Related Research Articles
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. The term is in contrast to miscarriage, which is an early pregnancy loss, and live birth, where the baby is born alive, even if it dies shortly after.

Obstetric ultrasonography, or prenatal ultrasound, is the use of medical ultrasonography in pregnancy, in which sound waves are used to create real-time visual images of the developing embryo or fetus in the uterus (womb). The procedure is a standard part of prenatal care in many countries, as it can provide a variety of information about the health of the mother, the timing and progress of the pregnancy, and the health and development of the embryo or fetus.

Cardiotocography (CTG) is a technical means of recording the fetal heartbeat and the uterine contractions during pregnancy. The machine used to perform the monitoring is called a cardiotocograph, more commonly known as an electronic fetal monitor (EFM).

Polyhydramnios is a medical condition describing an excess of amniotic fluid in the amniotic sac. It is seen in about 1% of pregnancies. It is typically diagnosed when the amniotic fluid index (AFI) is greater than 24 cm. There are two clinical varieties of polyhydramnios: chronic polyhydramnios where excess amniotic fluid accumulates gradually, and acute polyhydramnios where excess amniotic fluid collects rapidly.

Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS), also known as feto-fetal transfusion syndrome (FFTS), twin oligohydramnios-polyhydramnios sequence (TOPS) and stuck twin syndrome is a complication of disproportionate blood supply, resulting in high morbidity and mortality. It can affect monochorionic multiples, that is, multiple pregnancies where two or more fetuses share a chorion and hence a single placenta. Severe TTTS has a 60–100% mortality rate.
At the end of pregnancy, the fetus must take the journey of childbirth to leave the reproductive mother. Upon its entry to the air-breathing world, the newborn must begin to adjust to life outside the uterus.
The triple test, also called triple screen, the Kettering test or the Bart's test, is an investigation performed during pregnancy in the second trimester to classify a patient as either high-risk or low-risk for chromosomal abnormalities.
Gestational age is a measure of the age of a pregnancy which is taken from the beginning of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP), or the corresponding age of the gestation as estimated by a more accurate method if available. Such methods include adding 14 days to a known duration since fertilization, or by obstetric ultrasonography. The popularity of using such a definition of gestational age is that menstrual periods are essentially always noticed, while there is usually a lack of a convenient way to discern when fertilization occurred.

Prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM), previously known as premature rupture of membranes, is breakage of the amniotic sac before the onset of labor. Women usually experience a painless gush or a steady leakage of fluid from the vagina. Complications in the baby may include premature birth, cord compression, and infection. Complications in the mother may include placental abruption and postpartum endometritis.
A contraction stress test (CST) is performed near the end of pregnancy to determine how well the fetus will cope with the contractions of childbirth. The aim is to induce contractions and monitor the fetus to check for heart rate abnormalities using a cardiotocograph. A CST is one type of antenatal fetal surveillance technique.
Postterm pregnancy is when a woman has not yet delivered her baby after 42 weeks of gestation, two weeks beyond the typical 40 week duration of pregnancy. Post-mature births carry risks for both the mother and the baby, including fetal malnutrition, meconium aspiration syndrome, and stillbirths. After the 42nd week of gestation, the placenta, which supplies the baby with nutrients and oxygen from the mother, starts aging and will eventually fail. Postterm pregnancy is a reason to induce labor.

Fundal height, or McDonald's rule, is a measure of the size of the uterus used to assess fetal growth and development during pregnancy. It is measured from the top of the mother's uterus to the top of the mother's pubic symphysis. Fundal height, when expressed in centimeters, roughly corresponds to gestational age in weeks between 16 and 36 weeks for a vertex fetus. When a tape measure is unavailable, finger widths are used to estimate centimeter (week) distances from a corresponding anatomical landmark. However, landmark distances from the pubic symphysis are highly variable depending on body type. In clinical practice, recording the actual fundal height measurement from the palpable top of the uterus to the superior edge of the pubic symphysis is standard practice beginning around 20 weeks gestation.
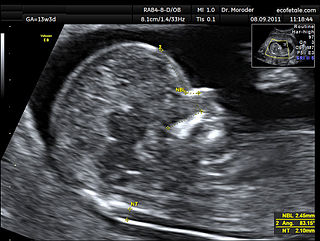
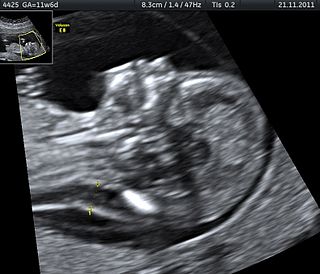
A nuchal scan or nuchal translucency (NT) scan/procedure is a sonographic prenatal screening scan (ultrasound) to detect chromosomal abnormalities in a fetus, though altered extracellular matrix composition and limited lymphatic drainage can also be detected.
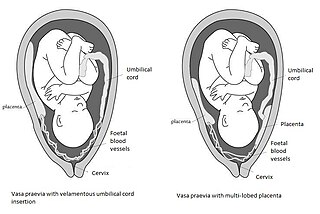
Vasa praevia is a condition in which fetal blood vessels cross or run near the internal opening of the uterus. These vessels are at risk of rupture when the supporting membranes rupture, as they are unsupported by the umbilical cord or placental tissue.
A biophysical profile (BPP) is a prenatal ultrasound evaluation of fetal well-being involving a scoring system, with the score being termed Manning's score. It is often done when a non-stress test (NST) is non reactive, or for other obstetrical indications.

For other uses see PUBS
A Doppler fetal monitor is a hand-held ultrasound transducer used to detect the fetal heartbeat for prenatal care. It uses the Doppler effect to provide an audible simulation of the heart beat. Some models also display the heart rate in beats per minute (BPM). Use of this monitor is sometimes known as Doppler auscultation. The Doppler fetal monitor is commonly referred to simply as a Doppler or fetal Doppler. It may be classified as a form of Doppler ultrasonography.

The lecithin–sphingomyelin ratio is a test of fetal amniotic fluid to assess for fetal lung immaturity. Lungs require surfactant, a soap-like substance, to lower the surface pressure of the alveoli in the lungs. This is especially important for premature babies trying to expand their lungs after birth. Surfactant is a mixture of lipids, proteins, and glycoproteins, lecithin and sphingomyelin being two of them. Lecithin makes the surfactant mixture more effective.
Vibroacoustic stimulation (VAS), sometimes referred to as fetal vibroacoustic stimulation or fetal acoustic stimulation test (FAST), is the application of a vibratory sound stimulus to the abdomen of a pregnant woman to induce FHR accelerations. The presence of FHR accelerations reliably predicts the absence of fetal metabolic acidemia. Vibroacoustic stimulation is typically used during a nonstress test (NST).
Anthropometry is defined as the scientific study of the human body measurements and proportions. These studies are generally used by clinicians and pathologists for adequate assessments of the growth and development of the fetus at any specific point of gestational maturity. Fetal height, fetal weight, head circumference (HC), crown to rump length (CR), dermatological observations like skin thickness etc. are measured individually to assess the growth and development of the organs and the fetus as a whole and can be a parameter for normal or abnormal development also including adaptation of the fetus to its newer environment.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Neonatology : management, procedures, on-call problems, diseases, and drugs. Gomella, Tricia Lacy, Cunningham, M. Douglas, Eyal, Fabien G. (7th ed.). New York. 2013. ISBN 9780071768016. OCLC 830349840.CS1 maint: others (link)
- ↑ Smith, C. V.; Nguyen, H. N.; Phelan, J. P.; Paul, R. H. (1986). "Intrapartum assessment of fetal well-being: a comparison of fetal acoustic stimulation with acid-base determinations". Am J Obstet Gynecol. 155 (4): 726–728. doi:10.1016/s0002-9378(86)80007-2. PMID 3766625.
- ↑ Chervenak, Frank A.; Kurjak, Asim (2006). Textbook of Perinatal Medicine, Second Edition (Two Volumes). Informa Healthcare. ISBN 1-84214-333-6.
- 1 2 Association of Women’s Health, Obstetric, and Neonatal Nurses (2005). Lyndon, Audrey Lyndon; Ali, Linda Usher (eds.). Fetal Heart Monitoring: Principles and Practices (3rd ed.). Dubuque, IA: Kendall/Hunt Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-7575-6234-1.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ↑ Cousins, L. M.; Poeltler, D. M.; Faron, S.; Catanzarite, V.; Daneshmand, S.; Casele, H. (October 2012). "Nonstress testing at ≤ 32.0 weeks' gestation: a randomized trial comparing different assessment criteria". Am J Obstet Gynecol. Mosby, Inc. 207 (4): 311.e1–311.e7. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2012.06.032. PMID 23021694.