
Norfolk Island is an external territory of Australia located in the Pacific Ocean between New Zealand and New Caledonia, 1,412 kilometres (877 mi) directly east of Australia's Evans Head and about 900 kilometres (560 mi) from Lord Howe Island. Together with the neighbouring Phillip Island and Nepean Island, the three islands collectively form the Territory of Norfolk Island. At the 2021 census, it had 2,188 inhabitants living on a total area of about 35 km2 (14 sq mi). Its capital is Kingston.

The Pitcairn Islands, officially Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie and Oeno Islands, are a group of four volcanic islands in the southern Pacific Ocean that form the sole British Overseas Territory in the Pacific Ocean. The four islands—Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie and Oeno—are scattered across several hundred miles of ocean and have a combined land area of about 18 square miles (47 km2). Henderson Island accounts for 86% of the land area, but only Pitcairn Island is inhabited. The inhabited islands nearest to the Pitcairn Islands are Mangareva, 688 km to the west, as well as Easter Island, 1,929 km to the east.
Spoken English shows great variation across regions where it is the predominant language. The United Kingdom has a wide variety of accents, and no single "British accent" exists. This article provides an overview of the numerous identifiable variations in pronunciation. Such distinctions usually derive from the phonetic inventory of local dialects, as well as from broader differences in the Standard English of different primary-speaking populations.
Norfolk is a county in England.

Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, Pacificans, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of Oceania or any other island located in the Pacific Ocean.
Norfuk or Norf'k is the language spoken on Norfolk Island by the local residents. It is a blend of 18th-century English and Tahitian, originally introduced by Pitkern-speaking settlers from the Pitcairn Islands. Along with English, it is the co-official language of Norfolk Island.
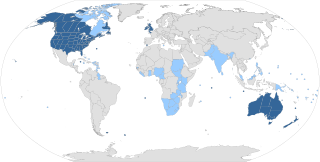
The English-speaking world comprises the 88 countries and territories in which English is an official, administrative, or cultural language. In the early 2000s, between one and two billion people spoke English, making it the largest language by number of speakers, the third largest language by number of native speakers and the most widespread language geographically. The countries in which English is the native language of most people are sometimes termed the Anglosphere. Speakers of English are called Anglophones.
Pitkern, also known as Pitcairn-Norfolk or Pitcairnese, is a language spoken on Pitcairn and Norfolk islands. It is a mixture of English and Tahitian, and has been given many classifications by scholars, including cant, patois, and Atlantic creole. Although spoken on Pacific Ocean islands, it has been described as an Atlantic or semi-Atlantic creole due to the lack of connections with other English-based creoles of the Pacific. There are fewer than 50 speakers on Pitcairn Island, a number which has been steadily decreasing since 1971.
"Come Ye Blessed" is a territorial song of the British overseas territory of the Pitcairn Islands, and is the official territorial song of the Australian territory of Norfolk Island and is sung at most island events.

The Indigenous peoples of Oceania are Aboriginal Australians, Papuans, and Austronesians. These indigenous peoples have a historical continuity with pre-colonial societies that developed on their territories. With the notable exceptions of Australia, New Zealand, Hawaii, New Caledonia, Guam, and Northern Mariana Islands, indigenous peoples make up the majority of the populations of Oceania.

Norfolk Island Airport, is the only airport on Norfolk Island, an external territory of Australia. The island is located in the Pacific Ocean between Australia, New Zealand, and New Caledonia. The airport is operated by the Norfolk Island Regional Council, and is on the west side of the island.
The languages of Australia are the major historic and current languages used in Australia and its offshore islands. Over 250 Australian Aboriginal languages are thought to have existed at the time of first European contact. English is the majority language of Australia today. Although English has no official legal status, it is the de facto official and national language. Australian English is a major variety of the language with a distinctive accent and lexicon, and differs slightly from other varieties of English in grammar and spelling.
Alice Inez Buffett was a political figure and linguist from the Australian territory of Norfolk Island.
Pitcairn Islanders, also referred to as Pitkerners and Pitcairnese, are the native inhabitants of the Pitcairn Islands, a British Overseas Territory including people whose families were previously inhabitants and maintaining cultural connections. Most Pitcairn Islanders are descendants of the Bounty mutineers.
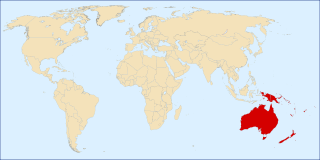
The following outline is provided as an overview and topical guide to Oceania.

Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania vary, with it being defined in various ways, often geopolitically or geographically. In the geopolitical conception used by the United Nations, International Olympic Committee, and many atlases, the Oceanic region includes Australia and the nations of the Pacific from Papua New Guinea east, but not the Malay Archipelago or Indonesian New Guinea. The term is sometimes used more specifically to denote Australasia as a geographic continent, or biogeographically as a synonym for either the Australasian realm or the Oceanian realm.
Norfolk Islanders, also referred to as just Islanders, are the inhabitants or residents of Norfolk Island, an external territory of Australia. The Islanders have their own unique identity and are predominantly people of Pitcairn and English descent and to a lesser extent of Scottish and Irish.

The Norfolk Island Labor Party, also known simply as Norfolk Labor, was the Norfolk Island branch of the Australian Labor Party. It operated as a sub-branch of the ACT Labor Party.

The Norfolk Island Liberal Party, more commonly referred to simply as the Norfolk Liberals, is the Norfolk Island wing of the Liberal Party of Australia. It currently operates as the "Norfolk Island Interest Branch" of the Canberra Liberals.











