
Inuit religion is the shared spiritual beliefs and practices of the Inuit, an indigenous people from Alaska, northern Canada, parts of Siberia and Greenland. Their religion shares many similarities with some Alaska Native religions. Traditional Inuit religious practices include animism and shamanism, in which spiritual healers mediate with spirits. Today many Inuit follow Christianity, but traditional Inuit spirituality continues as part of a living, oral tradition and part of contemporary Inuit society. Inuit who balance indigenous and Christian theology practice religious syncretism.
In Inuit mythology, Issitoq is a deity that punishes those who break taboos. He usually takes the form of a giant flying eye.

The Sun and the Moon is an unipkaaqtuat, a story in Inuit folklore. The traditional explanation for the movement of the Sun and Moon through the sky is a brother and sister are constantly chasing each other across the sky. The story also explains the dappled gray appearance of the Moon as soot smeared on his face.
In Inuit mythology, an inua is a spirit or soul that exists in all people, animals, lakes, mountains, and plants. This is not an individual soul, but rather "the vital force representing a chain or continuum of all the individual spirits of that genus which had lived, were living, or were to live."

Sedna is the goddess of the sea and marine animals in Inuit mythology, also known as the Mother of the Sea or Mistress of the Sea. The story of Sedna, which is a creation myth, describes how she came to rule over Adlivun, the Inuit underworld.
In Inuit religion, Silap Inua or Sila is similar to mana or ether, the primary component of everything that exists; it is also the breath of life and the method of locomotion for any movement or change. Silla was believed to control everything that goes on in one's life.
In Inuit mythology, Alignak is a lunar deity and god of weather, water, tides, eclipses, and earthquakes.

Chandra, also known as Soma, is the Hindu god of the Moon, and is associated with the night, plants and vegetation. He is one of the Navagraha and Dikpala.

Numen is a Latin term for "divinity", "divine presence", or "divine will." The Latin authors defined it as follows: Cicero writes of a "divine mind", a god "whose numen everything obeys," and a "divine power" "which pervades the lives of men." It causes the motions and cries of birds during augury. In Virgil's recounting of the blinding of the one-eyed giant, Polyphemus, from the Odyssey, in his Aeneid, he has Odysseus and his men first "ask for the assistance of the great numina". Reviewing public opinion of Augustus on the day of his funeral, the historian Tacitus reports that some thought "no honor was left to the gods" when he "established the cult of himself" "with temples and the effigies of numina". Pliny the Younger in a letter to Paternus raves about the "power," the "dignity," and "the majesty;" in short, the "numen of history." Lucretius uses the expression numen mentis, or "bidding of the mind," where "bidding" is numen, not, however, the divine numen, unless the mind is to be considered divine, but as simply human will.

Tarqeq, also known as Saturn LII is a natural satellite of Saturn. Its discovery was announced by Scott S. Sheppard, David C. Jewitt, Jan Kleyna, and Brian G. Marsden on 13 April 2007 from observations taken between 5 January 2006 and 22 March 2007. It is named after Tarqeq, the Inuit moon god, and is a member of the Inuit group of irregular satellites. It is about seven kilometres in diameter. The Cassini spacecraft observed Tarqeq over 1.5 days on 15–16 January 2014.

The Netsilik (Netsilingmiut) are Inuit who live predominantly in Kugaaruk and Gjoa Haven of the Kitikmeot Region, Nunavut and to a smaller extent in Taloyoak and the north Qikiqtaaluk Region, in Canada. They were, in the early 20th century, among the last northern indigenous peoples to encounter missionaries from the south.

The goddess Chía, is a triple lunar deity in the religion of the Muisca who inhabited the Altiplano Cundiboyacense in pre-Columbian times. Of central importance to the pantheon, she was worshipped across various Muisca lands.
Larry Beck, full name Lawrence James Beck, was an American sculptor born in Seattle, Washington. Beck was one quarter Native Alaskan, a cause of both conflict and inspiration during his career. His work ranged from industrial assemblages and happenings in the 60's to large, abstract public commissions in the 70's to Yup'ik masks inspired by traditional Yup'ik pieces, but rendered with modern industrial and manufactured materials which he began in the 80's and was working on up until his death.
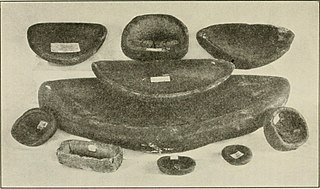
The qulliq, is the traditional oil lamp used by Arctic peoples, including the Inuit, the Chukchi and the Yupik peoples.

Uvavnuk was an Inuk woman born in the 19th century, now considered an oral poet. The story of how she became an angakkuq, and the song that came to her, were collected by European explorers of Arctic Canada in the early 1920s. Her shamanistic poem-song, best known as "Earth and the Great Weather", has been anthologised many times.
Central Inuit are the Inuit of Northern Canada, their designation determined by geography and their tradition of snowhouses ("igloos"), fur clothing, and sled dogs. They are differentiated from Alaska's Iñupiat, Greenland's Kalaallit, and Russian Inuit. Central Inuit are subdivided into smaller groupings which include the Caribou, Netsilik, Iglulik, and Baffinland Inuit. Though Copper Inuit are geographically located in the central Arctic, they are considered to be socially and ideologically distinct from the Central Inuit.

A lunar deity or moon deity is a deity who represents the Moon, or an aspect of it. These deities can have a variety of functions and traditions depending upon the culture, but they are often related. Lunar deities and Moon worship can be found throughout most of recorded history in various forms.
Sun and Moon, The Sun and the Moon, or variants may refer to:
Idlirvirissong, or Irdlirvirisissong, is an evil spirit in the religion of the Inuit of Baffin Island and the Greenlandic Inuit.









