
Red 1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) gauge.
Orange 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) gauge.
Railway stations in Tanzania include:


Railway stations in Tanzania include:

( all 1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) gauge)
In 1949 a line was built to link the Tanganyika groundnut scheme plantations around Nachingwea with the port of Mtwara. The scheme famously foundered and the railway was abandoned in 1962. Proposals have been made for a new railway to link Mtwara to iron ore deposits in the west, perhaps linking via Songea to Liganga. [7]
A short 610 mm (2 ft) line lasted from 1879 to 1888. [8]


Formerly also called TanZam Railway.
1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) gauge to match Zambian/Southern African networks.

1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) and 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) are too close to allow 3-rail dual gauge; you have to have 4-rail dual gauge. But if you have 4-rail gauge, then you can include 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) gauge (standard gauge) at the cost of slightly longer sleepers.
The container port at Dar es Salaam is served by both 1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) and 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) railway gauge tracks. [12]
Transport in Tanzania includes road, rail, air and maritime networks. The road network is 86,472 kilometres (53,731 mi) long, of which 12,786 kilometres (7,945 mi) is classified as trunk road and 21,105 kilometres (13,114 mi) as regional road. The rail network consists of 3,682 kilometres (2,288 mi) of track. Commuter rail service is in Dar es Salaam only. There are 28 airports, with Julius Nyerere International being the largest and the busiest. Ferries connect Mainland Tanzania with the islands of Zanzibar. Several other ferries are active on the countries' rivers and lakes.
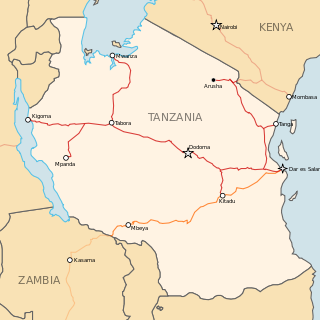
The Central Line, formerly known as the Tanganyika Railway is the most important railway line in Tanzania, apart from TAZARA. It runs west from Dar es Salaam to Kigoma on Lake Tanganyika via Dodoma. Extensions of the central route branch to the cities of Mwanza on Lake Victoria, Tanga, Singida and Mpanda.

The Catholic Church in Tanzania is part of the worldwide Catholic Church, under the spiritual leadership of the Pope in Rome.

Rail transport in Tanzania is conducted by two companies. It has historically used narrow gauge trackage, but planning and construction of new standard gauge lines is underway as of 2017.
Rail transport in Zambia is primarily provided by two systems:
The Tanzania FA Cup is the top knockout tournament of the Tanzanian football.
Kidatu is a town in central Tanzania, located in Kilombero District, Morogoro Region. The local population is about 3,300. The primary economic activity is the large Illovo sugar cane plantation and factory which produces 130,000 tonnes of sugar per year.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Tanzania:

Tanzania Ports Authority (TPA) is a parastatal public corporation acting under the aegis of the Ministry of Infrastructure Development, that has the responsibility "to manage and operate" the ocean ports and lake ports of the country of Tanzania. The Tanzania Ports Authority headquarters are located in Mchafukoge ward of Ilala District in Dar es Salaam Region. It is a member of the Port Management Association of Eastern and Southern Africa.
Exim Bank (Tanzania) (EBT), is a commercial bank in Tanzania, the second-largest economy in the East African Community. The bank is licensed by the Bank of Tanzania, which is the country's central bank and national banking regulator.

The Tanzania Railways Corporation(TRC) is a state-owned enterprise that runs one of Tanzania's two main railway networks. the Headquarters are located in Mchafukoge, Ilala District, Dar es Salaam Region.

Rail transport in Tanzania began in the late 19th century.
The Tanzanian Championship is the second tier of league football in Tanzania. The league is made up of sixteen teams that play thirty rounds, home and away.The league was formed in 1930.
The First League Tanzania is the third tier of league football in Tanzania. The league is divided into two groups, with each group having eight teams. A round-robin format is played and followed by a play-off tournament for promotion and relegation.
The Isaka–Kigali Standard Gauge Railway is a planned railway line linking the town of Isaka in Tanzania to the city of Kigali in Rwanda.

The Tanzania Standard Gauge Railway (SGR) is a railway system, under construction and partially in operation, serving Tanzania and linking it to the neighbouring countries of Rwanda, Uganda and Burundi, and through these to the Democratic Republic of the Congo, as part of the East African Railway Master Plan. The new, electrified standard gauge railway is intended to replace the outdated metre-gauge railway system.

The Tanzam Highway leads from Lusaka in Zambia to Dar es Salaam in Tanzania. The highway was built from 1968 to 1973 in several stages and was intended to provide seaport access for Zambia and to expand the transport options for Zambia, Malawi and the then Zaire.