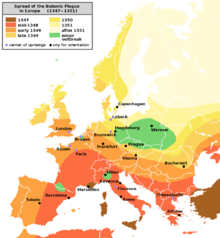
John II, called John the Good, was King of France from 1350 until his death in 1364. When he came to power, France faced several disasters: the Black Death, which killed nearly one-third to one-half of its population; popular revolts known as Jacqueries; free companies of routiers who plundered the country; and English aggression that resulted in catastrophic military losses, including the Battle of Poitiers of 1356, in which John was captured.

The Jacquerie was a popular revolt by peasants that took place in northern France in the early summer of 1358 during the Hundred Years' War. The revolt was centred in the valley of the Oise north of Paris and was suppressed after over two months of violence. This rebellion became known as "the Jacquerie" because the nobles derided peasants as "Jacques" or "Jacques Bonhomme" for their padded surplice, called a "jacque". The aristocratic chronicler Jean Froissart and his source, the chronicle of Jean le Bel, referred to the leader of the revolt as Jacque Bonhomme, though in fact the Jacquerie 'great captain' was named Guillaume Cale. The word jacquerie became a synonym of peasant uprisings in general in both English and French.

John of Berry or John the Magnificent was Duke of Berry and Auvergne and Count of Poitiers and Montpensier. He was Regent of France from 1380 to 1388 during the minority of his nephew Charles VI. His brothers were King Charles V of France, Duke Louis I of Anjou and Duke Philip the Bold of Burgundy.

In the New Testament, Salome was a follower of Jesus who appears briefly in the canonical gospels and in apocryphal writings. She is named by Mark as present at the crucifixion and as one of the Myrrhbearers, the women who found Jesus's empty tomb. Interpretation has further identified her with other women who are mentioned but not named in the canonical gospels. In particular, she is often identified as the wife of Zebedee, the mother of James and John, two of the Twelve apostles. In medieval tradition Salome was counted as one of the Three Marys who were daughters of Saint Anne, so making her the sister or half-sister of Mary, mother of Jesus.

Charles of Valois, the fourth son of King Philip III of France and Isabella of Aragon, was a member of the House of Capet and founder of the House of Valois, whose rule over France would start in 1328.

The first phase of the Hundred Years' War between England and France lasted from 1337 to 1360. It is sometimes referred to as the Edwardian War because it was initiated by King Edward III of England, who claimed the French throne in defiance of King Philip VI of France. The dynastic conflict was caused by disputes over the French feudal sovereignty over Aquitaine and the English claims over the French royal title. The Kingdom of England and its allies dominated this phase of the war.

Froissart's Chronicles are a prose history of the Hundred Years' War written in the 14th century by Jean Froissart. The Chronicles open with the events leading up to the deposition of Edward II in 1327, and cover the period up to 1400, recounting events in western Europe, mainly in England, France, Scotland, the Low Countries and the Iberian Peninsula, although at times also mentioning other countries and regions such as Italy, Germany, Ireland, the Balkans, Cyprus, Turkey and North Africa.

Charles II, called the Magnanimous was Count of Alençon and Count of Perche (1325–1346), as well as Count of Chartres and Count of Joigny (1335–1336) as husband of Joan of Joigny.

Louis of Évreux was a prince, the only son of King Philip III of France and his second wife Maria of Brabant, and thus a half-brother of King Philip IV of France.

Geoffroi de Charny was the third son of Jean de Charny, the lord of Charny, and Marguerite de Joinville, daughter of Jean de Joinville, the biographer and close friend of France’s King Louis IX. A renowned knight who fought on the French side during the early years of the Hundred Years’ War, Charny wrote a semi-autobiographical poem, The Book of Geoffroi de Charny, and a set of questions on chivalric matters for the short-lived Company of the Star, France’s counterpart to England’s Order of the Garter. Although a prose treatise called the Book of Chivalry has also long been accredited to him, recent findings indicate this to have been more likely by his son of the same name, Geoffroi II de Charny, who died in 1398. Charny is also widely associated with the first known showings of the Shroud of Turin, though there are now doubts that he was responsible for these.

Robert III of Artois was an French nobleman of the House of Artois. He was the Lord of Conches-en-Ouche, of Domfront, and of Mehun-sur-Yèvre, and in 1309 he received as appanage the county of Beaumont-le-Roger in restitution for the County of Artois, which he claimed. He was also briefly Earl of Richmond in 1341 after the death of John III, Duke of Brittany.

Guy I of Châtillon, Count of Blois, son of Hugh II of Châtillon and Beatrix of Dampierre, was Count of Blois and Lord of Avesnes 1307–1342.

Louis II of Châtillon, son of Guy I, Count of Blois and Margaret of Valois, was count of Blois and lord of Avesnes from 1342 to 1346.

The Three Marys are women mentioned in the canonical gospels' narratives of the crucifixion and resurrection of Jesus. Mary was the most common name for Jewish women of the period.

Joan I was ruling Countess of Auvergne and Boulogne from 1332 to 1360 and Queen of France by her marriage to King John II.
Guillaume de Nangis, also known as William of Nangis, was a French chronicler.
Joan of Valois was the daughter of Charles, Count of Valois and his second wife Catherine I of Courtenay, titular empress of Constantinople.

Isabella of Valois was a Duchess of Bourbon by marriage to Peter I, Duke of Bourbon. She was the daughter of Charles of Valois by his third wife Mahaut of Châtillon.

The Hundred Years' War was a series of armed conflicts fought between the kingdoms of England and France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from English claims to the French throne initially made by Edward III of England. The war grew into a broader military, economic and political struggle involving factions from across Western Europe, fueled by emerging nationalism on both sides. The periodization of the war typically charts it as taking place over 116 years. However, it was an intermittent conflict which was frequently interrupted by external factors, such as the Black Death, and several years of truces.
William XII of Auvergne (1300–1332) was Count of Auvergne and Count of Boulogne between 1325 and 1332. He was the eldest son of Robert VII of Auvergne and Blanche of Bourbon, daughter of Robert, Count of Clermont.