Related Research Articles

The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies or the Thirteen American Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America founded in the 17th and 18th centuries. The American Enlightenment led these colonies to the American Revolutionary War. They declared independence as the United States of America in July 1776, which was achieved by 1783 under the Treaty of Paris.

Thomas West, 3rd Baron De La Warr, was an English merchant and politician, for whom the bay, the river, and, consequently, a Native American people and U.S. state, all later called "Delaware", were named. He was a member of the House of Lords from the death of his father in 1602 until his own death in 1618, and was also governor of the Virginia colony.

The Massachusetts Bay Colony (1628–1691), more formally the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, was an English settlement on the east coast of North America around the Massachusetts Bay, the northernmost of the several colonies later reorganized as the Province of Massachusetts Bay. The lands of the settlement were in southern New England, with initial settlements on two natural harbors and surrounding land about 15.4 miles (24.8 km) apart—the areas around Salem and Boston, north of the previously established Plymouth Colony. The territory nominally administered by the Massachusetts Bay Colony covered much of central New England, including portions of Massachusetts, Maine, New Hampshire, and Connecticut.

Events from the 1630s in Canada.
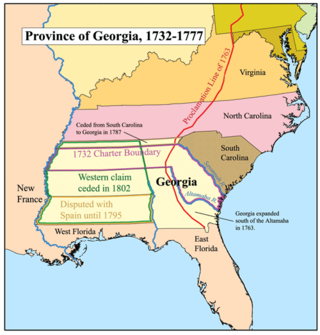
The Southern Colonies within British America consisted of the Province of Maryland, the Colony of Virginia, the Province of Carolina, and the Province of Georgia. In 1763, the newly created colonies of East Florida and West Florida would be added to the Southern Colonies by Great Britain until the Spanish Empire took back Florida. These colonies were the historical core of what would become the Southern United States, or "Dixie". They were located south of the Middle Colonies, albeit Virginia and Maryland were also considered as the Chesapeake Colonies.
John Haynes, also sometimes spelled Haines, was a colonial magistrate and one of the founders of the Connecticut Colony. He served one term as governor of the Massachusetts Bay Colony and was the first governor of Connecticut, ultimately serving eight separate terms. Although Colonial Connecticut prohibited Governors from serving consecutive terms at the time, "John Haynes was so popular with the colonists that he served alternately as governor and often as deputy governor from 1639 to his death in 1653."

William Claiborne also, spelled Cleyburne was an English pioneer, surveyor, and an early settler in the colonies/provinces of Virginia and Maryland and around the Chesapeake Bay. Claiborne became a wealthy merchant and planter, as well as a major political figure in the mid-Atlantic colonies. He featured in disputes between the colonists of Virginia and the later settling of Maryland, partly because of his earlier trading post on Kent Island in the mid-way of the Chesapeake Bay, which provoked the first naval military battles in North American waters. Claiborne repeatedly attempted and failed to regain Kent Island from the Maryland Calverts, sometimes by force of arms, after its inclusion in the lands that were granted by a 1632 Royal Charter to the Calvert family. Kent Island had become Maryland territory after the surrounding lands were granted to Sir George Calvert, first Baron and Lord Baltimore (1579–1632) by the reigning King of England, Charles I.

Sir William Berkeley was an English colonial administrator who served as the governor of Virginia from 1660 to 1677. One of the Lords Proprietors of the Province of Carolina, as governor of Virginia he implemented policies that bred dissent among the colonists and sparked Bacon's Rebellion. A favourite of King Charles I, the king first granted him the governorship in 1642. Berkeley was unseated following the execution of Charles I, but his governorship was restored by King Charles II in 1660.

Roger Ludlow (1590–1664) was an English lawyer, magistrate, military officer, and colonist. He was active in the founding of the Colony of Connecticut, and helped draft laws for it and the nearby Massachusetts Bay Colony. Under his and John Mason's direction, Boston's first fortification, later known as Castle William and then Fort Independence was built on Castle Island in Boston harbor. Frequently at odds with his peers, he eventually also founded Fairfield and Norwalk before leaving New England entirely.

John Winthrop the Younger was an early governor of the Connecticut Colony, and he played a large role in the merger of several separate settlements into the unified colony.

William Randolph I was an English-born planter, merchant and politician in colonial Virginia who played an important role in the development of the colony. Born in Moreton Morrell, Warwickshire, Randolph moved to the colony of Virginia sometime between 1669 and 1673, and married Mary Isham a few years later. His descendants include many prominent individuals including Thomas Jefferson, John Marshall, Paschal Beverly Randolph, Robert E. Lee, Peyton Randolph, Edmund Randolph, John Randolph of Roanoke, George W. Randolph, and Edmund Ruffin. Due to his and Mary's many progeny and marital alliances, they have been referred to as "the Adam and Eve of Virginia".
Captain Samuel Mathews was a Virginia planter, political figure, and the father of Governor Samuel Mathews.
Lt. Col. Samuel Mathews (1630–1660), Commonwealth Governor of Virginia, of Warwick County in the English Colony of Virginia, was a member of the House of Burgesses, the Governor's Council, and served as Commonwealth Governor of Virginia from 1656 until he died in office in January, 1660. There was no Royal Governorship at the time of the "Protectorate", and the Governor technically answered to the Cromwellian Parliament, although Royalist sentiment was prevalent in the colony of Virginia at this time. The former Royalist governor Berkeley arrived to replace him March 13, 1660.

The English overseas possessions, also known as the English colonial empire, comprised a variety of overseas territories that were colonised, conquered, or otherwise acquired by the former Kingdom of England during the centuries before the Acts of Union of 1707 between the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland created the Kingdom of Great Britain. The many English possessions then became the foundation of the British Empire and its fast-growing naval and mercantile power, which until then had yet to overtake those of the Dutch Republic, the Kingdom of Portugal, and the Crown of Castile.

William Farrar was a landowner and politician in colonial Virginia. He was a subscriber to the third charter of the Virginia Company who immigrated to the colony from England in 1618. After surviving the Jamestown massacre of 1622, he moved to Jordan's Journey. In the following year, Farrar became involved in North America's first breach of promise suit when he proposed to Cecily Jordan.
Edmund Rossingham was the nephew of and factor or agent for Sir George Yeardley, who was Governor of the Colony of Virginia, three times between November 1616 and November 1627, and his wife Temperance Flowerdew. Rossingham was a member of the first assembly of the Virginia House of Burgesses at Jamestown, Virginia in 1619 for Flowerdew Hundred Plantation, Yeardley's plantation.
Sir Richard Kemp was a planter and politician in the Colony of Virginia. Kemp served as the Colony's Secretary and on the Governor's Council from 1634 to 1649. As the council's senior member, he also served as the acting Colonial Governor of Virginia from 1644 to 1645 during travels by Governor Sir William Berkeley. Kemp had also worked closely relation with Berkeley's predecessor, Sir John Harvey.
George Reade was a prominent landowner, military officer, judge, and politician who served as a member of the House of Burgesses and as Acting Governor of Virginia Colony. He is the great-great-grandfather of the first President of the United States, George Washington.
Christopher Wormeley was a British military officer who served as governor of Tortuga before becoming the secretary of state for the Virginia Colony (1635-1649) as well as captain of the fort at Old Point Comfort beginning in 1638. He also served on the Virginia Governor's Council (1637-1642), as would his younger brother Ralph Wormeley Sr. and son Christopher Wormeley Jr..
References
- ↑ "Governor of Virginia" . Retrieved 23 September 2007.
- ↑ "WorldStatesmen.org" . Retrieved 23 September 2007.
- ↑ Tarter, Brent. "Sir John Harvey (ca. 1581 or 1582–by 1650)". Encyclopedia Virginia/Dictionary of Virginia Biography . Retrieved 11 March 2015.
- ↑ Brock, Robert A. (1888). Virginia and Virginians. H.H. Hardesty. pp. 20. ISBN 0-87152-110-5.
- ↑ "Declaration of Sir John Harvey", The Virginia Magazine of History and Biography, vol. 1, no. 4, Virginia Historical Society, 1894, pp. 425–30.
- ↑ Cooke, John Esten (1883). Virginia: A History of the People. Houghton, Mifflin and Co. pp. 166.
- ↑ "America and West Indies: December 1636." Calendar of State Papers Colonial, America and West Indies: Volume 1, 1574-1660. Ed. W Noel Sainsbury. London: Her Majesty's Stationery Office, 1860. 242-243. British History Online Retrieved 9 June 2019.
- ↑ Grahame, James (1836). The History of the United States of North America: From the Plantation of the British Colonies till their Revolt and Declaration of Independence. Smith, Elder & Co. pp. 57.
- ↑ Chalmers, George (1845). An Introduction to the History of the Revolt of the American Colonies: Being a Comprehensive View of its Origin, Derived from the State Papers Contained in the Public Offices of Great Britain. J. Munroe & Co. pp. 35-36. ISBN 0-405-03278-1.
- ↑ Billings, Warren M. (1975). The Old Dominion in the Seventeenth Century: A Documentary History of Virginia, 1606-1689 . UNC Press. pp. 236. ISBN 0-8078-1237-4.
- ↑ Fiske, John (1900). Old Virginia and Her Neighbours. Houghton, Mifflin and Company. pp. 280.
- ↑ Calder Roth, ed. (1999). The Virginia Landmarks Register: Boldrup Plantation Archeological Site. University of Virginia Press.


