
In physics, angular momentum is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important quantity in physics because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Motorcycles, frisbees and rifled bullets all owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes have spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system but does not uniquely determine it.

The lion is a large cat of the genus Panthera native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, deep-chested body, short, rounded head, round ears, and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphic; adult male lions are larger than females and have a prominent mane. It is a social species, forming groups called prides. A lion's pride consists of a few adult males, related females, and cubs. Groups of female lions usually hunt together, preying mostly on large ungulates. The lion is an apex and keystone predator; although some lions scavenge when opportunities occur and have been known to hunt humans, the species typically does not.

In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmission must be taken into account. This applies especially to radio-frequency engineering because the short wavelengths mean that wave phenomena arise over very short distances. However, the theory of transmission lines was historically developed to explain phenomena on very long telegraph lines, especially submarine telegraph cables.

In electrical engineering, impedance is the opposition to alternating current presented by the combined effect of resistance and reactance in a circuit.

Snell's law is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing through a boundary between two different isotropic media, such as water, glass, or air. The law is named for Willebrord Snellius, a Dutch astronomer and mathematician, known in the English world as Snell.

Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. Introducing the constant of proportionality, the resistance, one arrives at the usual mathematical equation that describes this relationship:
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by , , or .

The Ford Mustang is a series of American automobiles manufactured by Ford. In continuous production since 1964, the Mustang is currently the longest-produced Ford car nameplate. Currently in its sixth generation, it is the fifth-best selling Ford car nameplate. The namesake of the "pony car" automobile segment, the Mustang was developed as a highly styled line of sporty coupes and convertibles derived from existing model lines, initially distinguished by "long hood, short deck" proportions.

Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The flow of electric current creates a magnetic field around the conductor. The field strength depends on the magnitude of the current, and follows any changes in current. From Faraday's law of induction, any change in magnetic field through a circuit induces an electromotive force (EMF) (voltage) in the conductors, a process known as electromagnetic induction. This induced voltage created by the changing current has the effect of opposing the change in current. This is stated by Lenz's law, and the voltage is called back EMF.

The straight-six engine is an internal combustion engine, with six cylinders mounted in a straight line along the crankcase with all the pistons driving a common crankshaft.

Two-terminal components and electrical networks can be connected in series or parallel. The resulting electrical network will have two terminals, and itself can participate in a series or parallel topology. Whether a two-terminal "object" is an electrical component or an electrical network is a matter of perspective. This article will use "component" to refer to a two-terminal "object" that participate in the series/parallel networks.
Molar concentration is a measure of the concentration of a chemical species, in particular of a solute in a solution, in terms of amount of substance per unit volume of solution. In chemistry, the most commonly used unit for molarity is the number of moles per liter, having the unit symbol mol/L or mol⋅dm−3 in SI unit. A solution with a concentration of 1 mol/L is said to be 1 molar, commonly designated as 1 M. To avoid confusion with SI prefix mega, which has the same abbreviation, small caps ᴍ or italicized M are also used in journals and textbooks.

Bloomberg L.P. is a privately held financial, software, data, and media company headquartered in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. It was co-founded by Michael Bloomberg in 1981, with Thomas Secunda, Duncan MacMillan, Charles Zegar, and a 12% ownership investment by Merrill Lynch.
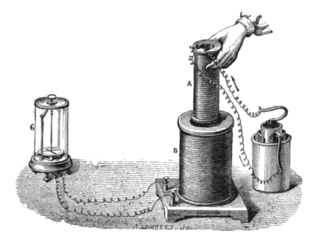
Faraday's law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism predicting how a magnetic field will interact with an electric circuit to produce an electromotive force (emf)—a phenomenon known as electromagnetic induction. It is the fundamental operating principle of transformers, inductors, and many types of electrical motors, generators and solenoids.

"LS engine" is the colloquial name given to the 3rd and 4th generation small-block V-8 gasoline engine used in General Motors' vehicles. The name evolved from the need to differentiate the Gen 3/Gen 4 small blocks from the original Gen 1/Gen 2 small blocks released in 1954, which are commonly referred to as "Small Block Chevrolets". The "LS" name originates from the engine RPO code of the first Gen 3 small block, the LS1, introduced in the 1997 Corvette. The term "LS engine" is used to describe any Gen 3 or Gen 4 Small Block Chevrolet, including those that do not specifically include "LS" as part of their RPO code. Sometimes referred to as an "LSx", with the lower case "x" standing in for one of the many RPO code variations of the motor, the term can cause confusion since GM now sells an aftermarket LS cylinder block named "LSX" with a capital "X". The original RPO code "LS1" is still sometimes used, if not confusingly, to describe the entire Gen 3/Gen 4 engine family.

The Ford F-Series is a series of trucks marketed and manufactured by Ford since the 1948 model year. Slotted above the Ford Ranger in the Ford truck model range, the F-Series is marketed as a range of full-sized pickup trucks. Alongside the F-150, the F-Series also includes the Super Duty series, which includes the heavier-duty F-250 through F-450 pickups, F-450/F-550 chassis cabs, and F-600/F-650/F-750 Class 6-8 commercial trucks. The most popular version of the model line is the F-150 pickup truck, currently in its 14th generation. From 1953 to 1985, the entry-level F-series pickup was the ½ ton F-100.

Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions.

The Chrysler Hemi engines, known by the trademark Hemi, are a series of American I6 and V8 gasoline engines built by Chrysler with overhead valve hemispherical combustion chambers. Three different types of Hemi engines have been built by Chrysler for automobiles: the first from 1951 to 1958, the second from 1964 to 1971, and the third beginning in 2003. Although Chrysler is most identified with the use of "Hemi" as a marketing term, many other auto manufacturers have incorporated similar designs. The engine block and cylinder heads were cast and manufactured at Indianapolis Foundry.

A V8 engine is an eight-cylinder piston engine in which two banks of four cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.

Introduced by the Italian-French mathematician and astronomer Joseph-Louis Lagrange in 1788 from his work Mécanique analytique, Lagrangian mechanics is a formulation of classical mechanics and is founded on the stationary action principle.

















