She was the first Navy ship named for the gato, a species of small catshark.

USS Scamp (SS-277), a Gato-class submarine, was the first ship of the United States Navy to be named for the scamp grouper, a member of the family Serranidae.
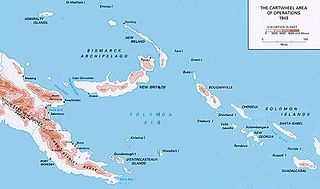
Operation Cartwheel (1943–1944) was a major military operation for the Allies in the Pacific theatre of World War II. Cartwheel was an operation aimed at neutralising the major Japanese base at Rabaul. The operation was directed by the Supreme Allied Commander in the South West Pacific Area (SWPA), General Douglas MacArthur, whose forces had advanced along the northeast coast of New Guinea and occupied nearby islands. Allied forces from the South Pacific Area, under Admiral William Halsey, advanced through the Solomon Islands toward Bougainville. The Allied forces involved were from Australia, the Netherlands, New Zealand, the US and various Pacific Islands.

USS Drum (SS-228) is a Gato-class submarine of the United States Navy, the first Navy ship named after the drum, a type of fish. Drum is a museum ship in Mobile, Alabama, at Battleship Memorial Park.

The Battle of the Bismarck Sea took place in the South West Pacific Area (SWPA) during World War II when aircraft of the U.S. Fifth Air Force and the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) attacked a Japanese convoy carrying troops to Lae, New Guinea. Most of the Japanese task force was destroyed, and Japanese troop losses were heavy.

USS Greenling (SS-213), a Gato-class submarine, was the first ship of the United States Navy to be named for the greenling.

USS Guardfish (SS-217), a Gato-class submarine, was the first ship of the United States Navy to be named for the guardfish.

USS Croaker (SS/SSK/AGSS/IXSS-246), a Gato-class submarine, was the first ship of the United States Navy to be named for the croaker, any of various fishes which make throbbing or drumming noises.

Masatomi Kimura, was an admiral in the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II.

Skip bombing was a low-level bombing technique independently developed by several of the combatant nations in World War II, notably Italy, Australia, Britain, and the United States. It allows an aircraft to attack shipping by skipping the bomb across the water like a stone. Dropped at very low altitudes, the bomb never rises more than about 5 metres (16 ft) above the surface of the water, ensuring that it will hit the side of the ship as long as it is aimed correctly.
Kembu Maru was the name of a number of ships.
The Battle of the Bismarck Sea took place in the South West Pacific Area (SWPA) during World War II. During the course of the battle, aircraft of the U.S. 5th Air Force and the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) attacked a Japanese convoy that was carrying troops to Lae, New Guinea. Most of the task force was destroyed, and Japanese troop losses were heavy.
Aiyo Maru was a 2,746-ton transport ship of the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II.

Taimei Maru was a 2,883 ton transport ship of the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II.
Sin-ai Maru, also known as Shin-ai Maru was a 3,794 ton transport ship of the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II.
SS Kyokusei Maru (Kanji:旭盛丸) was a 3,794 GRT transport ship of the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II.
Oigawa Maru (大井川丸) was a 6,494 GRT transport ship of the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II.
Noshiro Maru was a Nippon Yusen Kaisen (NYK) Liner completed in 1934 and requisitioned by the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) in 1937 to transport troops to China following the Marco Polo Bridge Incident. She was later returned to civilian service before being converted to an armed merchant cruiser by the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) in 1941. She was bombed twice and torpedoed twice as a World War II troopship before being abandoned at Manila in 1944.

The Nojima Maru, also known as Noshima Maru or Nozima Maru, was an 8,215 ton coal ship, also used as troop transport ship by the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) during World War II.
SS Saarland was a 6,870 ton German passenger ship, which was sold to Japan in 1940, renamed Teiyo Maru and used as troop transport ship by the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) during World War II. It sank during the Battle of the Bismarck Sea with great loss of life.












