
Midwifery is the health science and health profession that deals with pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period, in addition to the sexual and reproductive health of women throughout their lives. In many countries, midwifery is a medical profession. A professional in midwifery is known as a midwife.

In the United States, a Certified Nurse-Midwife (CNM) is a nurse midwife who exceeds the International Confederation of Midwives' essential competencies for a midwife and is also an advanced practice registered nurse, having completed registered nursing and midwifery education leading to practice as a nurse midwife and credentialing as a Certified Nurse-Midwife. CNMs provide care of women across their lifespan, including pregnancy and the postpartum period, and well woman care and birth control. Certified Nurse-Midwives are recognized by the International Confederation of Midwives as a type of midwife in the U.S.

The Frontier Nursing Service (FNS) provides healthcare services to rural, underserved populations since 1925, and educates nurse-midwives since 1939.

Mary Carson Breckinridge was an American nurse midwife and the founder of the Frontier Nursing Service (FNS), which provided comprehensive family medical care to the mountain people of rural Kentucky. FNS served remote and impoverished areas off the road and rail system but accessible by horseback. She modeled her services on European practices and sought to professionalize American nurse-midwives to practice autonomously in homes and decentralized clinics. Although Breckinridge's work demonstrated efficacy by dramatically reducing infant and maternal mortality in Appalachia, at a comparatively low cost, her model of nurse-midwifery never took root in the United States.

Nursing in Australia is a healthcare profession. Nurses and midwives form the majority (54%) of Australian health care professionals. Nurses are either registered or enrolled. Registered nurses have broader and deeper education than enrolled nurses. Nurse practitioners complete a yet higher qualification. Nurses are not limited to working in hospitals, instead working in a variety of settings. Australian nurses are in demand as traveling nurses, particularly those with advanced qualifications.
A birth attendant, also known as skilled birth attendant, is a health professional who provides basic and emergency care to women and their newborns during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. A birth attendant, who may be a midwife, physician, obstetrician, or nurse, is trained to be present at ("attend") childbirth, whether the delivery takes place in a health care institution or at home, to recognize and respond appropriately to medical complications, and to implement interventions to help prevent them in the first place, including through prenatal care. Different birth attendants are able to provide different levels of care.

Dame Mary Rosalind Paget, DBE, ARRC, was a noted British nurse, midwife and reformer. She was the first superintendent, later inspector general, of the Queen's Jubilee Institute for District Nursing, which was renamed as the Queen's Institute of District Nursing in 1928 and as the Queen's Nursing Institute in 1973.
Ruth Watson Lubic, CNM, EdD, FAAN, FACNM, is an American nurse-midwife and applied anthropologist who pioneered the role of nurse-midwives as primary care providers for women, particularly in maternity care. Lubic is considered to be one of the leaders of the nurse-midwifery movement in the United States.
Childbirth in rural Appalachia has long been a subject of concern amongst the population because infant mortality rates are higher in Appalachia than in other parts of the United States. Additionally, poor health in utero, at birth, and in childhood can contribute to poor health throughout life. The region's low income, geographic isolation, and low levels of educational attainment reduce both access to and utilization of modern medical care. Traditional medical practices, including lay midwifery, persisted longer in Appalachia than in other U.S. regions.

Zepherina Philadelphia Smith was an English nurse and social reformer who promoted increased education and training for midwives. Her work led to the Royal College of Midwives.
Doris Clifton Gordon was a New Zealand doctor, obstetrician, university lecturer and women's health reformer. She was known as 'Dr Doris', famous for her work in rural general practice, for raising the status of obstetrics, improving obstetrics education of medical students and doctors, and working for the welfare of mothers and children.
In the United States, certified nurse midwives (CNMs) are advanced practice registered nurses in nurse midwifery, the nursing care of women during pregnancy and the postpartum period. CNMs are considered as midwives.
Midwives in the United States assist childbearing women during pregnancy, labor and birth, and the postpartum period. Some midwives also provide primary care for women including well-woman exams, health promotion, and disease prevention, family planning options, and care for common gynecological concerns. Before the turn of the 20th century, traditional midwives were informally trained and helped deliver almost all births. Today, midwives are professionals who must undergo formal training. Midwives in the United States formed the Midwifery Education, Regulation, and Association task force to establish a framework for midwifery.
Mary Francis Hill Coley was an American lay midwife who ran a successful business providing a range of birth services and who starred in a critically acclaimed documentary film used to train midwives and doctors. Her competence projected an image of black midwives as the face of an internationally esteemed medical profession, while working within the context of deep social and economic inequality in health care provided to African Americans. Her life story and work exist in the context of Southern granny midwives who served birthing women outside of hospitals.
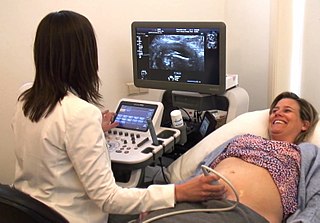
A midwife is a health professional who cares for mothers and newborns around childbirth, a specialisation known as midwifery.

Mamie Odessa Hale was a leader in public health and a midwife consultant who worked in Arkansas for the Department of Health from 1945 to 1950. During this time, Hale's objective was to educate and train 'granny midwives.' Her efforts were in place to address the public health disparity between black and white women that was currently evident.
Dora Kwartiorkor Opoku OBE was a midwife and educationist who was an authority in the field of medical research ethics.

Joan Elsa Donley was a Canadian-born New Zealand nurse and midwife. Donley was a key figure who shaped midwifery and the homebirth movement in New Zealand.

Carolyn Conant Van Blarcom was an American nurse and midwife reformer. In 1913, she became the first American nurse to become a licensed midwife. She made pioneering contributions in preventing childhood blindness. Van Blarcom also played instrumental role in establishing a school for midwives, and extensively contributed in reforming some of the important health institutions in America including the Maryland State Sanatorium for Tuberculosis.
Margaret Currie Neilson Lamb FRCN (1907–1992) was the first nurse to chair the General Nursing Council in Scotland.













