Related Research Articles

Obstetric ultrasonography, or prenatal ultrasound, is the use of medical ultrasonography in pregnancy, in which sound waves are used to create real-time visual images of the developing embryo or fetus in the uterus (womb). The procedure is a standard part of prenatal care in many countries, as it can provide a variety of information about the health of the mother, the timing and progress of the pregnancy, and the health and development of the embryo or fetus.
Fetal distress, also known as non-reassuring fetal status, is a condition during pregnancy or labor in which the fetus shows signs of inadequate oxygenation. Due to its imprecision, the term "fetal distress" has fallen out of use in American obstetrics. The term "non-reassuring fetal status" has largely replaced it. It is characterized by changes in fetal movement, growth, heart rate, and presence of meconium stained fluid.

Infant respiratory distress syndrome (IRDS), also called respiratory distress syndrome of newborn, or increasingly surfactant deficiency disorder (SDD), and previously called hyaline membrane disease (HMD), is a syndrome in premature infants caused by developmental insufficiency of pulmonary surfactant production and structural immaturity in the lungs. It can also be a consequence of neonatal infection and can result from a genetic problem with the production of surfactant-associated proteins.
HELLP syndrome is a complication of pregnancy; the acronym stands for hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count. It usually begins during the last three months of pregnancy or shortly after childbirth. Symptoms may include feeling tired, retaining fluid, headache, nausea, upper right abdominal pain, blurry vision, nosebleeds, and seizures. Complications may include disseminated intravascular coagulation, placental abruption, and kidney failure.

Gestational hypertension or pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) is the development of new hypertension in a pregnant woman after 20 weeks' gestation without the presence of protein in the urine or other signs of pre-eclampsia. Gestational hypertension is defined as having a blood pressure greater than 140/90 on two occasions at least 6 hours apart.

Polyhydramnios is a medical condition describing an excess of amniotic fluid in the amniotic sac. It is seen in about 1% of pregnancies. It is typically diagnosed when the amniotic fluid index (AFI) is greater than 24 cm. There are two clinical varieties of polyhydramnios: chronic polyhydramnios where excess amniotic fluid accumulates gradually, and acute polyhydramnios where excess amniotic fluid collects rapidly.
The triple test, also called triple screen, the Kettering test or the Bart's test, is an investigation performed during pregnancy in the second trimester to classify a patient as either high-risk or low-risk for chromosomal abnormalities.

Prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM), previously known as premature rupture of membranes, is breakage of the amniotic sac before the onset of labor. Women usually experience a painless gush or a steady leakage of fluid from the vagina. Complications in the baby may include premature birth, cord compression, and infection. Complications in the mother may include placental abruption and postpartum endometritis.
A nonstress test (NST) is a screening test used in pregnancy to assess fetal status by means of the fetal heart rate and its responsiveness. A cardiotocograph is used to monitor the fetal heart rate and presence or absence of uterine contractions. The test is typically termed "reactive" or "nonreactive".
The alkali denaturation test, also known as A or Apt test, is a medical test used to differentiate fetal or neonatal blood from maternal blood found in a newborn's stool or vomit, or from maternal vaginal blood.
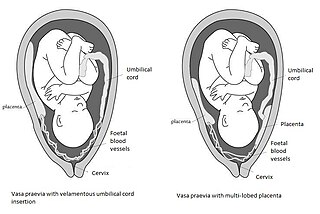
Vasa praevia is a condition in which fetal blood vessels cross or run near the internal opening of the uterus. These vessels are at risk of rupture when the supporting membranes rupture, as they are unsupported by the umbilical cord or placental tissue.

Percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling (PUBS), also called cordocentesis, fetal blood sampling, or umbilical vein sampling is a diagnostic genetic test that examines blood from the fetal umbilical cord to detect fetal abnormalities. Fetal and maternal blood supply are typically connected in utero with one vein and two arteries to the fetus. The umbilical vein is responsible for delivering oxygen rich blood to the fetus from the mother; the umbilical arteries are responsible for removing oxygen poor blood from the fetus. This allows for the fetus’ tissues to properly perfuse. PUBS provides a means of rapid chromosome analysis and is useful when information cannot be obtained through amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling, or ultrasound ; this test carries a significant risk of complication and is typically reserved for pregnancies determined to be at high risk for genetic defect. It has been used with mothers with immune thrombocytopenic purpura.
Fetal-maternal haemorrhage is the loss of fetal blood cells into the maternal circulation. It takes place in normal pregnancies as well as when there are obstetric or trauma related complications to pregnancy.

The lecithin–sphingomyelin ratio is a test of fetal amniotic fluid to assess for fetal lung immaturity. Lungs require surfactant, a soap-like substance, to lower the surface tension of the fluid coating the alveolar epithelium in the lungs. This is especially important for premature babies trying to expand their lungs after birth. Surfactant is a mixture of lipids, proteins, and glycoproteins, lecithin and sphingomyelin being two of them. Lecithin makes the surfactant mixture more effective.

Complete androgen insensitivity syndrome (CAIS) is an AIS condition that results in the complete inability of the cell to respond to androgens. As such, the insensitivity to androgens is only clinically significant when it occurs in individuals who are exposed to significant amounts of testosterone at some point in their lives. The unresponsiveness of the cell to the presence of androgenic hormones prevents the masculinization of male genitalia in the developing fetus, as well as the development of male secondary sexual characteristics at puberty, but does allow, without significant impairment, female genital and sexual development in those with the condition.
The surfactant–albumin ratio is a test for assessing fetal lung maturity. The test, though no longer commercially available, used an automatic analyzer to measure the polarized fluorescent light emitted from a sample of amniotic fluid that had been challenged with a fluorescent probe that interacted competitively with both lecithin (phosphatidylcholine) and albumin in such a way that direct quantitative measurements of both substances could be attained. Higher amounts of lecithin – in reference to albumin – is indicative of lung maturity. When this test was still used in practice, the Standards of Laboratory Practice set the threshold for lung maturity at 55 mg of lecithin per gram of albumin.

Right-sided aortic arch is a rare anatomical variant in which the aortic arch is on the right side rather than on the left. During normal embryonic development, the aortic arch is formed by the left fourth aortic arch and the left dorsal aorta. In people with a right-sided aortic arch, instead the right dorsal aorta persists and the distal left aorta disappears.

Paraovarian cysts or paratubal cysts are epithelium-lined fluid-filled cysts in the adnexa adjacent to the fallopian tube and ovary. The terms are used interchangeably, and depend on the location of the cyst.
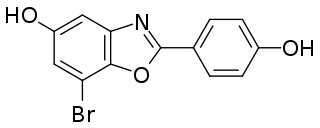
WAY-200070 is a synthetic, nonsteroidal, highly selective agonist of ERβ. It possesses 68-fold selectivity for ERβ over ERα (EC50 = 2 nM and 155 nM, respectively). WAY-200070 has been found to enhance serotonergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission in the central nervous system, and produces antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like effects in animals. It has been proposed as a potential novel antidepressant/anxiolytic agent. WAY-200070 has also been found to produce antidiabetic effects in animals, and may also be beneficial for the treatment of certain inflammatory conditions.
Anthropometry is defined as the scientific study of the human body measurements and proportions. These studies are generally used by clinicians and pathologists for adequate assessments of the growth and development of the fetus at any specific point of gestational maturity. Fetal height, fetal weight, head circumference (HC), crown to rump length (CR), dermatological observations like skin thickness etc. are measured individually to assess the growth and development of the organs and the fetus as a whole and can be a parameter for normal or abnormal development also including adaptation of the fetus to its newer environment.
References
- ↑ Wijnberger LD, de Kleine M, Voorbij HA, et al. (April 2009). "Prediction of fetal lung immaturity using gestational age, patient characteristics and fetal lung maturity tests: a probabilistic approach". Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 281 (1): 15–21. doi:10.1007/s00404-009-1033-0. PMC 2780670 . PMID 19381669.
- ↑ Ghidini A, Poggi SH, Spong CY, Goodwin KM, Vink J, Pezzullo JC (April 2005). "Role of lamellar body count for the prediction of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome in non-diabetic pregnant women". Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 271 (4): 325–8. doi:10.1007/s00404-004-0653-7. PMID 15221326. S2CID 20536867.
3. Laboratory Testing To Assess Fetal Lung
Maturity Darlynn J. Lafler, BS MT(ASCP)CLS, and Arturo Mendoza, MD From the Sharp Mary Birch Hospital for Women Department of Pathology, San Diego, CA laboratorymedicine> July 2001> number 7> volume 32