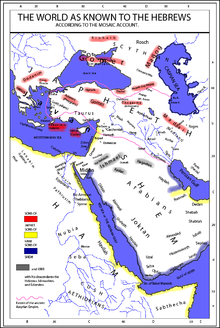
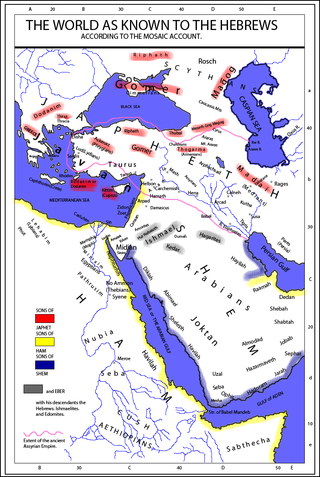
Japheth is one of the three sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis, in which he plays a role in the story of Noah's drunkenness and the curse of Ham, and subsequently in the Table of Nations as the ancestor of the peoples of the Aegean Sea, Anatolia, Caucasus, Greece, and elsewhere in Eurasia. In medieval and early modern European tradition he was considered to be the progenitor of the European peoples.

Ionia was an ancient region on the western coast of Anatolia, to the south of present-day İzmir, Turkey. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionians who had settled in the region before the archaic period.
Tarshish occurs in the Hebrew Bible with several uncertain meanings, most frequently as a place far across the sea from Phoenicia and the Land of Israel. Tarshish was said to have exported vast quantities of important metals to Phoenicia and Israel. The same place name occurs in the Akkadian inscriptions of Assyrian king Esarhaddon and also on the Phoenician inscription of the Nora Stone in Sardinia; its precise location was never commonly known, and was eventually lost in antiquity. Legends grew up around it over time so that its identity has been the subject of scholarly research and commentary for more than two thousand years.

The Hebrews were an ancient Semitic-speaking people. Historians mostly consider the Hebrews as synonymous with the Israelites, with the term "Hebrew" denoting an Israelite from the nomadic era that preceded the establishment of the united Kingdom of Israel. However, in some instances, the designation "Hebrews" may also be used historically in a wider sense, referring to the Phoenicians or other ancient civilizations, such as the Shasu on the eve of the Late Bronze Age collapse. It appears 34 times within 32 verses of the Hebrew Bible. Some scholars regard "Hebrews" as an ethnonym, while others do not, and others still hold that the multiple modern connotations of ethnicity may not all map well onto the sociology of ancient Near-Eastern groups.

The Generations of Noah, also called the Table of Nations or Origines Gentium, is a genealogy of the sons of Noah, according to the Hebrew Bible, and their dispersion into many lands after the Flood, focusing on the major known societies. The term 'nations' to describe the descendants is a standard English translation of the Hebrew word "goyim", following the c. 400 CE Latin Vulgate's "nationes", and does not have the same political connotations that the word entails today.

Via Maris is one modern name for an ancient trade route, dating from the early Bronze Age, linking Egypt with the northern empires of Syria, Anatolia and Mesopotamia – along the Mediterranean coast of modern-day Egypt, Israel, Turkey and Syria. In Latin, Via Maris means "way of the sea", a translation of the Greek ὁδὸν θαλάσσης found in Isaiah 9:1 of the Septuagint, itself a translation of the Hebrew דֶּ֤רֶךְ הַיָּם֙ . It is a historic road that runs in part along the Israeli Mediterranean coast. It was the most important route from Egypt to Syria which followed the coastal plain before crossing over into the plain of Jezreel and the Jordan valley.

Enoch is a biblical figure and patriarch prior to Noah's flood, and the son of Jared and father of Methuselah. He was of the Antediluvian period in the Hebrew Bible.

The Ionians were one of the four major tribes that the Greeks considered themselves to be divided into during the ancient period; the other three being the Dorians, Aeolians, and Achaeans. The Ionian dialect was one of the three major linguistic divisions of the Hellenic world, together with the Dorian and Aeolian dialects.
Tiras is, according to the Book of Genesis and 1 Chronicles, the seventh and youngest son of Japheth in the Hebrew Bible. A brother of biblical Javan, its geographical locale is sometimes associated by scholars with the Tershi or Tirsa, one of the groups which made up the Sea Peoples "thyrsenes" (Tyrrhenians), a naval confederacy which terrorized Egypt and other Mediterranean nations around 1200 BCE. These Sea People are referred to as "Tursha" in an inscription of Ramesses III, and as "Teresh of the Sea" on the Merneptah Stele.
Kittim was a settlement in present-day Larnaca on the east coast of Cyprus, known in ancient times as Kition, or Citium. On this basis, the whole island became known as "Kittim" in Hebrew, including the Hebrew Bible. However the name seems to have been employed with some flexibility in Hebrew literature. It was often applied to all the Aegean islands and even to "the W[est] in general, but esp[ecially] the seafaring W[est]". Flavius Josephus records in his Antiquities of the Jews that
Elishah or Eliseus was the son of Javan according to the Book of Genesis (10:4) in the Masoretic Text. The Greek Septuagint of Genesis 10 lists Elisa not only as the son of Javan, but also a grandson of Japheth. His name is spelled differently in Hebrew to the prophet Elisha, ending in a hei instead of an ayin.

The term Japhetites refers to the descendants of Japheth, one of the three sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis. The term was used in ethnological and linguistic writings from the 18th to the 20th centuries as a Biblically derived racial classification for the European peoples, but is now considered obsolete. Medieval ethnographers believed that the world had been divided into three large-scale groupings, corresponding to the three classical continents: the Semitic peoples of Asia, the Hamitic peoples of Africa, and the Japhetic peoples of Europe.
Dodanim or Rodanim, was, in the Book of Genesis, a son of Javan. Dodanim's brothers, according to Genesis 10:4, were Elishah, Tarshish and Chittim. He is usually associated with the people of the island of Rhodes as their progenitor. "-im" is a plural suffix in Hebrew, and the name may refer to the inhabitants of Rhodes. Traditional Hebrew manuscripts are split between the spellings Dodanim and Rodanim — one of which is probably a copyist's error, as the Hebrew letters for R and D are quite similar graphically. The Samaritan Pentateuch, as well as 1 Chronicles 1:7, have Rodanim, while the Septuagint has Rodioi. The Dodanim were considered either kin to the Greeks or simply Greeks.
The name of Greece differs in Greek compared with the names used for the country in other languages and cultures, just like the names of the Greeks. The ancient and modern name of the country is Hellas or Hellada (Greek: Ελλάς, Ελλάδα; in polytonic: Ἑλλάς, Ἑλλάδα), and its official name is the Hellenic Republic, Helliniki Dimokratia. In English, however, the country is usually called Greece, which comes from the Latin Graecia.

Yohanan Aharoni was an Israeli archaeologist and historical geographer, chairman of the Department of Near East Studies and chairman of the Institute of Archaeology at Tel-Aviv University.
Pirathon was an ancient town mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. Its exact whereabouts are not known. The Hebrew name agrees closely with that of modern Fara'ata, seven miles WSW of Shechem, leading to common identification of the two, though Conder and Kitchener claim that the earliest reference to the name "Fera'ata" dates to the 14th century. They also state that the Samaritan Chronicle refers to the town as Ophrah, though the Chronicle identifies Fer'ata as west of Shechem. Its tribal affiliation with Ephraim in Judges 12:15 has been questioned on the grounds that Fara'ata lies north of the main course of Wadi Qana, which formed the southern border of Manasseh. However, the Wadi Qana this far east has divided in to numerous tributaries. The village sits on a prominent hill, and the valley to its north and west drains into the Wadi Qana, so it might well have been reckoned to Ephraim.
According to Greek mythology, Ion was eponymous ancestor of the Ionians.
Bozkath was a town in the Kingdom of Judah mentioned in the Hebrew Bible/Old Testament. The town was located in the lowland hills of Judah, otherwise known as the Shephelah, but its precise location is unknown.

Since early modern times, a number of biblical ethnonyms from the Table of Nations in Genesis 10 have been used as a basis for classifying human racial and national identities. The connection between Genesis 10 and contemporary ethnic groups began during classical antiquity, when authors such as Josephus, Hippolytus and Jerome analyzed the biblical list.

1 Chronicles 1 is the first chapter of the Books of Chronicles in the Hebrew Bible or the First Book of Chronicles in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. The book is compiled from older sources by an unknown person or group, designated by modern scholars as "the Chronicler", and had the final shape established in late fifth or fourth century BCE. The content of this chapter is the genealogy list from Adam to Israel (=Jacob) in the following structure: Adam to Noah ; Noah's descendants from his three sons Shem, Ham, and Japheth: the Japhethites, Hamites, Semites ; the sons of Abraham ; the sons of Isaac. This chapter belongs to the section focusing on the list of genealogies from Adam to the lists of the people returning from exile in Babylon.