
Armina is a genus of sea slugs, specifically nudibranchs, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Arminidae.

The Polyceridae are a taxonomic family of sea slugs, dorid nudibranchs, marine gastropod mollusks within the superfamily Polyceroidea.

Liotiidae is a family of small sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the clade Vetigastropoda.
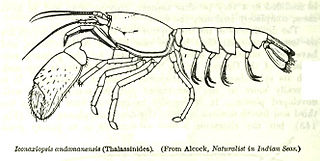
Eiconaxius is a genus of mud lobster that includes the following species:

Cylindrobulla is a genus of sea snails or bubble snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the clade Sacoglossa.

Dermatobranchus is a genus of sea slugs, or nudibranchs, marine gastropod molluscs in the family Arminidae.
Admetula is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Cancellariidae, the nutmeg snails.

Microsveltia is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Cancellariidae, the nutmeg snails.

Colubraria is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Colubrariidae. Members of this genus lack a radula and feed by sucking blood from fish.

Conomitra is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Volutomitridae.

Metula is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the family Colubrariidae.

Arca is a genus of edible saltwater clams in the family Arcidae, the Ark Clams.

Euphyllia is a genus of large-polyped stony coral. Several species are commonly found in marine aquariums. The genus includes the following species:

Megabalanus tintinnabulum is a species of large barnacle in the family Balanidae. It is the type species of the genus. The specific name comes from the Latin tintinnabulum meaning a handbell and probably refers to the fact that small groups of barnacles resemble clusters of miniature bells.

Ancylomenes pedersoni, sometimes known as Pederson's shrimp and Pederson's cleaner shrimp, is a species of cleaner shrimp. It is part of the genus Ancylomenes and was described in 1958 by Fenner A. Chace Jr. as Periclimenes pedersoni. Ancylomenes pedersoni is found in the Caribbean Sea, often associated with a sea anemone, at depths of 1 to 15 metres. They are often found on the reefs off Bermuda.

Conus is a genus of venomous and predatory sea snails, or cone snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Conidae. Prior to 2009, it included all cone snail species but is now more precisely defined, as are other cone snail genera.
Eirene is a genus of hydrozoans in the family Eirenidae.

Nanhaipotamon is a genus of freshwater crabs, in the subfamily Potamiscinae, found in southern China and Taiwan. As of 2018, 18 species have been described. The genus is named after the South China Sea, for it occurs mostly in coastal areas. The genus was first described by R. Bott in 1968 as Isolapotamon (Nanhaipotamon), i.e., a subgenus of Isolapotamon.
Cellaria is a genus of bryozoans belonging to the family Cellariidae.

Liagoraceae is a family of red algae (Rhodophyta) in the order Nemaliales. The type genus is LiagoraJ.V.Lamouroux.















