Related Research Articles
The enzyme cystathionine γ-lyase (EC 4.4.1.1, CTH or CSE; also cystathionase; systematic name L-cystathionine cysteine-lyase (deaminating; 2-oxobutanoate-forming)) breaks down cystathionine into cysteine, 2-oxobutanoate (α-ketobutyrate), and ammonia:
In enzymology, a tryptophan dehydrogenase (EC 1.4.1.19) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme 3-chloro-D-alanine dehydrochlorinase (EC 4.5.1.2) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme carbamoyl-serine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.13) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme cysteine-S-conjugate β-lyase (EC 4.4.1.13) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme D-cysteine desulfhydrase (EC 4.4.1.15) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme D-serine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.18), with systematic name D-serine ammonia-lyase (pyruvate-forming), catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme Glucosaminate ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.9) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme homocysteine desulfhydrase (EC 4.4.1.2) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme L-2-amino-4-chloropent-4-enoate dehydrochlorinase (EC 4.5.1.4) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme L-serine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.17) catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme methionine γ-lyase (EC 4.4.1.11, MGL) is in the γ-family of PLP-dependent enzymes. It degrades sulfur-containing amino acids to α-keto acids, ammonia, and thiols:
The enzyme Serine-sulfate ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.10) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme (2R)-sulfolactate sulfo-lyase catalyzes the reaction

Threonine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.19, systematic name L-threonine ammonia-lyase (2-oxobutanoate-forming), also commonly referred to as threonine deaminase or threonine dehydratase, is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of L-threonine into α-ketobutyrate and ammonia:
The enzyme 4-(2-carboxyphenyl)-2-oxobut-3-enoate aldolase (EC 4.1.2.34) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme tryptophanase (EC 4.1.99.1) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme tyrosine phenol-lyase (EC 4.1.99.2) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme ethanolamine-phosphate phospho-lyase (EC 4.2.3.2) catalyzes the chemical reaction
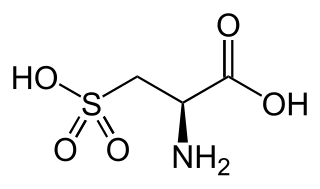
Cysteic acid also known as 3-sulfo-l-alanine is the organic compound with the formula HO3SCH2CH(NH2)CO2H. It is often referred to as cysteate, which near neutral pH takes the form −O3SCH2CH(NH3+)CO2−.
References
- Denger K, Smits TH, Cook AM (2006). "L-Cysteate sulpho-lyase, a widespread pyridoxal 5′-phosphate-coupled desulphonative enzyme purified from Silicibacter pomeroyi DSS-3(T)". Biochem. J. 394 (Pt 3): 657–64. doi:10.1042/BJ20051311. PMC 1383715 . PMID 16302849.