Transport in Tanzania includes road, rail, air and maritime networks. The road network is 86,472 kilometres (53,731 mi) long, of which 12,786 kilometres (7,945 mi) is classified as trunk road and 21,105 kilometres (13,114 mi) as regional road. The rail network consists of 3,682 kilometres (2,288 mi) of track. Commuter rail service is in Dar es Salaam only. There are 28 airports, with Julius Nyerere International being the largest and the busiest. Ferries connect Mainland Tanzania with the islands of Zanzibar. Several other ferries are active on the countries' rivers and lakes.

Dodoma, officially Dodoma City, is the capital of Tanzania and the administrative capital of both Dodoma Municipal Council and the entire Dodoma Region, with a population of 765,179. In 1974, the Tanzanian government announced that Tanzania's federal capital would be moved from Dar es Salaam to Dodoma for social and economic reasons and to centralise the capital within the country. It became the official capital in 1996.

Kigoma is a city and lake port in Kigoma-Ujiji District in Tanzania, on the northeastern shores of Lake Tanganyika and close to the border with Burundi and The Democratic Republic of the Congo. It serves as the capital for the surrounding Kigoma Region and has a population of 232,388. The city is situated at an elevation of 775 metres (2,543 ft).

Tabora is the capital of Tanzania's Tabora Region and is classified as a municipality by the Tanzanian government. It is also the administrative seat of Tabora Urban District. According to the 2012 census, the district had a population of 226,999.

Rukwa Region(Mkoa wa Rukwa in Swahili) is one of Tanzania's 31 administrative regions The region covers a land area of 27,765 km2 (10,720 sq mi), which is comparable in size to the combined land area of the nation state of Haiti. Rukwa Region is bordered to the north by Katavi Region, to the east by Songwe Region, to the south by the nation of Zambia and to the west by Lake Tanganyika, which forms a border between Tanzania and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The regional capital is the municipality of Sumbawanga. According to the 2022 national census, the region had a population of 1,540,519.

Mbeya is a city located in south west Tanzania, Africa, with an urban population of 649,000 in 2023. Mbeya is the capital of the surrounding rural Mbeya region.

Mbeya Region is one of Tanzania's 31 administrative regions. The region covers an area of 35,954 km2 (13,882 sq mi). The region is comparable in size to the combined land area of the nation state of Guinea Bissau. Mbeya Region is bordered to the east by Singida Region, Iringa Region and Njombe Region. The region is bordered to the south by Malawi and Lake Nyasa. To the north the region borders southern Tabora Region. Lastly, Mbeya is bordered to the west by Songwe Region. The regional capital is the city of Mbeya. According to the 2022 national census, the region had a population of 2,343,754.

Sikonge District is one of the seven districts of the Tabora Region of Tanzania. The town of Sikonge is the administrative seat. The district has an area of 27,873 square kilometres (10,762 sq mi), but 26,834 square kilometres (10,361 sq mi) of it is in forest and game reserves. It is bordered to the northwest by Urambo District, to the north by Uyui District, to the east by Manyoni District of Singida Region, to the south by Chunya District of Mbeya Region, and to the southwest by Mlele District of Katavi Region.

Tabora Urban is one of the seven districts in the Tabora Region of Tanzania. This district is mostly the city of Tabora and its suburbs. It is bordered almost completely by the Uyui District. It has a small border with Nzega District to the north. Its administrative seat is the city of Tabora.
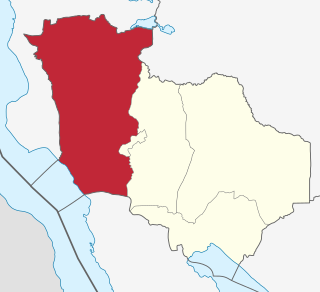
Mpanda District is one of the five districts of the Katavi Region of Tanzania. Its administrative seat is the city of Mpanda. The district is bordered to the northwest by the Kigoma Region, to the northeast by the Tabora Region, to the east by the Mbeya Region, to the southeast by the Sumbawanga Urban District, to the southwest by the Nkasi District and to the west by Lake Tanganyika.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Tanzania:

Makambako is a medium-sized town and district in the Njombe Region of the Tanzanian Southern Highlands, located roughly 40 miles north of Njombe city by road. It is located at junction of the A104 and B4 roads between Njombe, Iringa, and Mbeya. Its population according to the 2002 Tanzanian census was 51,049.
Mpanda is a city in Katavi Region of Tanzania, East Africa with a postcode number 50100. It is the administrative centre of Katavi Region, Mpanda District and is itself one of the four districts of the region.

Katavi Region is one of Tanzania's 31 administrative regions. The region covers an area of 45,843 km2 (17,700 sq mi). The region is comparable in size to the combined land area of the nation state of Estonia. Katavi Region is bordered to the east by Tabora Region, and to the south by Rukwa Region and Songwe Region. Lastly, Katavi borders DRC on Lake Tanganyika to the west. The region derives its name from Katavi, the spirit of lake Tanganyika. The regional capital city is Mpanda. According to the 2022 national census, the region had a population of 1,152,958.
FPCT Tumaini Secondary School, is the private school located in the Southern part of Tanzania in Katavi region, formerly Rukwa Region.
The Ufipa Plateau is a highland in southwestern Tanzania. It lies mostly in Rukwa Region, near the border with Zambia. The plateau is named for the Fipa people who inhabit it.
The Iringa–Sumbawanga High Voltage Power Line, also Iringa–Mbeya–Tunduma–Sumbawanga High Voltage Power Line, is a high voltage electricity power line, under development in Tanzania. The 400 kiloVolts power line will connect the high voltage substation at Iringa, to another high voltage substation at Sumbawanga.

Mpimbwe District is a district council in the Katavi Region of Tanzania's Southern Highlands established in 2012. The district lies in the south of the region on Lake Rukwa.

Nsimbo District is a district council in the Katavi Region of Tanzania's Southern Highlands established in 2012. The district lies in the middle of the region east of the city of Mpanda. It is a tropical environment of mostly forest reserves and agricultural economy.