Animism is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct spiritual essence. Animism perceives all things—animals, plants, rocks, rivers, weather systems, human handiwork, and in some cases words, as animated and alive. Animism is used in anthropology of religion as a term for the belief system of many Indigenous peoples, in contrast to the relatively more recent development of organized religions. Animism focuses on the metaphysical universe, with a specific focus on the concept of the immaterial soul.

The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic, also called the Old Stone Age, is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehistoric technology. It extends from the earliest known use of stone tools by hominins, c. 3.3 million years ago, to the end of the Pleistocene, c. 11,650 cal BP.

Sex is the trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing organism produces male or female gametes. Male plants and animals produce small mobile gametes, while females produce larger, non-motile ones. Organisms that produce both types of gametes are called hermaphrodites. During sexual reproduction, male and female gametes fuse to form zygotes, which develop into offspring that inherit traits from each parent.

Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with the spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritual energies into the physical world for the purpose of healing, divination, or to aid human beings in some other way.

Inuit religion is the shared spiritual beliefs and practices of the Inuit, an indigenous people from Alaska, northern Canada, parts of Siberia and Greenland. Their religion shares many similarities with some Alaska Native religions. Traditional Inuit religious practices include animism and shamanism, in which spiritual healers mediate with spirits. Today many Inuit follow Christianity, but traditional Inuit spirituality continues as part of a living, oral tradition and part of contemporary Inuit society. Inuit who balance indigenous and Christian theology practice religious syncretism.

Isobel Gowdie was a Scottish woman who confessed to witchcraft at Auldearn near Nairn during 1662. Scant information is available about her age or life and, although she was probably executed in line with the usual practice, it is uncertain whether this was the case or if she was allowed to return to the obscurity of her former life as a cottar’s wife. Her detailed testimony, apparently achieved without the use of violent torture, provides one of the most comprehensive insights into European witchcraft folklore at the end of the era of witch-hunts.

In European folklore of the medieval and early modern periods, familiars were believed to be supernatural entities that would assist witches and cunning folk in their practice of magic. According to records of the time, those alleging to have had contact with familiar spirits reported that they could manifest as numerous forms, usually as an animal, but sometimes as a human or humanoid figure, and were described as "clearly defined, three-dimensional... forms, vivid with colour and animated with movement and sound", as opposed to descriptions of ghosts with their "smoky, undefined form[s]".

Vijayadashami, also known as Dussehra, Dasara or Dashain, is a major Hindu festival celebrated every year at the end of Navaratri. It is observed on the tenth day of the month of Ashvin, the seventh in the Hindu Luni-Solar Calendar. The festival which typically falls in the Gregorian calendar months of September and October.

Guy Fawkes Night, also known as Guy Fawkes Day, Bonfire Night and Fireworks Night, is an annual commemoration observed on 5 November, primarily in Great Britain, involving bonfires and fireworks displays. Its history begins with the events of 5 November 1605 O.S., when Guy Fawkes, a member of the Gunpowder Plot, was arrested while guarding explosives the plotters had placed beneath the House of Lords. The Catholic plotters had intended to assassinate Protestant king James I and his parliament. Celebrating that the king had survived, people lit bonfires around London; and months later, the Observance of 5th November Act mandated an annual public day of thanksgiving for the plot's failure.

Brugmansia is a genus of seven species of flowering plants in the nightshade family Solanaceae. They are woody trees or shrubs, with pendulous flowers, and have no spines on their fruit. Their large, fragrant flowers give them their common name of angel's trumpets, a name sometimes used for the closely related genus Datura.
Sympathetic magic, also known as imitative magic, is a type of magic based on imitation or correspondence.

Filipino witches are the users of black magic and related practices from the Philippines. They include a variety of different kinds of people with differing occupations and cultural connotations which depend on the ethnic group they are associated with. They are completely different from the Western notion of what a witch is, as each ethnic group has their own definition and practices attributed to witches. The curses and other magics of witches are often blocked, countered, cured, or lifted by Filipino shamans associated with the indigenous Philippine folk religions.
Nature worship also called naturism or physiolatry is any of a variety of religious, spiritual and devotional practices that focus on the worship of the nature spirits considered to be behind the natural phenomena visible throughout nature. A nature deity can be in charge of nature, a place, a biotope, the biosphere, the cosmos, or the universe. Nature worship is often considered the primitive source of modern religious beliefs and can be found in pantheism, panentheism, deism, polytheism, animism, totemism, shamanism, some theism and paganism including Wicca. Common to most forms of nature worship is a spiritual focus on the individual's connection and influence on some aspects of the natural world and reverence towards it. Due to their admiration of nature, the works of Edmund Spenser, Anthony Ashley-Cooper and Carl Linnaeus were viewed as nature worship.
Neoshamanism refers to new forms of shamanism. It usually means shamanism practiced by Western people as a type of New Age spirituality, without a connection to traditional shamanic societies. It is sometimes also used for modern shamanic rituals and practices which, although they have some connection to the traditional societies in which they originated, have been adapted somehow to modern circumstances. This can include "shamanic" rituals performed as an exhibition, either on stage or for shamanic tourism, as well as modern derivations of traditional systems that incorporate new technology and worldviews.

A large minority of people in North Asia, particularly in Siberia, follow the religio-cultural practices of shamanism. Some researchers regard Siberia as the heartland of shamanism.

Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from 8.5 micrometres (0.00033 in) to 33.6 metres (110 ft). They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology.

Inuit art, also known as Eskimo art, refers to artwork produced by Inuit, that is, the people of the Arctic previously known as Eskimos, a term that is now often considered offensive. Historically, their preferred medium was walrus ivory, but since the establishment of southern markets for Inuit art in 1945, prints and figurative works carved in relatively soft stone such as soapstone, serpentinite, or argillite have also become popular.

Navaratri is an annual Hindu festival observed in the honour of the goddess Ambika and Durga. It spans over nine nights, first in the month of Chaitra, and again in the month of Sharada. It is observed for different reasons and celebrated differently in various parts of the Hindu Indian cultural sphere.
The San religion is the traditional religion and mythology of the San people. It is poorly attested due to their interactions with Christianity.
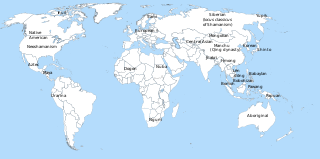
Shamanism is a religious practice present in various cultures and religions around the world. Shamanism takes on many different forms that vary greatly by region and culture, shaped by the distinct histories of its practitioners.















