There are a number of systems of transport in Burundi, including road and water-based infrastructure, the latter of which makes use of Lake Tanganyika. Furthermore, there are also some airports in Burundi.
Transport in Tanzania includes road, rail, air and maritime networks. The road network is 86,472 kilometres (53,731 mi) long, of which 12,786 kilometres (7,945 mi) is classified as trunk road and 21,105 kilometres (13,114 mi) as regional road. The rail network consists of 3,682 kilometres (2,288 mi) of track. Commuter rail service is in Dar es Salaam only. There are 28 airports, with Julius Nyerere International being the largest and the busiest. Ferries connect Mainland Tanzania with the islands of Zanzibar. Several other ferries are active on the countries' rivers and lakes.

Ujiji is the oldest town in western Tanzania and is located in Kigoma-Ujiji District of Kigoma Region. Originally a Swahili settlement and then an Arab slave trading post by the mid-nineteenth century nominally under the Sultanate of Zanzibar, the town is the oldest in western Tanzania. In 1900, the population was estimated at 10,000 and in 1967 about 41,000. The site is a registered National Historic Site.

Tabora is the capital of Tanzania's Tabora Region and is classified as a municipality by the Tanzanian government. It is also the administrative seat of Tabora Urban District. According to the 2012 census, the district had a population of 226,999.

Kigoma Region is one of Tanzania's 31 administrative regions, with the city of Kigoma as the reigonal capital. Kigoma Region borders Kagera Region, Geita Region, Katavi Region, Tabora Region, DRC and Burundi According to the 2012 national census, the region had a population of 2,127,930, which was higher than the pre-census projection of 1,971,332. For 2002–2012, the region's 2.4 percent average annual population growth rate was tied for the fourteenth highest in the country. It was also the sixteenth most densely populated region with 57 people per square kilometer. With a size of 45,066 square kilometres (17,400 sq mi), the region is slightly smaller than Estonia.
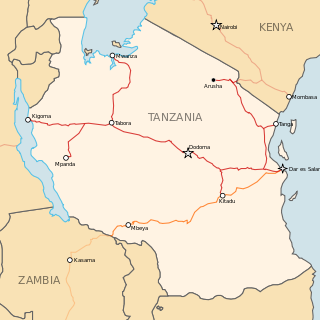
The Central Line, formerly known as the Tanganyika Railway is the most important railway line in Tanzania, apart from TAZARA. It runs west from Dar es Salaam to Kigoma on Lake Tanganyika via Dodoma. Extensions of the central route branch to the cities of Mwanza on Lake Victoria, Tanga, Singida and Mpanda.

MV Liemba, formerly Graf Goetzen or Graf von Goetzen, is a passenger and cargo ferry that runs along the eastern shore of Lake Tanganyika. The Marine Services Company Limited of Tanzania sails her, with numerous stops to pick up and set down passengers, between the ports of Kigoma, Tanzania and Mpulungu, Zambia.

Rail transport in Tanzania is conducted by two companies. It has historically used narrow gauge trackage, but planning and construction of new standard gauge lines is underway as of 2017.

Uvinza is one of the eight administrative districts of Kigoma Region in Tanzania. Uvinza is bordered to the northwest by Kigoma District and Kigoma-Ujiji District. North of the district is bordered by Kasulu District. Lake Tanganyika borders the district on the west. Mpanda District in Katavi Region borders the district to the south and Kaliua District in Tabora Region borders the district to the east. The district is named in honor of the Vinza people whom the western part of district was their historic kingdom. Southern Uvinza District is home to the Mahale Mountains National Park. A unique park that is home to both Chimpanzees and lions in the same habitat.
There are several planned railway lines in Rwanda, including a line to Tanzania. Historical railways are limited to three industrial railways.

Railway stations in Tanzania include:

Tanzania Ports Authority (TPA) is a parastatal public corporation acting under the aegis of the Ministry of Infrastructure Development, that has the responsibility "to manage and operate" the ocean ports and lake ports of the country of Tanzania. The Tanzania Ports Authority headquarters are located in Mchafukoge ward of Ilala District in Dar es Salaam Region. It is a member of the Port Management Association of Eastern and Southern Africa.

The Tanzania Railways Corporation(TRC) is a state-owned enterprise that runs one of Tanzania's two main railway networks. the Headquarters are located in Mchafukoge, Ilala District, Dar es Salaam Region.

Rail transport in Tanzania began in the late 19th century.

Marine Services Company Limited (MSCL) is a Tanzanian company that operates ferries, cargo ships and tankers on three of the African Great Lakes, namely Lake Victoria, Lake Tanganyika and Lake Nyasa. It provides services to neighbouring Burundi, DR Congo, Zambia and Malawi.

Katavi Region is one of Tanzania's 31 administrative regions. The region covers an area of 45,843 km2 (17,700 sq mi). The region is comparable in size to the combined land area of the nation state of Estonia. Katavi Region is bordered to the east by Tabora Region, and to the south by Rukwa Region and Songwe Region. Lastly, Katavi borders DRC on Lake Tanganyika to the west. The region derives its name from Katavi, the spirit of lake Tanganyika. The regional capital city is Mpanda. According to the 2022 national census, the region had a population of 1,152,958.

The Tanzania Standard Gauge Railway (SGR) is a railway system, under construction and partially in operation, serving Tanzania and linking it to the neighbouring countries of Rwanda, Uganda and Burundi, and through these to the Democratic Republic of the Congo, as part of the East African Railway Master Plan. The new, electrified standard gauge railway is intended to replace the outdated metre-gauge railway system.
The Uvinza–Musongati–Gitega Railway is a planned railway line linking the town of Uvinza in Tanzania to the city of Gitega in Burundi, passing through the town of Musongati, Burundi, close to the common border between the two countries.
The Port of Bujumbura is a port on Lake Tanganyika serving the city of Bujumbura, Burundi.
Société de l’Armement Nord des Grands Lacs , is a private company that operates a fleet of cargo boats on Lake Tanganyika. It is based in the Port of Bujumbura in Burundi.















