
Transportation in Malawi is poorly developed. The country of almost 14 million has 39 airports, 6 with paved runways and 33 with unpaved runways. It has 797 kilometres of railways, all narrow-gauge and about 45 percent of its roads are paved. Though it is landlocked, Malawi also has 700 km (435 mi) of waterways on Lake Malawi and along the Shire River.
Transport in Tanzania includes road, rail, air and maritime networks. The road network is 86,472 kilometres (53,731 mi) long, of which 12,786 kilometres (7,945 mi) is classified as trunk road and 21,105 kilometres (13,114 mi) as regional road. The rail network consists of 3,682 kilometres (2,288 mi) of track. Commuter rail service is in Dar es Salaam only. There are 28 airports, with Julius Nyerere International being the largest and the busiest. Ferries connect Mainland Tanzania with the islands of Zanzibar. Several other ferries are active on the countries' rivers and lakes.
This article is about the transport in Zambia.

The Tazara Railway, also called the Uhuru Railway or the Tanzam Railway, is a railway in East Africa linking the port of Dar es Salaam in east Tanzania with the town of Kapiri Mposhi in Zambia's Central Province. The single-track railway is 1,860 km (1,160 mi) long and is operated by the Tanzania-Zambia Railway Authority (TAZARA).

Zambia Railways (ZR) is the national railway company of Zambia, one of the two major railway organisations in Zambia. The other system is the binational TAZARA Railway (TAZARA) that interconnects with the ZR at Kapiri Mposhi and provides a link to the Tanzanian port of Dar es Salaam.

The Cape to Cairo Railway was an unfinished project to create a railway line crossing Africa from south to north. It would have been the largest and most important railway of that continent. It was planned as a link between Cape Town in South Africa and Port Said in Egypt.

Kilombero District is a district in Morogoro Region, south-western Tanzania.
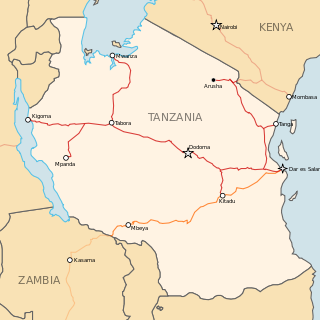
The Central Line, formerly known as the Tanganyika Railway is the most important railway line in Tanzania, apart from TAZARA. It runs west from Dar es Salaam to Kigoma on Lake Tanganyika via Dodoma. A branch leads to Mwanza on Lake Victoria.

Rail transport in Tanzania is conducted by two companies. It has historically used narrow gauge trackage, but planning and construction of new standard gauge lines is underway as of 2017.
Rail transport in Zambia is primarily provided by two systems:
The Trans Africa Railway Corporation is a company that runs the break of gauge transshipment station at Kidatu, Tanzania.
There are several planned railway lines in Rwanda, including a line to Tanzania. Historical railways are limited to three industrial railways.

Railway stations in Tanzania include:

The East African Railway Master Plan is a proposal for rejuvenating the railways serving Tanzania, Kenya, and Uganda and adding railways to serve Rwanda and Burundi. The objective is to further the economic development of eastern Africa by increasing the efficiency and speed, and lowering the cost, of transporting cargo between major ports on the Indian Ocean coast and the interior.
Malawi Railways is the national rail network in Malawi, run by a government corporation until privatisation in 1999. As of 1 December 1999 the Central East African Railways, a consortium led by Railroad Development Corporation, won the right to operate the network.

The Tanzania Railways Corporation(TRC) is a state-owned enterprise that runs one of Tanzania's two main railway networks.

The history of rail transport in Tanzania began in the late nineteenth century.

Narrow-gauge railways are common in Africa, where great distances, challenging terrain and low cost have made the narrow gauges attractive. Many nations, particularly in Southern Africa, including the extensive South African Railway network (Spoornet), use a 3 ft 6 in gauge. Metre gauge is also common, as in the case of the Uganda Railway. There used to be extensive 2 ft and 600 mm gauge networks in countries such as Morocco, Congo, Angola, Namibia and South Africa, but these have mostly been dismantled or converted. Some also survive in Egypt: in the countryside around Luxor, narrow-gauge railways are used for the transportation of sugar cane.

The Dar es Salaam commuter rail, informally known as Treni ya Mwakyembe, is an urban and suburban commuter rail network serving the Tanzanian commercial city of Dar es Salaam. It is one of the two initiatives taken by the government to ease travel within the congested city; the other being the Dar es Salaam bus rapid transit system. Services are provided by the Tanzania-Zambia Railway Authority (TAZARA) and Tanzania Railways Limited (TRL).
The Lobito–Dar es Salaam Railway is a planned narrow gauge railway line that connects the Angolan port city of Lobito to the Tanzanian port city of Dar es Salaam, through the Zambian city of Kapiri Mposhi. It is an African transcontinental railroad connecting the Atlantic and Indian oceans and it is financed by China.











