
Athens is the capital and largest city of Greece. A major coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica region and is the southernmost capital on the European mainland. With its urban area's population numbering over three and a quarter million, it is the eighth largest urban area in the European Union. The Municipality of Athens, which constitutes a small administrative unit of the entire urban area, had a population of 643,452 (2021) within its official limits, and a land area of 38.96 km2 (15.04 sq mi).

Megalopoli is a town in the southwestern part of the regional unit of Arcadia, southern Greece. It is located in the same site as ancient Megalopolis. When it was founded in 371 BC, it was the first large urbanization in rustic Arcadia. Its theater had a capacity of 20,000 visitors, making it one of the largest ancient Greek theaters.
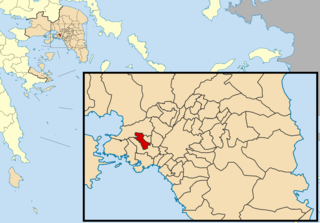
Phthiotis is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the administrative region of Central Greece. The capital is the city of Lamia. It is bordered by the Malian Gulf to the east, Boeotia in the south, Phocis in the south, Aetolia-Acarnania in the southwest, Evrytania in the west, Karditsa regional unit in the north, Larissa regional unit in the north, and Magnesia in the northeast. The name dates back to ancient times. It is best known as the home of Achilles.
Korydallos is both a town and a municipality in the Piraeus regional unit, Greece. It is located in the southwestern part of Athens agglomeration.

Agrinio is the largest city of the Aetolia-Acarnania regional unit of Greece and its largest municipality, with 89,691 inhabitants (2021) as well as the second largest city in Western Greece after Patras. It is the economic center of Aetolia-Acarnania, although its capital is the town of Mesolonghi. The settlement dates back to ancient times. Ancient Agrinion was 3 kilometres northeast of the present city; some walls and foundations of which have been excavated. In medieval times and until 1836, the city was known as Vrachori (Βραχώρι).

Dion is a village and municipal unit in the municipality of Dion-Olympos in the Pieria regional unit, Greece. It is located at the foot of Mount Olympus at a distance of 17 km from the capital city of Katerini.

Nea Smyrni is a municipality and a town in South Athens, Greece. At the 2021 census, it had 72,853 inhabitants. It was named after the former Greek city Smyrna, whence many refugees arrived and settled in the Nea Smyrni area following the 1922 catastrophe of Asia Minor and the Burning of Smyrna which left big parts of the city's christian population massacred by Turkish mobs and military, during the Greco-Turkish war.

Troezen is a small town and a former municipality in the northeastern Peloponnese, Greece, on the Argolid Peninsula. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Troizinia-Methana, of which it is a municipal unit. It is part of the Islands regional unit. Population 4,668 (2021).
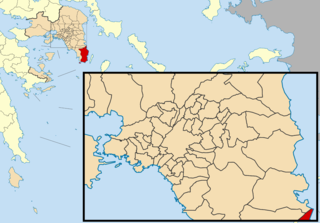
Lavreotiki is a municipality at the southeasternnmost tip of the Attica peninsula in the Greek regional unit of East Attica. Its municipal seat is the town of Laurium (Lavrio).

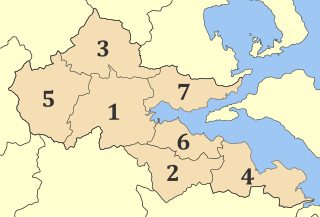
Kleitoria is a village and a municipal unit in Achaea, Peloponnese, Greece. It was also the new name of the former municipality Lefkasio, of which it was the seat, between 2008 and 2011. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Kalavryta, and became a municipal unit of this municipality. The municipal unit has an area of 253.221 km2. The site of the ancient city of Cleitor is nearby.

Kalloni is a town in the west-central part of the island of Lesbos, Greece. It is the seat of the West Lesbos municipality and the Kalloni municipal unit within it. Prior to 2011 the current municipal unit was a municipality. The name also existed in ancient times, though the conventional transcription of the classical name in English is "Callone".

Visaltia is a municipality in the Serres regional unit, Greece. The seat of the municipality is in Nigrita. It was named after the ancient region Bisaltia. The ancient city of Berge is located here.

The Ladon Lake or the Ladon Reservoir is an artificial lake in the upper part of the river Ladon, in the northwestern part of Arcadia, Greece. The 50 m high dam was built in 1955. The reservoir is situated in a sparsely populated, mountainous area. It is completely in the municipality Gortynia, municipal units Kleitor, Kontovazaina and Tropaia.

Sparta is a city and municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. It lies at the site of ancient Sparta within the Evrotas Valley. The municipality was merged with six nearby municipalities in 2011, for a total population of 32,786, of whom 17,773 lived in the city.
Skotani, is a small mountain village and a community in the municipal unit of Paia, Achaea, Greece. The community includes the village Agios Georgios. Skotani is 5 km east of Chovoli, 7 km northeast of Dafni, 7 km southwest of Kleitoria and 20 km south of Kalavryta. Its elevation is about 700 m above sea level.
Paos is a village and a community in Achaea, Greece. It is part of the municipal unit of Paia. The community includes the small villages Dechounaiika, Palaios Paos, Potamia and Vesini. It is 25 km southwest of Kalavryta, and 50 km northwest of Tripoli. The Greek National Road 33 passes through the village. Its central road is named "111".
Thaliades was a town in Arcadian Azania in ancient Greece, situated on the river Ladon between the towns Halus and Thelpusa. There was a temple of Eleusinian Demeter, with statues of Demeter, her daughter and Dionysos. It was part of the city-state of Kleitor. The ruins that have been found 1 km west of Vachlia are believed to be the remains of Thaliades.

Pournaria is a village and a community in the municipal unit of Kleitor, Arcadia, Greece. In 2021, it had a population of 93. The community includes the village Mouria. Pournaria is situated on a hillside, at 500 m elevation. Mouria is 3 km to the southwest of Pournaria, on the northern shore of the Ladon reservoir. Pournaria is 9 km northeast of Tropaia, 10 km southeast of Paos and 42 km northwest of Tripoli.
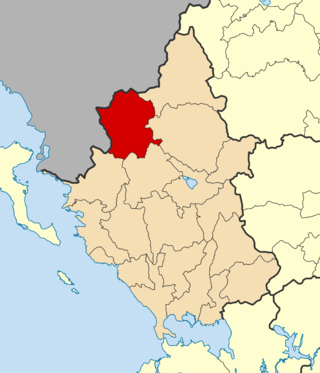
Pogoni is a municipality in the Ioannina regional unit, Epirus, Greece. The seat of the municipality is the village Kalpaki. The municipality has an area of 701.059 km2. Its population was 6,848 at the 2021 census.

Paionia is a municipality in the Kilkis regional unit of Central Macedonia, Greece. The seat of the municipality is the town Polykastro. The municipality is named after the ancient region of Paeonia. It has an area of 919.276 km2.

















