Related Research Articles

James Ross Island is a large island off the southeast side and near the northeastern extremity of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which it is separated by Prince Gustav Channel. Rising to 1,630 metres (5,350 ft), it is irregularly shaped and extends 64 km in a north–south direction. It was charted in October 1903 by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskiöld, who named it for Sir James Clark Ross, the leader of a British expedition to this area in 1842 that discovered and roughly charted a number of points along the eastern side of the island. The style, "James" Ross Island is used to avoid confusion with the more widely known Ross Island in McMurdo Sound.

The Prince Charles Mountains are a major group of mountains in Mac. Robertson Land in Antarctica, including the Athos Range, the Porthos Range, and the Aramis Range. The highest peak is Mount Menzies, with a height of 3,228 m (10,591 ft). Other prominent peaks are Mount Izabelle and Mount Stinear. These mountains, together with other scattered peaks, form an arc about 420 km (260 mi) long, extending from the vicinity of Mount Starlight in the north to Goodspeed Nunataks in the south.

Barilari Bay is a bay 12 nautical miles (22 km) long and 6 nautical miles (11 km) wide, between Cape Garcia and Loqui Point on the west coast of Graham Land. The glaciers Birley, Lawrie, Weir and Bilgeri feed the bay.

Brand Peak is a sharp snow-covered peak located 10 nautical miles (19 km) east-southeast of the Eternity Range and 4 nautical miles (7 km) northwest of Mount Duemler, in Palmer Land. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey in 1974, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Timothy Brand, a United States Antarctic Research Program biologist at Palmer Station in 1974.

Deadmond Glacier is a glacier about 6 nautical miles (11 km) long, flowing from the east side of Evans Peninsula on Thurston Island into Cadwalader Inlet. It was discovered by the U.S. Navy Bellingshausen Sea Expedition in February 1960, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Lieutenant Commander Robert B. Deadmond, executive officer of USS Burton Island, forming part of this expedition.
The Journal Peaks are two groups of separated peaks and nunataks which trend east–west for about 8 nautical miles (15 km). They rise 17 nautical miles (31 km) southeast of the Seward Mountains in central Palmer Land, Antarctica. The peaks were mapped by the United States Geological Survey from U.S. Navy aerial photography, 1966–69, and were named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names after the Antarctic Journal of the United States, established 1966, a publication of the Division of Polar Programs, National Science Foundation, reporting on the U.S. Antarctic Research Program and related activities.
Detour Island is an island lying 2.5 nautical miles (5 km) west of False Cape Renard, on the west side of Lemaire Channel in the Wilhelm Archipelago. It was first charted by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1903–05, under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, and was so named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1959 because the island lies near the entrance to the ships' passage west of Booth Island which provides an alternative route to Lemaire Channel when the latter is blocked by ice.
Guido Island is an island lying 1 nautical mile (2 km) northeast of Prioress Island in the Wauwermans Islands, in the Wilhelm Archipelago, Antarctica. It was shown on an Argentine government chart of 1950; the name "Isla Guido Spano" appears on a 1957 chart and is for Carlos Guido Spano (1829–1918), a famous Argentine poet.
Grimley Glacier is a tributary glacier, 15 nautical miles (28 km) long and 3 nautical miles (6 km) wide, lying 3 nautical miles north of Sunfix Glacier and flowing east-northeast into Casey Glacier in northern Palmer Land, Antarctica. The glacier was photographed from the air by the United States Antarctic Service on September 28, 1940, and by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition on December 22, 1947. It was surveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in December 1960 and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Peter H. Grimley of FIDS, a geologist at Horseshoe Island and Stonington Island in 1960.
Dobrowolski Island is a small island which lies close to the east coast of Anvers Island, 3 nautical miles (6 km) southwest of Ryswyck Point, in the Palmer Archipelago. It was charted in 1927 by Discovery Investigations personnel on the Discovery, who gave the name "Astrolabe Island". To avoid duplication, the name was changed in 1958 by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee, and the island is now named after Antoni B. Dobrowolski, assistant meteorologist of the Belgian Antarctic Expedition which explored this area in 1898.
Picnic Passage is a marine channel, 1.5 nautical miles (2.8 km) long and 0.5 nautical miles (0.9 km) wide, between Snow Hill Island and Seymour Island in the James Ross Island group. First surveyed in 1902 by Swedish Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Otto Nordenskjold. The United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) name arose from the excellent sledging conditions experienced during the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) resurveying of the area of 1952, which gave to the work a picnic-like atmosphere.
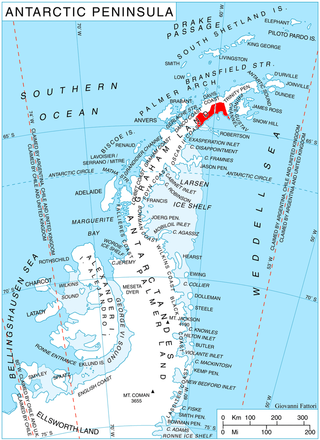
Edgeworth Glacier is a glacier 12 nautical miles (22 km) long, flowing south-southwestwards from the edge of Detroit Plateau below Wolseley Buttress and Paramun Buttress between Trave Peak and Chipev Nunatak into Mundraga Bay west of Sobral Peninsula, on the Nordenskjöld Coast of Graham Land. It was mapped from surveys by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (1960–61), and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Richard Lovell Edgeworth, the British inventor of the "portable railway," the first track-laying vehicle, in 1770.
The Förster Cliffs are a set of cliffs located east-northeast of Stark Point, running east–west for 2 nautical miles (4 km) and rising to 550 metres (1,800 ft) in northern James Ross Island. They were named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1987 after Reinhard Förster (1935–87), a West German geologist from the University of Munich, who was a member of the British Antarctic Survey field party to the area, 1985–86.
Loaf Rock is a rock lying 3 nautical miles (6 km) west of Biscoe Point, off the southwest coast of Anvers Island in the Palmer Archipelago, Antarctica. It was surveyed by the British Naval Hydrographic Survey Unit in 1956–57, and was so named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1958 because the rock is shaped like a flat loaf of bread.

Hauken Rock is a rock lying nearly 1 nautical mile (2 km) east of the Ornen Rocks and 2 nautical miles (4 km) northeast of Cape Melville, the eastern extremity of King George Island, in the South Shetland Islands. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1960 from association with Ornen Rocks. Hauken and Ørnen, the first two modern whale catchers, accompanied the floating factory ship Admiralen to the South Shetland Islands in January–February 1906.
The Hellerman Rocks are a group of seven small islets and rocks connected by a shoal, located 0.4 nautical miles (0.7 km) east of Hermit Island, off the southwest coast of Anvers Island, Antarctica. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Lieutenant Lance W. Hellerman of the U.S. Navy Reserve, Officer-in-Charge of Palmer Station in 1969.
McClary Ridge is a small, crescent-shaped ridge 5 nautical miles (9 km) south-southeast of Mount Hayes on the south side of Cole Peninsula in Graham Land, Antarctica. In December 1947 it was charted by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey and was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition under Finn Ronne. It was named by Ronne for George B. McClary of Winnetka, Illinois, a contributor to the expedition.

Lemaire Island is an island 4.5 nautical miles (8 km) long and 1.5 nautical miles (3 km) wide, lying 1 nautical mile (2 km) west of Duthiers Point off the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was discovered by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition, 1897–99, under Adrien de Gerlache, who named it for Charles Antoine Lemaire. The island is bordered by the Aguirre Passage which separates it from the Danco Coast.
References
- ↑ "Knight Island". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior . Retrieved 10 May 2013.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Knight Island". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Knight Island". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.