A lunar calendar is a calendar based on the monthly cycles of the Moon's phases, in contrast to solar calendars, whose annual cycles are based on the solar year. The most widely observed purely lunar calendar is the Islamic calendar. A purely lunar calendar is distinguished from a lunisolar calendar, whose lunar months are brought into alignment with the solar year through some process of intercalation – such as by insertion of a leap month. The details of when months begin vary from calendar to calendar, with some using new, full, or crescent moons and others employing detailed calculations.

Renewable energy is energy from renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind power and hydropower. Bioenergy and geothermal power are also significant in some countries. Some also consider nuclear power a renewable power source, although this is controversial. Renewable energy installations can be large or small and are suited for both urban and rural areas. Renewable energy is often deployed together with further electrification. This has several benefits: electricity can move heat and vehicles efficiently, and is clean at the point of consumption. Variable renewable energy sources are those that have a fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power. In contrast, controllable renewable energy sources include dammed hydroelectricity, bioenergy, or geothermal power.

The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light and infrared radiation with 10% at ultraviolet energies. It is by far the most important source of energy for life on Earth. The Sun has been an object of veneration in many cultures. It has been a central subject for astronomical research since antiquity.

The Solar System is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It was formed about 4.6 billion years ago when a dense region of a molecular cloud collapsed, forming the Sun and a protoplanetary disc. The Sun is a typical star that maintains a balanced equilibrium by the fusion of hydrogen into helium at its core, releasing this energy from its outer photosphere. Astronomers classify it as a G-type main-sequence star.

Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar power to generate electricity, solar thermal energy, and solar architecture. It is an essential source of renewable energy, and its technologies are broadly characterized as either passive solar or active solar depending on how they capture and distribute solar energy or convert it into solar power. Active solar techniques include the use of photovoltaic systems, concentrated solar power, and solar water heating to harness the energy. Passive solar techniques include orienting a building to the Sun, selecting materials with favorable thermal mass or light-dispersing properties, and designing spaces that naturally circulate air.

Sunlight is a portion of the electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun, in particular infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light. On Earth, sunlight is scattered and filtered through Earth's atmosphere as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon. When direct solar radiation is not blocked by clouds, it is experienced as sunshine, a combination of bright light and radiant heat (Atmospheric). When blocked by clouds or reflected off other objects, sunlight is diffused. Sources estimate a global average of between 164 watts to 340 watts per square meter over a 24-hour day; this figure is estimated by NASA to be about a quarter of Earth's average total solar irradiance.
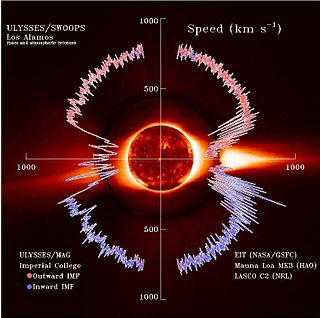
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between 0.5 and 10 keV. The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of materials found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei of elements such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon, sulfur, and iron. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as phosphorus, titanium, chromium, and nickel's isotopes 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superimposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field. The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface.

Voyager 1 is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and the interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. It was launched 16 days after its twin, Voyager 2. It communicates through the NASA Deep Space Network (DSN) to receive routine commands and to transmit data to Earth. Real-time distance and velocity data are provided by NASA and JPL. At a distance of 162.7 AU from Earth as of May 2024, it is the most distant humanmade object from Earth. The probe made flybys of Jupiter, Saturn, and Saturn's largest moon, Titan. NASA had a choice of either doing a Pluto or Titan flyby; exploration of the moon took priority because it was known to have a substantial atmosphere. Voyager 1 studied the weather, magnetic fields, and rings of the two gas giants and was the first probe to provide detailed images of their moons.

A solar flare is a relatively intense, localized emission of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other eruptive solar phenomena. The occurrence of solar flares varies with the 11-year solar cycle.

The solar mass (M☉) is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately 2×1030 kg. It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. This equates to about two nonillion (short scale), two quintillion (long scale) kilograms or 2000 quettagrams:

The solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a nearly periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun's surface. Over the period of a solar cycle, levels of solar radiation and ejection of solar material, the number and size of sunspots, solar flares, and coronal loops all exhibit a synchronized fluctuation from a period of minimum activity to a period of a maximum activity back to a period of minimum activity.
The solar luminosity (L☉) is a unit of radiant flux conventionally used by astronomers to measure the luminosity of stars, galaxies and other celestial objects in terms of the output of the Sun.

Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially used for electricity generation and as photosensors.

Solar irradiance is the power per unit area received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument. Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre (W/m2) in SI units.

A solar cell or photovoltaic cell is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by means of the photovoltaic effect. It is a form of photoelectric cell, a device whose electrical characteristics vary when it is exposed to light. Individual solar cell devices are often the electrical building blocks of photovoltaic modules, known colloquially as "solar panels". Almost all commercial PV cells consist of crystalline silicon, with a market share of 95%. Cadmium telluride thin-film solar cells account for the remainder. The common single-junction silicon solar cell can produce a maximum open-circuit voltage of approximately 0.5 to 0.6 volts.

A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electricity by using photovoltaic (PV) cells. PV cells are made of materials that produce excited electrons when exposed to light. The electrons flow through a circuit and produce direct current (DC) electricity, which can be used to power various devices or be stored in batteries. Solar panels are also known as solar cell panels, solar electric panels, or PV modules.

A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs approximately every six months, during the eclipse season in its new moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to the plane of Earth's orbit. In a total eclipse, the disk of the Sun is fully obscured by the Moon. In partial and annular eclipses, only part of the Sun is obscured. Unlike a lunar eclipse, which may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth, a solar eclipse can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world. As such, although total solar eclipses occur somewhere on Earth every 18 months on average, they recur at any given place only once every 360 to 410 years.

A small Solar System body (SSSB) is an object in the Solar System that is neither a planet, a dwarf planet, nor a natural satellite. The term was first defined in 2006 by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) as follows: "All other objects, except satellites, orbiting the Sun shall be referred to collectively as 'Small Solar System Bodies'".

India's solar power installed capacity was 81.813 GWAC as of 31 March 2024. India is the third largest producer of solar power globally.

Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to convert light into an electric current. Concentrated solar power systems use lenses or mirrors and solar tracking systems to focus a large area of sunlight to a hot spot, often to drive a steam turbine.


















