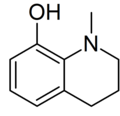 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 1-Methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolin-8-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H13NO | |
| Molar mass | 163.220 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Kairine is a derivative of tetrahydroquinoline which was first described by Wilhelm Fischer in 1883. Its name comes from the Greek kairos, meaning "the right time". [1] It is an antipyretic, formerly used against typhoid fever, but now largely obsolete due to severe side effects. Both kairine and its N-ethyl homolog show similar antipyretic activity. [2] [3] [4] [5]