Related Research Articles

Labrys is, according to Plutarch, the Lydian word for the double-bitted axe.. The Ancient Greek plural of labrys is labryes.

Aspergillus niger is a fungus and one of the most common species of the genus Aspergillus.

Micrococcus luteus is a Gram-positive, to Gram-variable, nonmotile, coccus, tetrad-arranging, pigmented, saprotrophic bacterium that belongs to the family Micrococcaceae. It is urease and catalase positive. An obligate aerobe, M. luteus is found in soil, dust, water and air, and as part of the normal microbiota of the mammalian skin. The bacterium also colonizes the human mouth, mucosae, oropharynx and upper respiratory tract. It was discovered by Sir Alexander Fleming before he discovered penicillin in 1928.

ATCC or the American Type Culture Collection is a nonprofit organization which collects, stores, and distributes standard reference microorganisms, cell lines and other materials for research and development. Established in 1925 to serve as a national center for depositing and distributing microbiological specimens, ATCC has since grown to distribute in over 150 countries. It is now the largest general culture collection in the world.
Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus is a bacterium that originally was considered to be a subspecies of L. casei, but genetic research found it to be a separate species in the L. casei clade, which also includes L. paracasei and L. zeae. It is a short Gram-positive homofermentative facultative anaerobic non-spore-forming rod that often appears in chains. Some strains of L. rhamnosus bacteria are being used as probiotics, and are particularly useful in treating infections of the female urogenital tract, most particularly very difficult to treat cases of bacterial vaginosis. The species Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus and Limosilactobacillus reuteri are commonly found in the healthy female genito-urinary tract and are helpful to regain control of dysbiotic bacterial overgrowth during an active infection. L. rhamnosus sometimes is used in dairy products such as fermented milk and as non-starter-lactic acid bacterium (NSLAB) in long-ripened cheese. While frequently considered a beneficial organism, L. rhamnosus may not be as beneficial to certain subsets of the population; in rare circumstances, especially those primarily involving weakened immune system or infants, it may cause endocarditis. Despite the rare infections caused by L. rhamnosus, the species is included in the list of bacterial species with qualified presumed safety (QPS) status of the European Food Safety Agency.
The LGBT community has adopted certain symbols for self-identification to demonstrate unity, pride, shared values, and allegiance to one another. LGBT symbols communicate ideas, concepts, and identity both within their communities and to mainstream culture. The two most-recognized international LGBT symbols are the pink triangle and the rainbow flag.
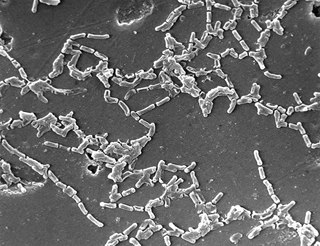
Mycobacterium chelonae is a species of the phylum Actinobacteria, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium. Mycobacterium chelonae is a rapidly growing mycobacterium, that is found all throughout the environment including sewage and tap water. It can occasionally cause opportunistic infections of humans.
Mycobacterium avium complex is a group of mycobacteria comprising Mycobacterium intracellulare and Mycobacterium avium that are commonly grouped because they infect humans together; this group, in turn, is part of the group of nontuberculous mycobacteria. These bacteria cause disease in humans called Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infection or Mycobacterium avium complex infection. These bacteria are common and are found in fresh and salt water, in household dust and in soil. MAC bacteria usually cause infection in those who are immunocompromised or those with severe lung disease.

Mycobacterium kansasii is a bacterium in the Mycobacterium family. The genus includes species known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis and leprosy, but this species is generally not dangerous to healthy people.
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobe, nonmotile bacterium that is often found in association with localized aggressive periodontitis, a severe infection of the periodontium. It is also suspected to be involved in chronic periodontitis. Less frequently, A. actinomycetemcomitans is associated with nonoral infections such as endocarditis. Its role in aggressive periodontitis was first discovered by Danish-born periodontist Jørgen Slots, a professor of dentistry and microbiology at the University of Southern California School of Dentistry.
Mycoplasma amphoriforme is a species of bacteria in the genus Mycoplasma. This genus of bacteria lacks a cell wall around their cell membrane. Without a cell wall, they are unaffected by many common antibiotics such as penicillin or other beta-lactam antibiotics that target cell wall synthesis. Mycoplasma are the smallest bacterial cells yet discovered, can survive without oxygen and are typically about 0.1 µm in diameter.

The Napo saki, also known as the Napo monk saki, is a species of saki monkey, a type of New World monkey. Its range includes parts of eastern Ecuador and northern Peru. The name is derived from the Napo River in its locality. This species was originally described by Lönnberg as the subspecies Pithecia monachus napensis and has been treated as a synonym of P. monachus monachus. Hershkovitz retained it under P. monachus in 1987, but it was raised to full species status in 2014.
Streptomyces flaveus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil.
Streptomyces humiferus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil near Moscow in Russia.
Labrys miyagiensis is a Gram-negative, aerobic motile and non-spore-forming bacteria from the family Xanthobacteraceae which has been isolated from grassland soil in Sendai in the Miyagi Prefecture in Japan.
Labrys okinawensis is a bacterium from the family Xanthobacteraceae which has been isolated from root nodule from the plant Entada phaseoloides in Okinawa in Japan.
Labrys portucalensis is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, non-motile, non-spore-forming and aerobic bacteria from the family Xanthobacteraceae which has been isolated from polluted soil in Estarreja in Portugal. Labrys portucalensis has the ability to degrade fluorobenzene.
Streptomyces poonensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces poonensis can degrade 4-hydroxybenzoate.
Streptomyces variabilis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces variabilis produces variapeptin, citropeptin and ammosamide D.
Streptomyces vitaminophilus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in the Nagano City in Japan. Streptomyces vitaminophilus produces the pyrrolomycin complex.
References
- 1 2 "Genus Labrys". LPSN. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- ↑ "Taxon Passport Labrys monachus". StrainInfo. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- 1 2 "Catalogue - Labrys monachus". Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen . Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- ↑ "Taxonomy - Labrys monachus". UniProt. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- ↑ "Labrys monachus Vassilyeva and Semenov (ATCC 43932)". ATCC. Retrieved 17 December 2016.