
Penang is a Malaysian state located on the northwest coast of Peninsular Malaysia along the Malacca Strait. It has two parts: Penang Island, where the capital city, George Town, is located, and Seberang Perai on the Malay Peninsula. These two halves are physically connected by the Penang Bridge and the Second Penang Bridge. The state shares borders with Kedah to the north and east, and Perak to the south.

George Town is the capital of the Malaysian state of Penang. It is the core city of the George Town Conurbation, Malaysia's second largest metropolitan area with a population of 2.84 million and the second highest contributor to the country's GDP. The city proper spans an area of 306 km2 (118 sq mi) encompassing Penang Island and surrounding islets, and had a population of 794,313 as of 2020.

The Tun Abdul Razak Complex, formerly the PenangUrban Centre, is a civic complex within the central business district of George Town in the Malaysian state of Penang. At the time of its completion in 1985, Komtar Tower, at 231.7 metres (760 ft), was the second tallest building in Asia and the tallest in Southeast Asia until 1986 when it was surpassed by One Raffles Place in Singapore. Other buildings in the complex include a hotel building, four shopping malls, an urban park, and a central transportation hub. The complex contains 1,420,000 square feet (132,000 m2) of office and retail space on a 27-acre (11 ha) superblock. It currently houses the administrative offices of the Penang state government and the chief minister of Penang.

Seberang Perai is a city in the Malaysian state of Penang. Located on the Malay Peninsula and separated from Penang Island by the Penang Strait, it shares borders with Kedah to the north and east, and Perak to the south. The city spans an area of 748 km2 (289 sq mi) and had a population of 946,092 as of 2020, making it the third largest city in Malaysia.

Rail transport in Malaysia consists of heavy rail, light rapid transit (LRT), mass rapid transit (MRT), monorails, airport rail links and a funicular railway line. Heavy rail is mostly used for intercity services and freight transport as well as some urban public transport, while rapid transit rails are used for intracity urban public transport in the capital city of Kuala Lumpur and the surrounding Klang Valley region. There are two airport rail link systems linking Kuala Lumpur with the Kuala Lumpur International Airport and Sultan Abdul Aziz Shah Airport. The longest monorail line in the country is also used for public transport in Kuala Lumpur, while the only funicular railway line is available in Penang.

Prangin Mall is a shopping mall within George Town in the Malaysian state of Penang. It is located at Prangin Road, next to Komtar Tower, and is linked to both Komtar and neighboring 1st Avenue Mall via overhead skybridges.

The State of Penang in Malaysia, home to the country's third largest city as well as part of Malaysia's second most populous conurbation, has a relatively well-developed transport infrastructure. The city-state is well-connected by land, air and sea; the Penang International Airport is one of Malaysia's busiest, while the Port of Penang is the main harbour and transshipment hub within northern Malaysia. The North–South Expressway, the main highway along western Peninsular Malaysia, runs through Penang, while the two geographically separate halves of the state are now linked by two bridges and a ferry service.

The Greater Penang Conurbation, also known as the George Town Conurbation, is the built-up urban or metropolitan area within and around the Malaysian state of Penang. Encompassing all of Penang, and parts of the neighbouring states of Kedah and Perak, the conurbation was home to over 2.84 million people as of 2020, the second largest in the country after the Klang Valley.
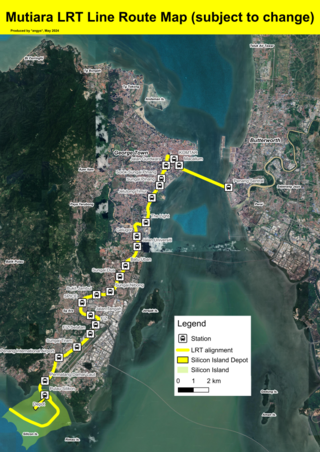
The Mutiara LRT line is a proposed light rapid transit system in Penang. The 29 kilometres (18 mi) line is planned to connect George Town's city centre with its southern suburbs of Jelutong, Gelugor and Bayan Lepas, with a link towards Seberang Perai across the Penang Strait. Once completed, it is owned by the Mass Rapid Transit Corporation (MRTC). The line, a component of the Penang Transport Master Plan (PTMP), is projected to contain 20 stations. Construction of the line is expected to begin in September or October 2024, and will be completed by 2030.

Prangin Road is a major thoroughfare in the city of George Town within the Malaysian state of Penang. The one-way road, one of the busiest in the city centre, forms the southernmost limit of the city's UNESCO World Heritage Site and runs along major landmarks such as Komtar and Prangin Mall.

Komtar is a state constituency in Penang, Malaysia, that has been represented in the Penang State Legislative Assembly since 2004. It covers George Town's city centre, including the eponymous Komtar, which houses Penang's administrative centre.
The Penang Transport Master Plan was drawn up to address the deteriorating traffic conditions in Penang and is projected to cost RM46 billion.

The Sia Boey Urban Archaeological Park, also colloquially known as the Sia Boey, is an urban archaeology park within the city of George Town in the Malaysian state of Penang. Located at Prangin Road, it is touted as the first Urban Archaeological Park in the country.

Central George Town is the city centre of George Town, the capital of the Malaysian state of Penang. It corresponds to the eponymous subdivision of George Town, which is mostly identical to the original city limits established when George Town was granted city status in 1957.

The Jalan Bukit Kukus Paired Road is a dual carriageway in the city of George Town within the Malaysian state of Penang. The municipally-funded 5.5 km (3.4 mi) road stretches across the valleys at the centre of Penang Island, connecting Paya Terubong, Balik Pulau and Bukit Jambul. Scheduled for completion by 2025, a 3.3 km (2.1 mi) stretch was opened for use in 2022. It is touted as the tallest elevated expressway in Malaysia, reaching the highest point of 59.4 m (195 ft) from the pile caps, or 61.5 m (202 ft) above ground.

Kek Lok Si Charitable Hospital is a non-profit hospital in George Town within the Malaysian state of Penang. Established in 2021, the 50-bed hospital at Ayer Itam is the first Buddhist hospital in the state and is run by the nearby Kek Lok Si Temple. The hospital provides services including internal medicine, orthopaedics, otorhinolaryngology, radiology, anesthesiology, nephrology, medical diagnostics, general surgery and hemodialysis.
The Tanjong Tokong line, also spelt as the Tanjung Tokong line, is a proposed light rail transit or monorail system in Penang. The 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) line is planned to connect George Town's city centre with its northern suburb of Tanjong Tokong. The line has eight stations, with potential extensions towards Tanjong Bungah and Batu Ferringhi.
The Ayer Itam line is a proposed light rail transit or monorail system in Penang. The 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) line is planned to connect George Town's city centre with its western suburbs of Ayer Itam and Paya Terubong. The line has 13 stations. The line is a component of the Penang Transport Master Plan and contains interchange stations towards the Mutiara line and Tanjong Tokong line.
The Macallum station is a proposed light rail transit complex located at Macallum Street Ghaut, next to the Tun Dr Lim Chong Eu Expressway in George Town, Penang. The station is projected to be part of the Mutiara line. Construction is expected to start in September or October 2024, and will be completed by 2030, in line with the completion of the Mutiara line.
The Bandar Sri Pinang station is a proposed light rail transit station located next to the Tun Dr Lim Chong Eu Expressway in George Town, Penang. The station is projected to be part of the Mutiara line. Construction is expected to start in September or October 2024, and will be completed by 2030, in line with the completion of the Mutiara line.














