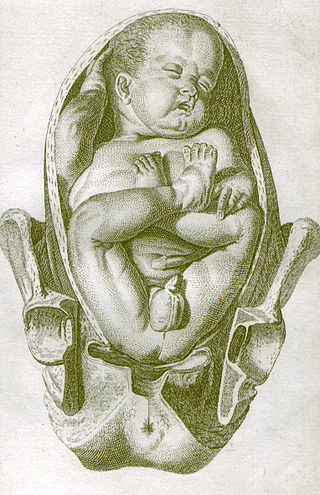
A breech birth is when a baby is born bottom first instead of head first, as is normal. Around 3–5% of pregnant women at term have a breech baby. Due to their higher than average rate of possible complications for the baby, breech births are generally considered higher risk. Breech births also occur in many other mammals such as dogs and horses, see veterinary obstetrics.

External cephalic version (ECV) is a process by which a breech baby can sometimes be turned from buttocks or foot first to head first. It is a manual procedure that is recommended by national guidelines for breech presentation of a pregnancy with a single baby, in order to enable vaginal delivery. It is usually performed late in pregnancy, that is, after 36 gestational weeks, preferably 37 weeks, and can even be performed in early labour.

Shoulder dystocia is when, after vaginal delivery of the head, the baby's anterior shoulder gets caught above the mother's pubic bone. Signs include retraction of the baby's head back into the vagina, known as "turtle sign". Complications for the baby may include brachial plexus injury, or clavicle fracture. Complications for the mother may include vaginal or perineal tears, postpartum bleeding, or uterine rupture.
Pelvimetry is the measurement of the female pelvis. It can theoretically identify cephalo-pelvic disproportion, which is when the capacity of the pelvis is inadequate to allow the fetus to negotiate the birth canal. However, clinical evidence indicate that all pregnant women should be allowed a trial of labor regardless of pelvimetry results.

In obstetrics, Leopold maneuvers are a common and systematic way to determine the position of a fetus inside the woman's uterus. They are named after the gynecologist Christian Gerhard Leopold. They are also used to estimate term fetal weight.

Huabeisaurus was a genus of dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous. It was a sauropod which lived in what is present-day northern China. The type species, Huabeisaurus allocotus, was first described by Pang Qiqing and Cheng Zhengwu in 2000. Huabeisaurus is known from numerous remains found in the 1990s, which include teeth, partial limbs and vertebrae. Due to its relative completeness, Huabeisaurus represents a significant taxon for understanding sauropod evolution in Asia. Huabeisaurus comes from Kangdailiang and Houyu, Zhaojiagou Town, Tianzhen County, Shanxi province, China. The holotype was found in the unnamed upper member of the Huiquanpu Formation, which is Late Cretaceous (?Cenomanian–?Campanian) in age based on ostracods, charophytes, and fission-track dating.

Obstetrical forceps are a medical instrument used in childbirth. Their use can serve as an alternative to the ventouse method.

A vaginal delivery is the birth of offspring in mammals through the vagina. It is the most common method of childbirth worldwide. It is considered the preferred method of delivery, with lower morbidity and mortality than Caesarean sections (C-sections).
Anterior shoulder in obstetrics refers to that shoulder of the fetus that faces the pubic symphysis of the mother during delivery. Depending upon the original position of the fetus, either the left or the right shoulder can be the anterior shoulder. It is known as the anterior shoulder as it faces the anterior of the mother. This distinction between the anterior and the posterior shoulder is important as the anterior shoulder is delivered first.
In obstetrics, position is the orientation of the fetus in the womb, identified by the location of the presenting part of the fetus relative to the pelvis of the mother. Conventionally, it is the position assumed by the fetus before the process of birth, as the fetus assumes various positions and postures during the course of childbirth.
Posterior shoulder in obstetrics refers to the shoulder of the fetus other than the anterior shoulder. Thus, the posterior shoulder faces the rectum of the mother during delivery. Whether left or the right shoulder becomes the posterior shoulder is dependent upon the original position of the fetus. It is known as the posterior shoulder as it faces the posterior of the mother. This distinction between the anterior and the posterior shoulder is important as the anterior shoulder is delivered first.

A shoulder presentation is a malpresentation at childbirth where the baby is in a transverse lie, thus the leading part is an arm, a shoulder, or the trunk. While a baby can be delivered vaginally when either the head or the feet/buttocks are the leading part, it usually cannot be expected to be delivered successfully with a shoulder presentation unless a cesarean section (C/S) is performed.
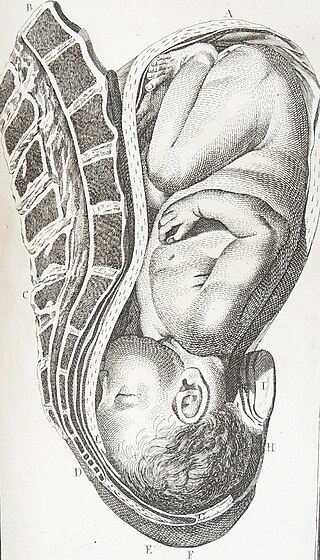
A cephalic presentation or head presentation or head-first presentation is a situation at childbirth where the fetus is in a longitudinal lie and the head enters the pelvis first; the most common form of cephalic presentation is the vertex presentation, where the occiput is the leading part. All other presentations are abnormal (malpresentations) and are either more difficult to deliver or not deliverable by natural means.
Mauriceau–Smellie–Veit maneuver or Mauriceau maneuver is an obstetric or emergent medical maneuver utilized in cases of breech delivery. This procedure entails suprapubic pressure by one obstetrician on the mother/uterus, while another obstetrician inserts left hand in vagina, palpating the fetal maxilla using the index and middle finger and gently pressing on the maxilla, bringing the neck to a moderate flexion. The left hand's palm should rest against the fetus' chest, while the right hand can grab either shoulder of the fetus and pull in the direction of the fetus' pelvis. The combined neck flexion, traction on the fetus toward the hip/pelvis, and the suprapubic pressure on the mother/uterus allows for delivery of the head of a breech infant, granted prior breech delivery steps are followed and the infant's occipitus is rotated/facing anteriorly relative to the mother.

The pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs, together with its embedded skeleton.
The fetal head, from an obstetrical viewpoint, and in particular its size, is important because an essential feature of labor is the adaptation between the fetal head and the maternal bony pelvis. Only a comparatively small part of the head at term is represented by the face. The rest of the head is composed of the firm skull, which is made up of two frontal, two parietal, and two temporal bones, along with the upper portion of the occipital bone and the wings of the sphenoid.
Locked twins is a rare complication of multiple pregnancy where two fetuses become interlocked during presentation before birth. It occurs in roughly 1 in 1,000 twin deliveries and 1 in 90,000 deliveries overall. Most often, locked twins are delivered via Caesarean section, given that the condition has been diagnosed early enough. The fetal mortality rate is high for the twin that presents first, with over 50% being stillborn.

Emergency childbirth is the precipitous birth of an infant in an unexpected setting. In planned childbirth, mothers choose the location and obstetric team ahead of time. Options range from delivering at home, at a hospital, a medical facility or a birthing center. Sometimes, birth can occur on the way to these facilities, without a healthcare team. The rates of unplanned childbirth are low. If the birth is imminent, emergency measures may be needed. Emergency services can be contacted for help in some countries.
Yuanjiawaornis is an extinct genus of large enantiornithean bird known from the early Cretaceous of present-day China. It is monotypic, with only type species Y. virisosus known.











