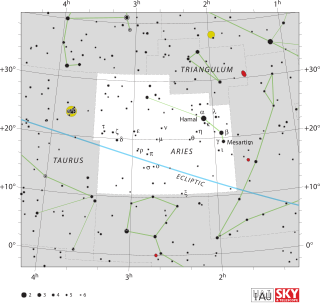
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the Northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram. Its old astronomical symbol is (♈︎). It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees.

Circinus is a small, faint constellation in the southern sky, first defined in 1756 by the French astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille. Its name is Latin for compass, referring to the drafting tool used for drawing circles. Its brightest star is Alpha Circini, with an apparent magnitude of 3.19. Slightly variable, it is the brightest rapidly oscillating Ap star in the night sky. AX Circini is a Cepheid variable visible with the unaided eye, and BX Circini is a faint star thought to have been formed from the merger of two white dwarfs. Two sun-like stars have planetary systems: HD 134060 has two small planets, and HD 129445 has a Jupiter-like planet. Supernova SN 185 appeared in Circinus in 185 AD and was recorded by Chinese observers. Two novae have been observed more recently, in the 20th century.

NGC 6791 is an open star cluster in the Lyra constellation. It was discovered by Friedrich August Theodor Winnecke in 1853. At roughly 8 billion years old, and with an iron to hydrogen abundance ratio that is more than twice that of the Sun, it is one of the oldest and most metal-rich clusters in the Milky Way. This is contrary to the typical rule-of-thumb where older means more metal-poor. Compounded with the fact that it has an unusually high population of stars, NGC 6791 is among the most studied clusters in the sky.

The New General Catalogue objectNGC 48 is a barred spiral galaxy located approximately 79.3 million light-years from the Solar System in the constellation Andromeda.

NGC 7048 is a planetary nebula in the constellation of Cygnus. The bright star to the lower left of the nebula is a magnitude 10.5 star, designated TYC 3589-4652-1. The nebula is slightly brighter along the west and east sides. This planetary nebula has an apparent magnitude of 12.1. NGC 7048 was discovered by Édouard Stephan on 19 October 1878 using a 31.5-inch reflector.

HD 149382 is a star in the constellation of Ophiuchus with an apparent visual magnitude of 8.943. This is too faint to be seen with the naked eye even under ideal conditions, although it can be viewed with a small telescope. Based upon parallax measurements, this star is located at a distance of about 240 light-years from the Earth.

NGC 6503 is a field dwarf spiral galaxy located at the edge of a region of space called the Local Void. The dwarf galaxy spans 30,000 light-years and lies approximately 17 million light-years away in the constellation of Draco. The spiral galaxy is especially colorful where bright red regions of gas can be seen scattered through its spiral arms. Bright blue regions contain stars that are forming. Dark brown dust areas are in the galaxy's arms and center.

NGC 5970 is a large barred-spiral galaxy located about 90 million light years away in the constellation Serpens Caput. It appears to have two satellite or companion galaxies. It is a member of the Virgo Cluster of galaxies. It was discovered on March 15, 1784 by the astronomer William Herschel.

NGC 1741 is a distant pair of interacting galaxies in the Eridanus constellation. It was discovered on 6 January 1878 by French astronomer Édouard Stephan. As a result of the collision, the galaxies are in a rapid starbust phase. The galaxies are classed as Wolf–Rayet galaxies due to their high content of rare Wolf–Rayet stars.

NGC 7002 is a large elliptical galaxy around 320 million Light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Indus. The galaxy was discovered by English astronomer John Herschel on September 30, 1834. NGC 7002 is also part of a group of galaxies that contains the nearby galaxy NGC 7004.

NGC 588 is a diffuse nebula located in the outskirts of the galaxy Messier 33, within the Triangulum constellation. It was discovered October 2 1861 by the German-Danish astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest.

NGC 7015 is a spiral galaxy located about 203 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation Equuleus. NGC 7015's calculated velocity is 4,881 km/s (3,033 mi/s). NGC 7015 was discovered by French astronomer Édouard Stephan on September 29, 1878. It is also part of a group of galaxies called [CHM2007] LDC 1450.

LEDA 135657 is a distant low surface brightness spiral galaxy located about 570 million light-years away in the constellation Cetus. It has an estimated diameter of 97,000 light-years.

NGC 7033 is a lenticular galaxy located about 390 million light-years away in the constellation of Pegasus. It is part of a pair of galaxies that contains the nearby galaxy NGC 7034. NGC 7033 was discovered by astronomer Albert Marth on September 17, 1863.

NGC 676 is a lenticular Seyfert 2 Galaxy about 18.7 Mly away in the constellation Pisces. It can be seen near the star α Piscium. Located close to the celestial equator, it is visible from both hemispheres. BD +04 0244, a star with a visual magnitude of 10.44, is superposed 5.1 arc seconds south-southwest of the nucleus. It is one of the 621 galaxies described in Marat Arakelian's catalog of high-surface-brightness galaxies.

NGC 1276 is an optical double star system located in the constellation Perseus. The system was discovered by astronomer John Dreyer on December 12, 1876. The pair consists of two 15th magnitude stars known as Pul -3 270349 and Pul -3 270357 that are unrelated as they lie at different distances from each other. Pul -3 270349 lies at a distance of 1,134.5587 parsecs (3,700.436 ly) and Pul -3 270357 lies at a distance of 1,774.6229 parsecs (5,788.046 ly).

NGC 5910 is an elliptical galaxy located about 540 million light-years away in the constellation Serpens. It was discovered by astronomer William Hershel on April 13, 1785. NGC 5910 is also a strong radio source with a conspicuous nuclear jet.

NGC 4326 is a barred spiral galaxy with a ring located about 330 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 13, 1784, who described it as "vF, S, R, bM, 1st of 3". It is a large galaxy, with a diameter of around 200,000 ly (61 kpc) making it nearly twice the size of the Milky Way. NGC 4326 is also classified as a LINER galaxy. Despite being listed in the Virgo Cluster catalog as VCC 623, it is not a member of the Virgo Cluster but instead a background galaxy.

NGC 4333 is a barred spiral galaxy with a ring structure located about 330 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 13, 1784, who described it as "F, pS, R, bM, 2nd of 3". NGC 4333 is also classified as a LINER galaxy. Despite being listed in the Virgo Cluster catalog as VCC 637, it is not a member of the Virgo Cluster but instead a background galaxy.


















